|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 11(1); 2017 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine changes in the ligamentum flavum thickness and remodeling of the spinal canal after anterior fusion during a 10-year follow-up.
Overview of Literature
Extreme lateral interbody fusion provides minimally invasive treatment of the lumbar spine; this anterior fusion without direct posterior decompression, so-called indirect decompression, can achieve pain relief. Anterior fusion may restore disc height, stretch the flexure of the ligamentum flavum, and increase the spinal canal diameter. However, changes in the ligamentum flavum thickness and remodeling of the spinal canal after anterior fusion during a long follow-up have not yet been reported.
Methods
We evaluated 10 patients with L4 spondylolisthesis who underwent stand-alone anterior interbody fusion using the iliac crest bone. Magnetic resonance imaging was performed 10 years after surgery. The cross-sectional area (CSA) of the dural sac and the ligamentum flavum at L1–2 to L5–S1 was calculated using a Picture Archiving and Communication System.
Results
Spinal fusion with correction loss (average, 4.75 mm anterior slip) was achieved in all patients 10 years postsurgery. The average CSAs of the dural sac and the ligamentum flavum at L1–2 to L5–S1 were 150 mm2 and 78 mm2, respectively. The average CSA of the ligamentum flavum at L4–5 (30 mm2) (fusion level) was significantly less than that at L1–2 to L3–4 or L5–S1. Although patients had an average anterior slip of 4.75 mm, the average CSA of the dural sac at L4–5 was significantly larger than at the other levels.
Indirect decompression using anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis has been reported [1]. Symptoms from lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis are a result of vertebral slipping and the thickening and flexure of the ligamentum flavum. Anterior fusion restores disc height and stretches the flexure of the ligamentum flavum, and consequently, the diameter of the spinal canal increases.
We have previously reported 39 cases of patients who underwent noninstrumented stand-alone ALIF for degenerative spondylolisthesis; 29 of these patients had more than 10 years of follow-up [1]. More than 75% of the patients showed satisfactory long-term clinical results [1].
A minimally invasive lateral transpsoas approach to the lumbar spine, also known as extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF), has been introduced. XLIF can be used to gain access to the lumbar spine via the psoas major muscle using a direct lateral approach [2]. Furthermore, mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion methods, such as oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) have been recently applied [345]. Both procedures achieve indirect decompression and correction of sagittal and coronal alignment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis [2345].
Two investigators reported radiographic changes after indirect decompression using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and results of stand-alone XLIF surgery and OLIF plus posterior pedicle screw fixation [67]. The cross-sectional area (CSA) of the dural sac was measured pre- and postoperatively. In 19 of the 21 patients, the MRI showed that the XLIF procedure without posterior fixation provided good surgical results and enlargement of the spinal canal after surgery [6]. Substantial improvement was found in all measured variables, with increases of 33.1% in central canal diameter [6]. In another study, the median CSA of the dural sac extension ratio was 30.2% after OLIF plus posterior pedicle screw fixation surgery in 28 patients, which correlated inversely with preoperative CSA [3]. In addition, the central canal diameter did not reach normal size after surgery based on measurements performed at pre- and postoperative time points [67]. As shown in Fig. 1, indirect decompression by OLIF for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis in our case could enlarge the spinal canal after surgery. However, the enlargement was not sufficient to lessen the thickness of the ligamentum flavum (Fig. 1). Nevertheless, there are no reports examining whether a change in ligamentum flavum thickness and the CSA of the dural sac occurs during long-term follow-up after anterior fusion surgery.
The aim of the present study was to determine if there is a change in the thickness of ligamentum flavum and the CSA of the dural sac 10 years after ALIF.
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Thirty-six patients were diagnosed with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 level with spinal stenosis between levels L4 and L5 diagnosed on radiographic examination, myelograms, computed tomography after myelography, and MRI. Patients who had previously undergone spinal surgery were excluded. We also excluded patients with spinal tumors, infection, and trauma.
The conditions for diagnosis of L4 spondylolisthesis and inclusion criteria for fusion surgery were (1) more than 5% slip of the L4 vertebra at a neutral position; or (2) more than 3 mm translation between flexion and extension position on radiographic evaluation. Thirty-six patients who underwent surgery were selected. We were able to complete a minimum of a 10-year follow-up after surgery in 10 of the 36 patients. Details of the backgrounds of the 10 patients are shown in Table 1.
Thirty-six patients underwent extraperitoneal anterior interbody fusion using an iliac bone graft (L4–L5 level). We did not use either anterior or posterior instrumentation, and we did not perform posterior decompression, such as laminotomy or laminectomy.
We evaluated the change in low back pain, leg pain, and leg numbness before and 10 years after surgery using a visual analogue scale (VAS) score (0, no pain or numbness; 10, worst pain or numbness).
Radiographic evaluation of bone union by radiographic and MRI profile views was performed a minimum of 10 years after surgery. Correction loss (anterior slip of the L4 vertebra) seen on the radiographic profile views was measured 10 years after surgery. Evaluation of bone union was blinded and performed by three observers. If at least two of the observers concurred, their evaluation of bone union was used to define the period of bone union.
Sagittal and axial plane T1- and T2-weighted MRI (1.5 tesla) was evaluated a minimum of 10 years after surgery in the 10 remaining patients. CSA of the dural sac and ligamentum flavum at L1–2 to L5–S1 was measured using a computer-linked digitizer (using the axial plane on T2-weighted imaging). Evaluation was performed by three surgeons blinded to the condition, and the average measurement by the surgeons was used for the final evaluation.
Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics of patients before and after surgery. Low back pain, leg pain, and leg numbness, as evaluated by VAS score, were significantly improved 10 years after surgery compared with before surgery. Evaluation of bone fusion is shown in Figs. 2, 3, 4. All 10 patients retained bone union at the final follow-up. Spinal fusion with correction loss (average, 4.75 mm anterior slip) was achieved in all patients 10 years after surgery.
The average CSAs of the dural sac and ligamentum flavum at L1–2 to L5–S1 were 150 mm2 and 78 mm2, respectively. The average CSA of the ligamentum flavum at L4–5 (30 mm2 at fusion level) was significantly less than at levels L1–2 to L3–4, and L5–S1 (p<0.05). Although patients had an average of 4.75 mm anterior slip, the average CSA of the dural sac at the L4–5 fusion group was significantly larger than at other levels (p<0.05) (Figs. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6).
In the present study, stability of L4–L5 induced a change in the lumbar ligamentum flavum and a sustained remodeling of the spinal canal during a 10-year follow-up. These findings may explain the complete pain relief after indirect decompression fusion surgery in patients with long-term correction loss.
Posture induces physiological changes in the CSA of the spinal canal and neural foramina in young asymptomatic volunteers as seen using MRI [7]. At the disk level, the CSA of the spinal canal varied significantly depending on the body position, most notably between the upright flexed (mean, 268 mm2) and the upright extended (mean, 224 mm2) positions (p<0.0001) [7]. The maximum thickness of the ligamentum flavum was significantly increased in the extended positions (p<0.0001) [7].
Several authors have reported indirect decompression using a large stand-alone XLIF cage without posterior decompression or pedicle screws, and a stand-alone XLIF showed evidence of solid arthrodesis and improvements in clinical symptoms in more than 80% of patients [8]. Other investigators reported radiographic changes and clinical benefit of stand-alone XLIF surgery. In 19 of the 21 patients in their study, radiographs and MRI showed that the XLIF procedure without posterior fixation provided good surgical results and enlargement of the spinal canal after surgery [6]. Substantial improvement was found in all measured variables, with increases of 41.9% in average disk height, 13.5% in foraminal height, 24.7% in foraminal area, and 33.1% in central canal diameter [6]. Other investigators reported a significant increase in dural sac dimensions of 54% in the anterior–posterior plane and 48% in the medial-lateral plane after XLIF surgery plus fixation of percutaneous pedicle screws, either unilaterally or bilaterally, in 15 patients [9]. In addition, significant improvements in disk height and spinal canal area have been reported after OLIF plus posterior percutaneous screws without direct decompression [3]. The median CSA of the thecal sac extension ratio was 30.2% after OLIF plus posterior percutaneous pedicle screw fixation surgery in 28 patients, and this correlated inversely with preoperative CSA [3]. However, in three reports using MRI evaluations, the central canal diameter did not reach the normal size after surgery, with measurements performed pre- and postoperatively. However, to our knowledge, the change in ligamentum flavum thickness and CSA of dural sac occurring during long-term follow-up after anterior fusion surgery has not yet been reported.
In practice, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is a multifactorial disease, closely associated with age, activity level, and the extent of mechanical stress [10]. Mechanical stress has been proposed to induce an inflammatory response that triggers ligamentum flavum hypertrophy [101112]. Some factors related to inflammatory response and fibrosis, such as tumor necrosis factor α, transforming growth factor β, connective tissue growth factor, platelet-derived growth factors, matrix metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases, have been reported to be involved in the development of the hypertrophied ligamentum flavum [1314151617]. However, changes in ligamentum flavum hypertrophy by stabilization or as a result of anti-inflammatory drug use in clinical cases have not been reported.
We have reported that endplate abnormalities (Modic type 1 changes) are related to inflammation and axonal growth into abnormal bone marrow induced by cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor α [18]. We performed posterior fixation without interbody fusion in patients with Modic type 1 signals before surgery. The Modic type 1 signals changed to normal bone marrow within 2 years of the surgery [19]. Considering the mechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy and these reports about Modic changes, stabilization of the spine may induce an anti-inflammatory effect, and ultimately ligamentum flavum hypotrophy.
Bae et al. [20] have reported risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration (ASD) in 128 patients who underwent instrumented lumbar interbody fusion. Postoperative radiological data showed that further segmental lordosis is a significant risk factor for ASD. This suggests that a larger bone graft or cage can restore lumbar lordosis; however, ASD may be induced after ALIF surgery. In the current study, we observed changes of the ligamentum flavum at the fusion site. Thus, to prevent ASD, appropriate cages for indirect decompression and stability that are sufficient to reduce pain may be recommended.
The present study has the following limitations. First, it is a small retrospective study with a restricted number of patients. Second, the timing of the change of the lumbar ligamentum flavum and remodeling of the spinal canal during the 10 years after surgery is not known. It is also not known if similar changes of the lumbar ligamentum flavum and remodeling of the spinal canal have occurred in cases of nonunion. We could not compare MRI before and after surgery, because we do not have a full MRI set before surgery or early after surgery for all patients. Further studies are required to clarify these points.
In conclusion, the average CSA of the ligamentum flavum at the level of fusion 10 years after indirect decompression using ALIF was significantly less than that before surgery, and the CSA of the dural sac at the level of fusion was significantly larger than at other levels. Stability of the spine may have induced the change of the lumbar ligamentum flavum and remodeling of the spinal canal.
Notes
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Takahashi K, Kitahara H, Yamagata M, et al. Long-term results of anterior interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1990;15:1211–1215. PMID: 2267618.


2. Ozgur BM, Aryan HE, Pimenta L, Taylor WR. Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF): a novel surgical technique for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J 2006;6:435–443. PMID: 16825052.


3. Fujibayashi S, Hynes RA, Otsuki B, Kimura H, Takemoto M, Matsuda S. Effect of indirect neural decompression through oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:E175–E182. PMID: 25394317.


4. Wakita H, Shiga Y, Ohtori S, et al. Less invasive corrective surgery using oblique lateral interbody fusion (OLIF) including L5-S1 fusion for severe lumbar kyphoscoliosis due to L4 compression fracture in a patient with Parkinson's disease: a case report. BMC Res Notes 2015;8:126PMID: 25889999.



5. Kanno K, Ohtori S, Orita S, et al. Miniopen oblique lateral L5-s1 interbody fusion: a report of 2 cases. Case Rep Orthop 2014;2014:603531PMID: 25400963.



6. Oliveira L, Marchi L, Coutinho E, Pimenta L. A radiographic assessment of the ability of the extreme lateral interbody fusion procedure to indirectly decompress the neural elements. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35(26 Suppl): S331–S337. PMID: 21160397.


7. Schmid MR, Stucki G, Duewell S, Wildermuth S, Romanowski B, Hodler J. Changes in cross-sectional measurements of the spinal canal and intervertebral foramina as a function of body position: in vivo studies on an open-configuration MR system. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999;172:1095–1102. PMID: 10587155.


8. Youssef JA, McAfee PC, Patty CA, et al. Minimally invasive surgery: lateral approach interbody fusion: results and review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35(26 Suppl): S302–S311. PMID: 21160394.


9. Elowitz EH, Yanni DS, Chwajol M, Starke RM, Perin NI. Evaluation of indirect decompression of the lumbar spinal canal following minimally invasive lateral transpsoas interbody fusion: radiographic and outcome analysis. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 2011;54:201–206. PMID: 22278781.


10. Sairyo K, Biyani A, Goel V, et al. Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: a multidisciplinary investigation based on clinical, biomechanical, histologic, and biologic assessments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:2649–2656. PMID: 16319751.


11. Moon HJ, Park YK, Ryu Y, Kim JH, Kwon TH, Chung HS. The angiogenic capacity from ligamentum flavum subsequent to inflammation: a critical component of the pathomechanism of hypertrophy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37:E147–E155. PMID: 21673619.


12. Sairyo K, Biyani A, Goel VK, et al. Lumbar ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is due to accumulation of inflammation-related scar tissue. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:E340–E347. PMID: 17495768.


13. Nakatani T, Marui T, Hitora T, Doita M, Nishida K, Kurosaka M. Mechanical stretching force promotes collagen synthesis by cultured cells from human ligamentum flavum via transforming growth factor-beta1. J Orthop Res 2002;20:1380–1386. PMID: 12472256.


14. Park JB, Lee JK, Park SJ, Riew KD. Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal stenosis associated with increased proteinase inhibitor concentration. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87:2750–2757. PMID: 16322626.


15. Zhong ZM, Zha DS, Xiao WD, et al. Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spine stenosis associated with the increased expression of connective tissue growth factor. J Orthop Res 2011;29:1592–1597. PMID: 21484860.


16. Zhang Y, Chen J, Zhong ZM, Yang D, Zhu Q. Is platelet-derived growth factor-BB expression proportional to fibrosis in the hypertrophied lumber ligamentum flavum? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:E1479–E1486. PMID: 21102276.


17. Lakemeier S, Schofer MD, Foltz L, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor, and matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3, and 9 in hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. J Spinal Disord Tech 2013;26:400–406. PMID: 22323068.


18. Ohtori S, Inoue G, Ito T, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-immunoreactive cells and PGP 9.5-immunoreactive nerve fibers in vertebral endplates of patients with discogenic low back Pain and Modic Type 1 or Type 2 changes on MRI. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:1026–1031. PMID: 16641780.


19. Ohtori S, Yamashita M, Yamauchi K, et al. Change in Modic type 1 and 2 signals after posterolateral fusion surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:1231–1235. PMID: 20173679.


20. Bae JS, Lee SH, Kim JS, Jung B, Choi G. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar interbody fusion with percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for adult low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis: minimum 3 years of follow-up. Neurosurgery 2010;67:1600–1607. PMID: 21107190.


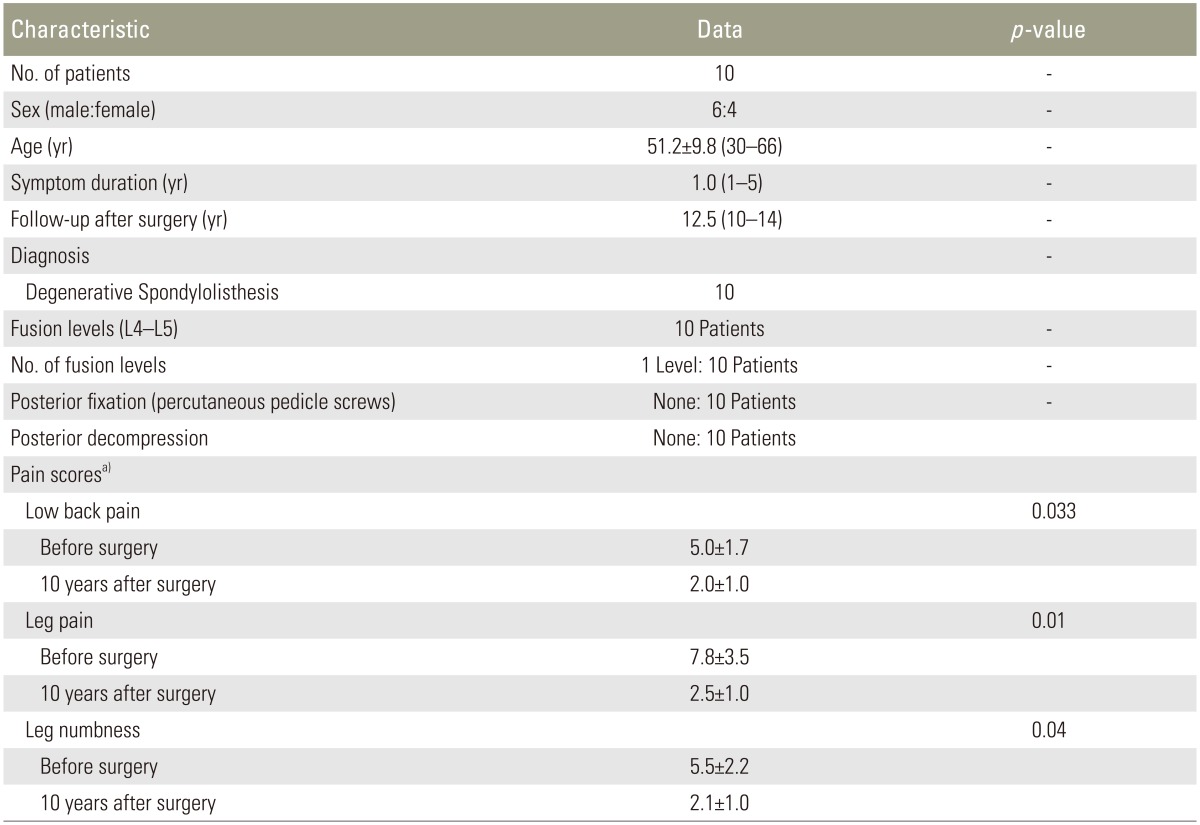
Fig. 1
L4 degenerative spondylolisthesis in a 56-year-old man. (A) Lateral radiograph before surgery. (B) Lateral radiograph 1 month after surgery (oblique lumbar interbody fusion [OLIF] plus posterior percutaneous pedicle screws). Sagittal and axial magnetic resonance imaging before surgery (C, E) and 1 month after surgery (D, F). Spinal canal enlarged after surgery; however, the enlargement was not sufficient and the thickness of the ligamentum flavum remained.
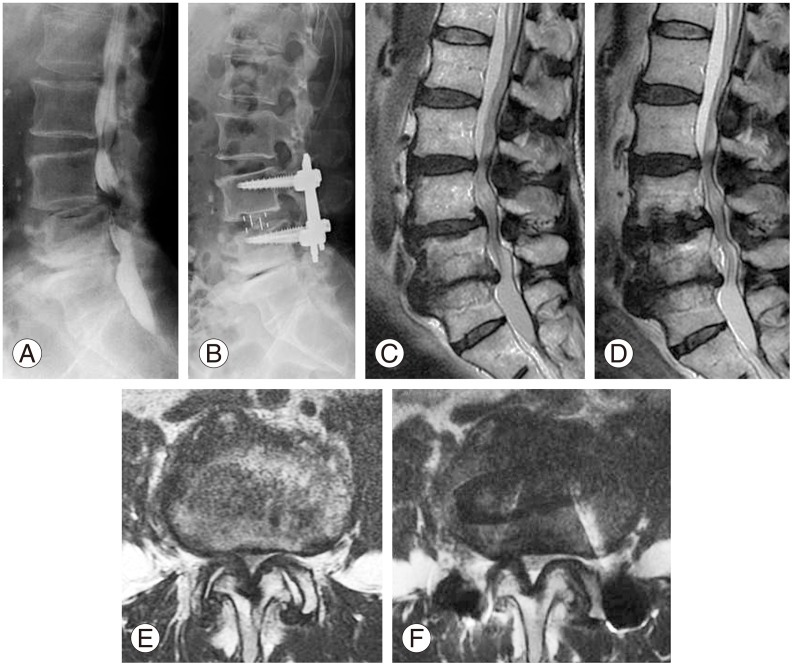
Fig. 2
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) surgery for L4 degenerative spondylolisthesis in a 56-year-old man. (A) Lateral radiograph 10 years after surgery. Patient shows fusion with anterior slip at L4. Sagittal (B) and axial magnetic resonance imaging (C–E) 10 years after ALIF surgery. Cross-sectional area (CSA) of the ligamentum flavum at the level of fusion (E) was significantly less and the CSA of the dural sac at the level of fusion (E) was significantly larger than at the upper 2 levels (C, D).
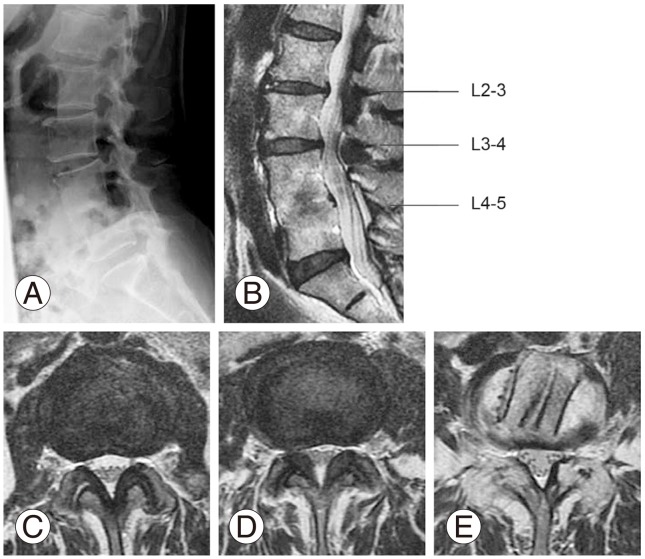
Fig. 3
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) surgery for L4 degenerative spondylolisthesis in a 61-year-old woman. (A) Lateral radiograph 10 years after surgery. Patient shows fusion with anterior slip at L4. Sagittal (B) and axial magnetic resonance imaging (C–E) 10 years after ALIF surgery. Cross-sectional area (CSA) of the ligamentum flavum at the level of fusion (E) was significantly less and the CSA of the dural sac at the level of fusion (E) was significantly larger than at the upper 2 levels (C, D).

Fig. 4
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) surgery for L4 degenerative spondylolisthesis in a 50-year-old man. (A) Lateral radiograph 10 years after surgery. Patient shows fusion with anterior slip at L4. Sagittal (B) and axial magnetic resonance imaging (C–E) 10 years after ALIF surgery. Cross-sectional area (CSA) of the ligamentum flavum at the level of fusion (E) was significantly less and the CSA of the dural sac at the level of fusion (E) was significantly larger than at the upper 2 levels (C, D).

Fig. 5
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) surgery for L4 degenerative spondylolisthesis in a 30-year-old man. (A) Lateral radiograph 10 years after surgery. Patient shows fusion with anterior slip at L4. Sagittal (B) and axial magnetic resonance imaging (C–E) 10 years after ALIF surgery. Cross-sectional area (CSA) of the ligamentum flavum at the level of fusion (E) was significantly less and the CSA of the dural sac at the level of fusion (E) was significantly larger than at the upper 2 levels (C, D).

Fig. 6
Average cross-sectional area (CSA) of the ligamentum flavum and the dural sac at each level. (A) Average CSA of the ligamentum flavum at L4–5 was significantly less than at other levels (*p<0.05). (B) Average CSA of the dural sac at L4–5 was significantly larger than at other levels (*p<0.05).

- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles in ASJ
-
Treatment of Surgical Site Infection in Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion2015 December;9(6)