 |
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 12(2); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to assess paraspinal muscle atrophy in patients who underwent minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MI-TLIF) and unilateral pedicle screw fixation using a novel contralateral intact muscle-controlled model.
Overview of Literature
The increased incidence of paravertebral lumbar muscle injuries after open techniques has raised the importance of implementing minimally invasive spine surgical techniques using tubular retractors and minimally invasive screw placement. The functional cross-sectional area (FCSA) represents the lean muscle mass; furthermore, FCSA is a useful marker of the contractile ability of a muscle following a spine surgery. However, the benefits of unilateral fixation and MI-TLIF on paraspinal muscles have not been defined.
Methods
We performed a retrospective imagenological review on eleven patients who underwent unilateral MI-TLIF and unilateral transpedicular screw lumbar placement. FCSAs of the multifidus and erector spinae were measured 1 year after surgery at adjacent levels and were compared to the contralateral intact muscles. Measurement differences between the surgical and nonsurgical sites were compared. The interobserver reliability was calculated using an intraclass correlation coefficient.
Results
The mean FCSA at the surgical site was 20.97┬▒5.07 cm2 at the superior level and 8.89┬▒2.87 cm2 at the inferior level. The mean FCSA at the contralateral nonsurgical site was 20.15┬▒5.95 cm2 at the superior level and 9.20┬▒2.66 cm2 at the inferior level was. The superior and inferior FCSA measurements showed no significant difference between the surgical and nonsurgical sites (p=0.5, p=0.922, respectively).
The multifidus and erector spinae (longissimus and iliocostalis) are essential for carrying the physiologic loads imposed on the spine; furthermore, they provide stability and functional movement [1]. The increased incidence of paravertebral lumbar muscle injuries after conventional open techniques have raised the importance of implementing minimally invasive spine surgical techniques using tubular retractors and minimally invasive screw placement [2345].
The muscle cross-sectional area (CSA) can be used to measure muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration using either computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [67891011121314151617181920]. Even without a decrease in the overall CSA within the muscle fascia borders [21], atrophy can occur, indicating the replacement of muscle with fat and fibrous tissue. The functional cross-sectional area (FCSA) represents the lean muscle mass and is a useful marker of the contractile ability of a muscle [17].
This study aimed to assess paraspinal muscle atrophy using FCSA in patients who underwent a minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MI-TLIF) and unilateral pedicle screw instrumentation using a novel contralateral intact muscle-controlled model.
We performed a retrospective comparative imagenological review on eleven patients who underwent a unilateral MI-TLIF and unilateral transpedicular screw lumbar placement from January 2010 to December 2013 at the ABC Medical Center, Mexico City, Mexico.
For the treatment of degenerative disc disease and spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine, all patients were voluntarily treated for 1 or 2 levels using MI-TLIF. All procedures were performed under general anesthesia with patients in the supine positon on a radiolucent operating table using a two-dimensional C-arm fluoroscope, electromyography, somatosensory evoked potentials, and motor evoked potentials. Following intubation, the patient was placed in the prone position; the lumbar spine was prepared and draped in a sterile fashion. A 2-cm incision was placed 1.5 cm lateral to the ipsilateral pedicle marked by anterior-posterior fluoroscopy. A monopolar dissection was made through the subcutaneous tissue. The thoracolumbar and muscle erector spinae fasciae were opened; the plane between the iliocostalis and longissimus muscles was recognized. A 16ŌĆō18-mm tubular retractor (METRx System; Medtronic, Dublin, Ireland) was inserted in between the muscles by dilating over a precisely placed guide tube over the facet joint. The facet complex was drilled out using a straight high-speed match head cutting drill. Discectomy and MI-TLIF were performed using Peek cages (JULIET OL; Spineart, Geneva, Switzerland) filled with a demineralized bone matrix. Following decompression and interbody fusion, using true AP and lateral views, fluoroscopic-guided pedicle screws were placed. The rod was secured through the same incision. The fascia and subcutaneous tissue were closed using Vycril 2-0, and the skin was closed using nylon 3-0.
A lumbar CT (Brilliance 64 scanner; Phillips Healthcare, Andover, MA, USA) was performed 1 year after surgery. Using 5-mm thick slices, images were obtained with patients placed in the supine position. Images were stored in a DICOM (digital imaging and communications in medicine) format and analyzed on a personal computer using OsiriX ver. 5.6 (32 bit; Pixmeo SARL, Bernex, Switzerland) with the following parameters: WLWW, CT abdomen; VR muscle-bone; and opacity, logarithmic inversion. FCSA was measured in selected axial images at the superior and inferior adjacent levels to the lumbar instrumentation. Avoiding nearby fat, bony structures, and other soft tissues, FCSA was drawn with an electronic pencil (Bamboo ver. 5.2.5; Wacom Co. Ltd., Kazo, Saitama, Japan) by two independent observers blinded to the surgical method. The sum of the multifidus and erector spinae FCSAs was calculated as one muscle mass due to difficulties in discriminating between the back musculature. FCSA was bilaterally measured 1 year after surgery (Fig. 1).
Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics Software ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Descriptive statistics were used for clinical and demographic data. FCSA was compared 1 year after surgery for the surgical and nonsurgical sites using the MannŌĆōWhitney U-test. The interobserver reliability was calculated using an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Clinical data and FCSA were evaluated in eleven patients 1 year after surgery. The mean age was 62.91┬▒15.86 years (range, 34 to 82 years; eight males and three females). The mean surgical time was 180 minutes (range, 120 to 300 minutes); the mean bleeding volume was 40 mL (range, 20 to 200 mL).
ICC was 0.981 (range, 0.865 to 0.99), indicating excellent interobserver reliability. Therefore, the mean FCSA from the two observer's measurements was used in the statistical analysis.
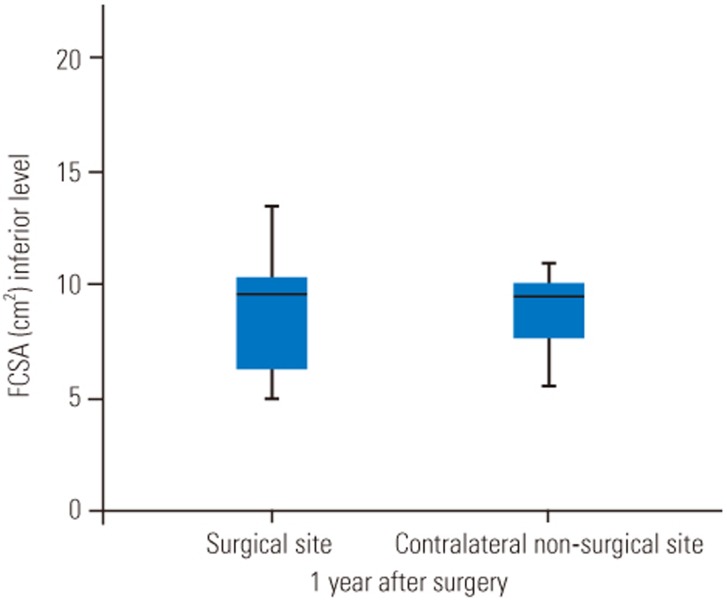
FCSA was measured at the surgical site and the contralateral side. The mean FCSA was 20.97┬▒5.07 cm2 in the surgical site at the superior level and 8.89┬▒2.87 cm2 at the inferior level. FCSA was 20.15┬▒5.95 cm2 in the contralateral nonsurgical site at the superior level and 9.20┬▒2.66 cm2 at the inferior level (Figs. 2, 3). There was no significant change between the surgical and nonsurgical sites in both superior and inferior FCSA measurements (superior level: Z=ŌłÆ0.624, p=0.5; inferior level: Z=ŌłÆ0.098, p=0.922). When using the control site as a reference, there was a +4.06% increase in surgical site muscles at the superior level and a ŌłÆ3.3% reduction at the inferior level.
It is important to assess muscle atrophy following spine surgery because there are reports on its correlation with chronic low back pain [6212223]. Although conventional open TLIF and pedicle screw fixation are beneficial, these techniques require extensive soft tissue and muscle dissection, which is associated with increased blood loss, higher infection rate, and prolonged hospital stay. Using MI-TLIF with a unilateral fixation reduces paraspinal muscles manipulation during surgery, decreasing paraspinal muscles damage, and theoretically, chronic low back pain risk.
Hu et al. [24] demonstrated that the reliability between CT and MRI to assess FCSA measurements is not significantly different and that they are acceptable methods for evaluating paraspinal muscle atrophy. Our study is a unique model that compares the surgical site with the contralateral nonsurgical site in the same patient 1 year after surgery using quantitative CT FCSA. Muscles were assessed proximal and distal to the arthrodesis; the operated level was not measured because it gave several artifacts. In patients with an abundant fatty infiltration, the muscles borders were irregular and difficult to trace; however, measurements were taken by two blinded observers with a high ICC (0.981), demonstrating that the use of previously described OsiriX parameters was adequate to identify muscle boundaries. However, differentiation between all intrinsic paraspinal muscles was difficult, particularly at the distal level (S1). Therefore, to address this problem, we assessed FCSA using the sum of all intrinsic paraspinal muscles. This measurement model wherein the contralateral side is the patient's control, overcomes age and sex differences regarding muscle volume and fat content (Fig. 1).
Using unilateral fixation with a mini-open approach prevents contralateral muscle damage, decreases surgical time and blood loss, and provides fusion. Our mini-open approach required one incision for MI-TLIF and fixation. The plane between the iliocostalis and longissimus muscles was recognized, preventing muscle damage during TLIF. The screws were placed and the rod secured through the same plane and incision. Even though contralateral fixation can be done using a mini-open or percutaneous technique, there is still an 84% and 20% risk, respectively, for a posterior rami medial branch nerve transection after pedicle screw insertion, putting the contralateral multifidus innervation at risk [25]. Cadaveric specimens showed an increased anatomic risk for medial branch nerve injury using a mini-open approach at the adjacent cranial level [25]; therefore, a unilateral fixation eliminates the risk for contralateral medial branch nerve injury, preserving the integrity and innervation of the contralateral multifidus. There were no significant differences in the fusion rate or complications between the unilateral or bilateral pedicle screw fixation [2627]; however, it is important to consider bilateral fixation in cases with preoperative instability, osteoporosis, high grade, and isthmic spondylolisthesis.
Previous studies have demonstrated a decrease in the adjacent FCSA ranging from ŌłÆ2% to ŌłÆ38% using an open approach compared with +9.9% to ŌłÆ12.2% using minimally invasive techniques [8914161928293031323334] (Table 1). In our study, the functional integrity assessed by FCSA showed no significant difference proximal and distal to the arthrodesis 1 year after surgery (p=0.5, p=0.922, respectively) (Figs. 2, 3).
A minimally invasive surgery aims for a simple minimal access through small incisions and to minimize substantial trauma to ligaments, muscles, and vertebrae while attaining a clinically positive effect. Using minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) TLIF and unilateral fixation prevents contralateral damage, minimizes ipsilateral muscle atrophy, and provides good therapeutic results. The main limitations of this study are as follows: First, it was a retrospective study; direct visualization of the paraspinal muscles was not assessed at the level of fusion. Second, the results were not compared with an open technique. However, the study aimed to demonstrate minimal paraspinal muscle contractile damage using MISS TLIF and unilateral instrumentation.
MI-TLIF and unilateral pedicle screw instrumentation using a mini-open approach caused minimal paraspinal muscle damage at the superior and inferior adjacent levels. Cross-sectional CT imaging may contribute to the functional muscle measurement after spine surgery. Further studies are required to confirm whether muscle injury is directly related to long-term clinical outcome.
Notes
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Notes
Contents of this work will be presented as an oral presentation in the SMISS Global Forum '15, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA.
References
1. Panjabi MM, Abumi K, Duranceau J, Crisco JJ. Biomechanical evaluation of spinal fixation devices: II. Stability provided by eight internal fixation devices. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1988;13:1135ŌĆō1134. PMID: 3206271.


2. Gejo R, Matsui H, Kawaguchi Y, Ishihara H, Tsuji H. Serial changes in trunk muscle performance after posterior lumbar surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1999;24:1023ŌĆō1028. PMID: 10332796.


3. Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery: part 2: histologic and histochemical analyses in humans. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1994;19:2598ŌĆō2602. PMID: 7855687.


4. Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery: a histologic and enzymatic analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996;21:941ŌĆō944. PMID: 8726197.


5. Mayer TG, Vanharanta H, Gatchel RJ, et al. Comparison of CT scan muscle measurements and isokinetic trunk strength in postoperative patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1989;14:33ŌĆō36. PMID: 2913665.


6. Barker KL, Shamley DR, Jackson D. Changes in the cross-sectional area of multifidus and psoas in patients with unilateral back pain: the relationship to pain and disability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:E515ŌĆōE519. PMID: 15543053.


7. Danneels LA, Vanderstraeten GG, Cambier DC, Witvrouw EE, De Cuyper HJ. CT imaging of trunk muscles in chronic low back pain patients and healthy control subjects. Eur Spine J 2000;9:266ŌĆō272. PMID: 11261613.



8. Fan S, Hu Z, Zhao F, Zhao X, Huang Y, Fang X. Multifidus muscle changes and clinical effects of one-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion: minimally invasive procedure versus conventional open approach. Eur Spine J 2010;19:316ŌĆō324. PMID: 19876659.


9. Gille O, Jolivet E, Dousset V, et al. Erector spinae muscle changes on magnetic resonance imaging following lumbar surgery through a posterior approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:1236ŌĆō1241. PMID: 17495782.


10. Hides JA, Belavy DL, Stanton W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of trunk muscles during prolonged bed rest. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:1687ŌĆō1692. PMID: 17621220.


11. Hyun JK, Lee JY, Lee SJ, Jeon JY. Asymmetric atrophy of multifidus muscle in patients with unilateral lumbosacral radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:E598ŌĆōE602. PMID: 17906560.


12. Kaser L, Mannion AF, Rhyner A, Weber E, Dvorak J, Muntener M. Active therapy for chronic low back pain: part 2. effects on paraspinal muscle cross-sectional area, fiber type size, and distribution. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:909ŌĆō901. PMID: 11317113.


13. Keller A, Gunderson R, Reikeras O, Brox JI. Reliability of computed tomography measurements of paraspinal muscle cross-sectional area and density in patients with chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003;28:1455ŌĆō1460. PMID: 12838105.


14. Kim DY, Lee SH, Chung SK, Lee HY. Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle strength: percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:123ŌĆō129. PMID: 15626992.


15. Lee JC, Cha JG, Kim Y, Kim YI, Shin BJ. Quantitative analysis of back muscle degeneration in the patients with the degenerative lumbar flat back using a digital image analysis: comparison with the normal controls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:318ŌĆō325. PMID: 18303466.


16. Motosuneya T, Asazuma T, Tsuji T, Watanabe H, Nakayama Y, Nemoto K. Postoperative change of the cross-sectional area of back musculature after 5 surgical procedures as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. J Spinal Disord Tech 2006;19:318ŌĆō322. PMID: 16826001.


17. Ranson CA, Burnett AF, Kerslake R, Batt ME, O'Sullivan PB. An investigation into the use of MR imaging to determine the functional cross sectional area of lumbar paraspinal muscles. Eur Spine J 2006;15:764ŌĆō773. PMID: 15895259.


18. Storheim K, Holm I, Gunderson R, Brox JI, Bo K. The effect of comprehensive group training on cross-sectional area, density, and strength of paraspinal muscles in patients sick-listed for subacute low back pain. J Spinal Disord Tech 2003;16:271ŌĆō279. PMID: 12792342.


19. Tsutsumimoto T, Shimogata M, Ohta H, Misawa H. Mini-open versus conventional open posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparison of paraspinal muscle damage and slip reduction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:1923ŌĆō1928. PMID: 19652636.


20. Mengiardi B, Schmid MR, Boos N, et al. Fat content of lumbar paraspinal muscles in patients with chronic low back pain and in asymptomatic volunteers: quantification with MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2006;240:786ŌĆō792. PMID: 16926328.


21. Parkkola R, Rytokoski U, Kormano M. Magnetic resonance imaging of the discs and trunk muscles in patients with chronic low back pain and healthy control subjects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993;18:830ŌĆō836. PMID: 8316880.


22. Hultman G, Nordin M, Saraste H, Ohlsen H. Body composition, endurance, strength, cross-sectional area, and density of MM erector spinae in men with and without low back pain. J Spinal Disord 1993;6:114ŌĆō123. PMID: 8504222.


23. Salminen JJ, Erkintalo-Tertti MO, Paajanen HE. Magnetic resonance imaging findings of lumbar spine in the young: correlation with leisure time physical activity, spinal mobility, and trunk muscle strength in 15-year-old pupils with or without low-back pain. J Spinal Disord 1993;6:386ŌĆō391. PMID: 8274805.


24. Hu ZJ, He J, Zhao FD, Fang XQ, Zhou LN, Fan SW. An assessment of the intra- and inter-reliability of the lumbar paraspinal muscle parameters using CT scan and magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011;36:E868ŌĆōE874. PMID: 21224757.


25. Regev GJ, Lee YP, Taylor WR, Garfin SR, Kim CW. Nerve injury to the posterior rami medial branch during the insertion of pedicle screws: comparison of mini-open versus percutaneous pedicle screw insertion techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:1239ŌĆō1242. PMID: 19444073.


26. Liu H, Xu Y, Yang SD, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation with posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e6882. PMID: 28538379.



27. Wang L, Wang Y, Li Z, Yu B, Li Y. Unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS-TLIF): a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Surg 2014;14:87PMID: 25378083.




28. Bresnahan LE, Smith JS, Ogden AT, et al. Assessment of paraspinal muscle cross-sectional area after lumbar decompression: minimally invasive versus open approaches. Clin Spine Surg 2017;30:E162ŌĆōE168. PMID: 28323694.


29. Ghiasi MS, Arjmand N, Shirazi-Adl A, et al. Cross-sectional area of human trunk paraspinal muscles before and after posterior lumbar surgery using magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Spine J 2016;25:774ŌĆō782. PMID: 25967560.



30. Min SH, Kim MH, Seo JB, Lee JY, Lee DH. The quantitative analysis of back muscle degeneration after posterior lumbar fusion: comparison of minimally invasive and conventional open surgery. Asian Spine J 2009;3:89ŌĆō95. PMID: 20404953.



31. Strube P, Putzier M, Streitparth F, Hoff EK, Hartwig T. Postoperative posterior lumbar muscle changes and their relationship to segmental motion preservation or restriction: a randomized prospective study. J Neurosurg Spine 2016;24:25ŌĆō31. PMID: 26360146.


32. Yoo JS, Min SH, Yoon SH, Hwang CH. Paraspinal muscle changes of unilateral multilevel minimally invasive transforaminal interbody fusion. J Orthop Surg Res 2014;9:130PMID: 25499767.



33. Suwa H, Hanakita J, Ohshita N, Gotoh K, Matsuoka N, Morizane A. Postoperative changes in paraspinal muscle thickness after various lumbar back surgery procedures. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2000;40:151ŌĆō154. PMID: 10842484.


34. Hyun SJ, Kim YB, Kim YS, et al. Postoperative changes in paraspinal muscle volume: comparison between paramedian interfascial and midline approaches for lumbar fusion. J Korean Med Sci 2007;22:646ŌĆō651. PMID: 17728503.



Fig.┬Ā1
Measurement of the functional cross-sectional area from the paraspinal muscles at the superior (A) and at the inferior adjacent levels (B) 1 year after surgery. There are no significant differences between the surgical and nonsurgical contralateral side.
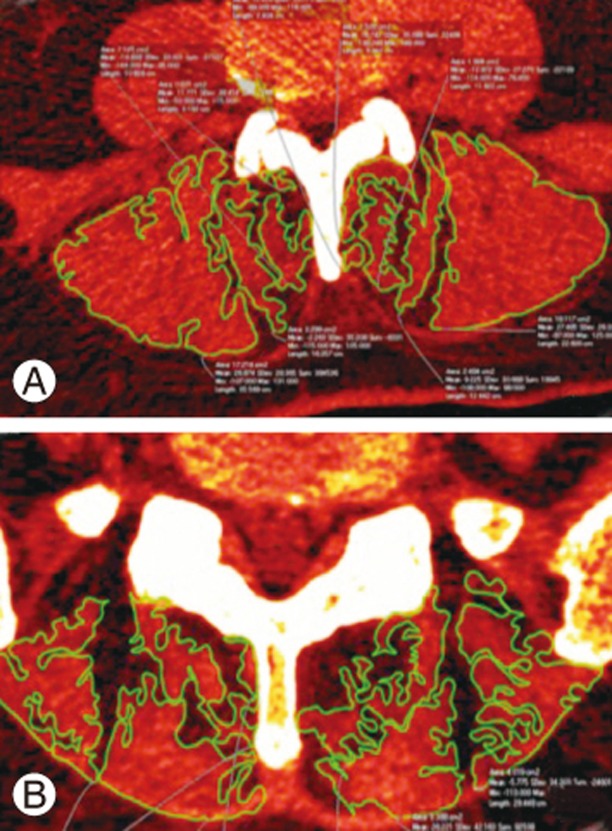
Fig.┬Ā2
Boxplot showing FCSA after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and unilateral screw pedicle fixation at the superior adjacent level. There was a mean percentage increase of 4.06% at the surgical site (p=0.5). FCSA, functional cross-sectional area.
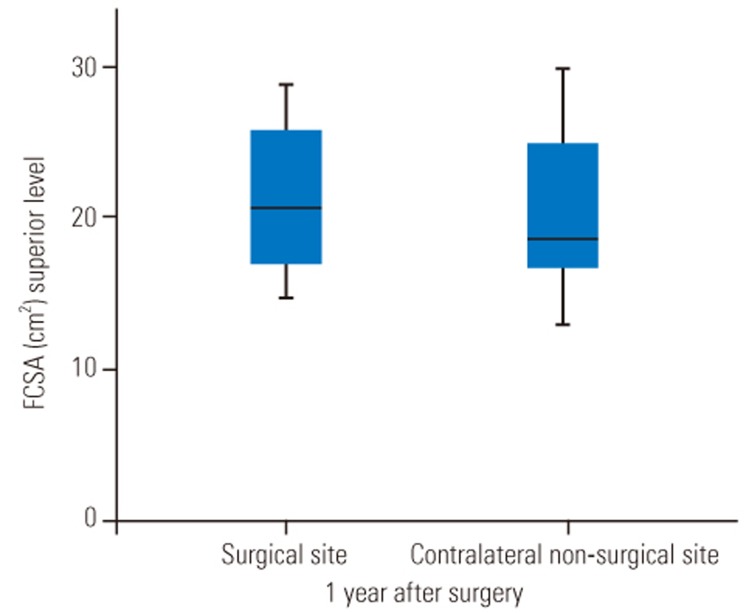
Fig.┬Ā3
Boxplot showing FCSA after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and unilateral screw pedicle fixation at the inferior adjacent level. There was a mean percentage reduction of 3.3% 1 year after surgery at the surgical site (p=0.922). FCSA, functional cross-sectional area.
Table┬Ā1
Muscle damage assessed using clinical imaging related to open and minimally invasive spine approaches
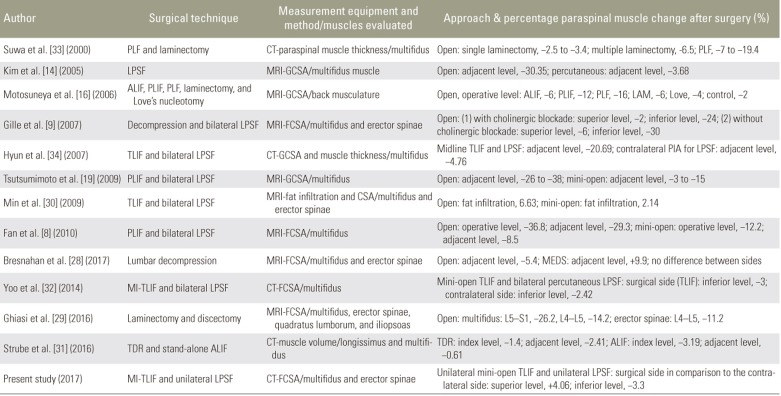
PLF, posterolateral lumbar fusion; CT, computed tomography; LPSF, lumbar pedicle screw fixation; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; GCSA, gross cross-sectional area; ALIF, anterior lumbar interbody fusion; PLIF, posterior lumbar interbody fusion; LAM, laminectomy; FCSA, functional cross-sectional area; TLIF, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion; PIA, paramedian interfascial approach; CSA, cross-sectional area; MEDS, micro endoscopic decompression of stenosis; MI, minimally invasive; TDR, total disc replacement.






