|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 17(5); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to clarify the influence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) on bone fusion after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF).
Overview of Literature
The negative effects of DISH on lumbar degenerative diseases have been reported, and DISH may be involved in the onset and severity of lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Patients with DISH have significantly more reoperations after posterior lumbar fusion, including TLIF. However, the effects of DISH on bone fusion after TLIF have not been reported.
Methods
The medical records of patients with intervertebral TLIF from 2012 to 2018 were retrospectively examined. The patients were divided into those with fusion and those with pseudoarthrosis, and the following data were compared: age, sex, DISH, diabetes mellitus, smoking, drinking, albumin levels, body mass index ≥30 kg/m2, and L5/S fixation. Statistical analyses were performed using regression models.
Results
In this study, 180 patients (78.6%) had fusion and 49 patients (21.4%) had pseudoarthrosis. The number of patients with DISH was significantly higher in the pseudoarthrosis group than in the fusion group (36.7% and 21.7%, respectively; univariate p=0.031, multivariate p=0.019). No significant differences in age, sex, diabetes mellitus, smoking, drinking, albumin levels, body mass index ≥30 kg/m2, and L5/S fixation were observed between the two groups. The risk factors for bone fusion were statistically analyzed in 57 patients with DISH. DISH with a caudal end below Th11 was an independent risk factor for pseudoarthrosis (univariate p=0.011, multivariate p=0.033).
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), proposed by Resnick et al. [1] in 1975, is a noninflammatory skeletal disease with an unknown etiology, characterized by calcification and ossification of soft tissues, predominantly ligaments and entheses. In addition to many reports of the effects of DISH on dysphagia and spinal trauma [2,3], its negative effects on lumbar degenerative disease have recently been reported. Yamada et al. [4] reported that DISH is involved in the onset and severity of lumbar spinal stenosis. Moreover, increased lumbar reoperation rates after posterior lumbar fusion, including transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), in patients with DISH extending to the lumbar spine have also been reported [5]. However, to the best of our knowledge, no reports clearly identified pseudoarthrosis after TLIF in patients with DISH.
Pseudarthrosis of the spine is a frequent complication of spinal fusion. The occurrence rate of pseudarthrosis after posterior lumbar fusion is reported to be 0%–41.4% [6–9]. The clinical significance of pseudoarthrosis varies; patients may have progressive pain, instability, or both. The actual incidence rate is greater than the reported rate because some patients with pseudoarthrosis do not present with symptoms. Pseudarthrosis of the lumbar spine resulting from bone fusion failure is typically evident 1 year after attempted spinal fusion [10–12]. Several factors predispose patients to pseudarthrosis, namely, poor surgical technique, metabolic abnormalities, excessive motion, trauma, infection, and smoking [13]. DISH is also a possible risk factor for pseudarthrosis. Because of the long lever arm associated with spinal ankylosis, we hypothesized that after TLIF, the incidence of pseudoarthrosis is higher in patients with DISH than in those without DISH.
This study aimed to clarify the effects of DISH on bone fusion after TLIF.
This study included consecutive patients who underwent one intervertebral TLIF at a single facility from 2012 to 2018. The surgical indications were severe leg pain, numbness that resists conservative therapy, severe muscle weakness, and bladder and rectal disorders, and the indications for fixation were lumbar spondylolisthesis with excessive instability in the X-ray sagittal section, intervertebral foraminal stenosis, and lateral hernia. All patients were decompressed and fixed based on preoperative magnetic resonance imaging and X-ray findings. During the study period, 1,004 patients underwent TLIF. The exclusion criteria were as follows: patients aged >50 years, those with previous spinal surgery, those with malignant neoplasms, those undergoing TLIF of two or more intervertebral disks, and those who had a follow-up of <12 months. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 229 patients were included in this study (Fig. 1).
The surgeons were four spine specialists, all of whom performed the same procedure. The procedure for TLIF was to remove one side of the facet joint, then scrape the intervertebral disk, fill the defect with autologous bone, insert a titanium cage, and insert pedicle screws. Only autogenous bone was used for grafts; no bone morphogenetic proteins were used. Bone grafts were used only to fill the disk space.
Bone fusion was evaluated at the final follow-up computed tomography (CT) at least 12 months after surgery, and two central slices of the cage (coronal and sagittal views) were used according to the bone fusion evaluation method of Ushirozako et al. [14]. Bone formation was graded according to the classification of Bridwell et al. [15] using the following three categories: grade I indicated bridging bone bonding with both adjacent vertebral bodies, grade II indicated bridging bone bonding with either the superior or inferior vertebral body, and grade III indicated incomplete bone bridging. Ushirozako et al. [14] defined grade I as bone fusion in the two CT slices and grade II or III as pseudoarthrosis. In our study, we defined bone fusion and pseudoarthrosis using the same evaluation method as that of Ushirozako et al. [14]. According to the definition of Resnick et al. [1] and Resnick and Niwayama [16], DISH was defined as continuous anterior or lateral vertebral cross-linking and fusion of three or more intervertebral disks in a standing whole spine X-ray. Additionally, the sacroiliac joint was assumed to have no degeneration or ankylosis (Fig. 2).
Bone fusion was the primary endpoint, and factors that could affect bone fusion (e.g., age, sex, diabetes mellitus, smoking, obesity [body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2], alcohol consumption, and albumin levels), and DISH were the secondary endpoints. L5/S fixation was also included as a secondary endpoint because achieving bone fusion in L5/S fixation is difficult [17]. The primary and secondary endpoints were analyzed statistically.
The patients’ data were collected by referring to their medical records. This study was a joint study between two orthopedic institutions, and the study was approved by the appropriate ethics committee (approval no., U21-10-007). The requirement for informed consent from individual patients was omitted because of the retrospective design of this study.
First, patients’ characteristics were investigated by classifying them into a group with DISH and a group without DISH. Groups with different categorical and continuous variables were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test and chi-square test, respectively. Subsequently, the factors affecting bone fusion were investigated. The risk factors were identified by classifying the patients into a group with fusion and a group with pseudoarthrosis, and the results were shown as odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals using logistic regression analysis. p-values <0.05 were used to denote statistical significance. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Fifty-seven patients (24.9%) had DISH and 172 patients (75.1%) did not have DISH. The levels of fixation were L3/4 in 31 patients (DISH group: 6, non-DISH group: 25), L4/5 in 126 patients (DISH group: 25, non-DISH group: 101), and L5/S in 72 patients (DISH group: 26, non-DISH group: 46). Statistical analyses showed that the DISH group had a higher proportion of male patients (77.2% and 55.8%, p<0.01), a higher number of older patients (73.1±8.5 years and 68.3±9.7 years, p<0.01), a higher prevalence of diabetes mellitus (31.6% and 14.0%, p<0.01), a higher number of patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 (17.5% and 2.3%, p<0.01), and a higher number of patients with L5/S fixation (45.6% and 26.7%, p<0.01) than the non-DISH group. In contrast, no significant differences in alcohol consumption, smoking, albumin levels, follow-up duration, and L3/4 or L4/5 fixation were observed between the two groups (Table 1).
Overall, 180 patients (78.6%) had fusion and 49 patients (21.4%) had pseudoarthrosis, and no significant difference in the follow-up duration was observed between the two groups (30.3±20.0 months and 27.1±18.5 months, p=0.41). Additionally, statistical analysis of the factors that may influence bone fusion in one intervertebral TLIF revealed that DISH was the only significant unfavorable factor in both the univariate and multivariate analyses (univariate p=0.031, multivariate p=0.019). No significant differences in age, sex, diabetes mellitus, smoking, BMI ≥30 kg/m2, alcohol consumption, albumin level, and L5/S fixation were found between the two groups (Table 2).
The reported etiological factors for DISH were age, sex, obesity, and metabolic abnormalities. The background of the patients in this study suggested a relationship between DISH and older age, male sex, diabetes mellitus, and obesity, similar to the results in previous reports [18–21].
Diabetes mellitus and smoking have been reported to be significant factors affecting bone fusion after lumbar fixation [22,23]; however, in our study, diabetes mellitus and smoking had no significant effect on bone fusion. Additionally, low nutritional status may have a negative effect on bone fusion. Therefore, alcohol consumption and albumin levels were also examined, and these factors had no significant effect. Although it has been reported that achieving bone fusion in L5/S posterior fixation is difficult because of increased shear forces, decreased compressive strength, and a wider range of motion [17,24,25], L5/S fixation did not statistically affect bone fusion in this study. The analyses in this study revealed DISH as the only statistically significant factor affecting bone fusion, indicating that DISH is an independent risk factor for pseudoarthrosis after one intervertebral TLIF. Otsuki et al. [26] reported that the number of reoperations in patients who underwent posterior lumbar fusion was significantly higher in the group with DISH than in the group without DISH. The authors also noted that the decrease in spinal flexibility owing to DISH increased the mechanical load on the remaining mobile vertebrae and increased reoperation rates [26]. It is possible that the results of this study, in which DISH was identified as a risk factor for pseudoarthrosis, may be because of the same mechanism.
The factors influencing bone fusion after one intervertebral TLIF in patients with DISH are unclear. Therefore, we performed a statistical analysis involving 57 patients with DISH (39 patients with fusion and 18 patients with pseudoarthrosis). Loss of flexibility extending below the thoracolumbar transition may cause more load on the lumbar spine. Therefore, we hypothesized that DISH extending below the thoracolumbar transition would cause a greater load on the fixed lumbar spine than DISH restricted to the midthoracic spine. Borkowski et al. [27] reported that in the spine below Th11, continuity with the sternum is lost, and the range of motion increases. Therefore, we hypothesized that mechanical loading would be greater in patients with DISH extending below Th11, and we compared the rate of bone fusion in patients with DISH extending below Th11 with that of patients with DISH not extending below Th11. The results showed that DISH with a caudal end below Th11 was an independent risk factor for pseudoarthrosis (univariate p=0.011, multivariate p=0.033). Additionally, of the 18 patients with pseudoarthrosis, 17 had DISH with a caudal end extending below Th11 (Table 3). The thoracolumbar transition (Th10–L2) is a region of biomechanical load because of the transition from the less mobile thoracic spine, associated with the sternum and ribs, to the more mobile lumbar spine [28]. Because the 10th rib is continuous with the sternum via the costal cartilage, DISH with a caudal end above Th10 may have little effect on the mobility of the thoracolumbar transition region. However, DISH extending below Th11 decreases the flexibility of the thoracolumbar transition and increases the load on the lumbar spine, which remains mobile; thus, the load on the fixation site increases and bone fusion is possibly affected. Fig. 3 shows a CT image of one pseudoarthrosis case after TLIF in patients with DISH extending below Th11.
Yamada et al. [5] investigated the postoperative outcomes of lumbar spine surgery in patients with DISH extending to the lumbar spine (L-DISH) and those without L-DISH and reported that reoperations were significantly more frequent in the L-DISH group than in the group without L-DISH. Considering this report, among patients with DISH extending below Th11, we expected that pseudoarthrosis would be more common in those with DISH extending to the caudal level, and we investigated this correlation. However, we found no correlation between the caudal level and the incidence of pseudoarthrosis among patients with DISH extending below Th11. Because the number of patients in this study was small and the follow-up period was short (≥1 year), finding a correlation between the caudal level and pseudoarthrosis may be possible with an increase in the number of patients and a longer follow-up period.
This study did not evaluate bone mineral density (BMD), bone metabolism markers, and osteoporosis drugs, which is considered a limitation. The relationship between BMD, bone metabolism markers, and DISH has been reported. Uehara et al. [29] reported that patients with DISH had significantly higher BMD than those without DISH, and the authors also reported that neither bone formation markers nor bone resorption markers were associated with DISH. The mechanism of high BMD in DISH is currently unknown; however, it is possible that the true vertebral body BMD is overestimated by projecting new bone onto the vertebral body in anterior-posterior imaging views. Alternatively, in addition to BMD, the mechanism may be related to bone quality, which is another important factor for bone strength [29,30]. Therefore, DISH merely promotes ligament ossification and does not directly promote bone fusion.
This study revealed that DISH is a risk factor for pseudoarthrosis after one intervertebral TLIF and that DISH with a caudal end extending below Th11 is also a risk factor for pseudoarthrosis. These results suggest that the loss of flexibility owing to DISH leads to excessive loading on the lumbar spine, which remains mobile. In particular, DISH with a caudal end extending below the thoracolumbar transition further reduces the mobility of the lumbar spine, and TLIF below the caudal end of DISH increases the mechanical load at the fixation site, which may be a risk factor for pseudoarthrosis.
Other limitations in this study were its retrospective design and small sample size. Additionally, selection bias cannot be ruled out because some cases could not be followed. The follow-up period was not standardized, and follow-up was defined as longer than 12 months after surgery, which included patients with a short follow-up period, which may be a limitation. Therefore, using this investigation as a pilot study, further research using a larger sample size and longer follow-up may help resolve several unclear issues in this study.
This study shows that DISH is an independent risk factor for pseudoarthrosis after one intervertebral TLIF and that DISH with a caudal end below Th11 is associated with a higher risk of pseudoarthrosis than DISH without a caudal end below Th11.
Care should be taken in following up postoperative lumbar surgery patients with DISH. Particular attention should be paid to DISH where the caudal end extends below the thoracolumbar transition region.
Fig. 2
Radiographs of representative cases of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). (A) Preoperative standing whole spine X-ray (anterior-posterior view) of a 68-year-old woman. The radiograph shows DISH from Th6 to Th11. (B) Preoperative standing whole spine X-ray (lateral view) of a 73-year-old man. The radiograph shows DISH from Th7 to Th11.
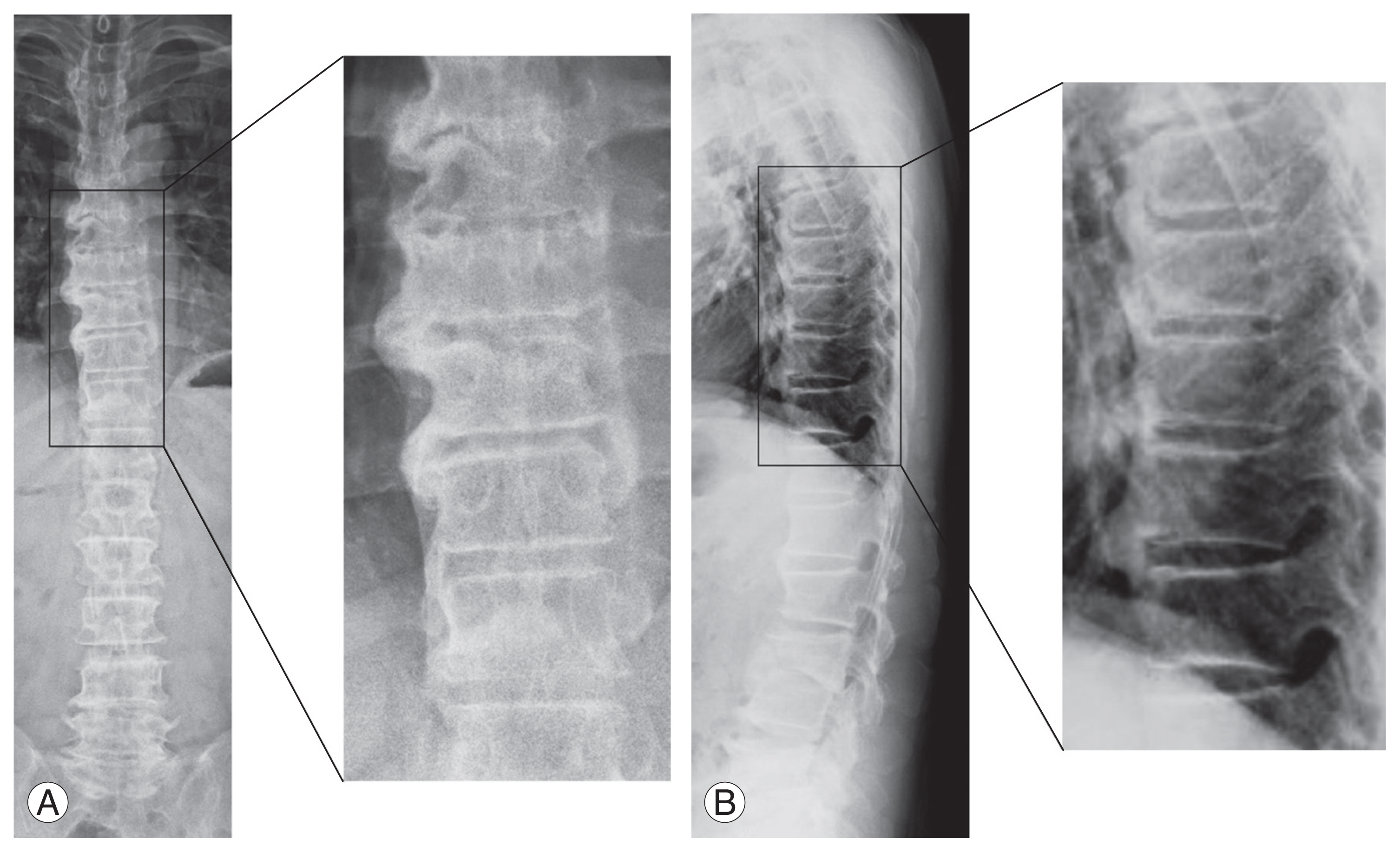
Fig. 3
A case of pseudoarthrosis after L5/S transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) in a 72-year-old man with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). (A, B) Preoperative standing whole spine X-ray anterior-posterior and lateral view. The radiograph shows DISH from Th8 to L1 in the anterior-posterior view and from Th5 to L1 in the lateral view. (C, D) Lumbar spine X-ray anterior-posterior and lateral view, 15 months postoperatively. (E, F) Computed tomography coronal and sagittal views, respectively, 15 months postoperatively. The coronal slice shows grade II, and the sagittal slice shows grade III, in Bridwell’s classification.

Table 1
Difference of characteristics between patients DISH (+) and DISH (−)
| Characteristic | DISH+ (n=57) | DISH- (n=172) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 44 (77.2) | 96 (55.8) | <0.01a) |
| Age (yr) | 73.1±8.5 | 68.3±9.7 | <0.01a) |
| Body mass index ≥30 kg/m2 | 10 (17.5) | 4 (2.3) | <0.01a) |
| Diabetes | 18 (31.6) | 24 (14.0) | <0.01a) |
| Drinking | 28 (49.1) | 70 (40.7) | 0.27 |
| Smoking | 10 (17.5) | 38 (22.1) | 0.47 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.33±0.29 | 4.32±0.32 | 0.84 |
| Follow-up period (mo) | 30.4±18.9 | 29.4±19.9 | 0.32 |
| Level of fixation | |||
| L3/4 | 6 (10.5) | 25 (14.5) | 0.44 |
| L4/5 | 25 (43.9) | 101 (58.7) | 0.05 |
| L5/S | 26 (45.6) | 46 (26.7) | <0.01a) |
Table 2
Factors affecting bone fusion after one intervertebral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion
| Variable | Fusion+ (n=180) | Pseudoarthrosis (n=49) | Univariate | Multivariate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||
| p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |||
| Age (yr) | 69.4±6.7 | 69.8±9.1 | 0.875 | 1.003 (0.963–1.045) | 0.887 |
|
|
|||||
| Male | 105 (58.3) | 35 (71.4) | 0.096 | 0.530 (0.228–1.228) | 0.138 |
|
|
|||||
| DISH | 39 (21.7) | 18 (36.7) | 0.031a) | 2.672 (1.175–5.873) | 0.019a) |
|
|
|||||
| Diabetes | 34 (18.9) | 8 (16.3) | 0.682 | 0.802 (0.324–1.980) | 0.632 |
|
|
|||||
| Smoking | 37 (20.6) | 11 (22.4) | 0.773 | 1.117 (0.463–2.698) | 0.805 |
|
|
|||||
| BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 13 (7.2) | 1 (2.0) | 0.180 | 0.183 (0.021–1.586) | 0.123 |
|
|
|||||
| Drinking | 79 (43.9) | 19 (38.8) | 0.522 | 0.544 (0.259–1.137) | 0.105 |
|
|
|||||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.31±0.31 | 4.36±0.31 | 0.441 | 1.727 (0.539–5.539) | 0.358 |
|
|
|||||
| L5/S fixation | 58 (32.2) | 14 (28.6) | 0.626 | 0.657 (0.312–1.381) | 0.268 |
Table 3
Factors affecting bone fusion after one intervertebral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in DISH patients
| Variable | Fusion+ (n=39) | Pseudoarthrosis (n=18) | Univariate | Multivariate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
||||
| p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |||
| Age (yr) | 72.3±9.1 | 74.6±6.6 | 0.491 | 1.020 (0.937–1.111) | 0.647 |
|
|
|||||
| Male | 29 (74.4) | 15 (83.3) | 0.457 | 0.847 (0.126–5.710) | 0.865 |
|
|
|||||
| Diabetes | 14 (35.9) | 4 (22.2) | 0.306 | 0.920 (0.194–4.354) | 0.916 |
|
|
|||||
| Smoking | 6 (15.4) | 4 (22.2) | 0.532 | 1.543 (0.287–8.300) | 0.613 |
|
|
|||||
| BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 9 (23.1) | 1 (5.6) | 0.109 | 0.179 (0.016–2.046) | 0.166 |
|
|
|||||
| DISH extending Th11 and below | 24 (61.5) | 17 (94.4) | 0.011a) | 11.751 (1.222–112.984) | 0.033a) |
|
|
|||||
| Drinking | 19 (48.7) | 9 (50.0) | 0.929 | 0.632 (0.143–2.795) | 0.545 |
|
|
|||||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.36±0.29 | 4.26±0.28 | 0.132 | 0.131 (0.010–1.729) | 0.123 |
|
|
|||||
| L5/S fixation | 19 (48.7) | 7 (38.9) | 0.492 | 1.094 (0.292–4.100) | 0.895 |
References
1. Resnick D, Shaul SR, Robins JM. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): Forestier’s disease with extraspinal manifestations. Radiology 1975;115:513–24.


2. Mosher HP. Exostoses of the cervical vertebrae as a cause for difficulty in swallowing. Laryngoscope 1926;36:181–2.

3. Diederichs G, Engelken F, Marshall LM, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): relation to vertebral fractures and bone density. Osteoporos Int 2011;22:1789–97.



4. Yamada K, Satoh S, Hashizume H, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis is associated with lumbar spinal stenosis requiring surgery. J Bone Miner Metab 2019;37:118–24.



5. Yamada K, Satoh S, Abe Y, Yanagibashi Y, Hyakumachi T, Masuda T. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis extended to the lumbar segment is a risk factor of reoperation in patients treated surgically for lumbar stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018;43:1446–53.


6. Wu RH, Fraser JF, Hartl R. Minimal access versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: meta-analysis of fusion rates. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:2273–81.

7. Formica M, Vallerga D, Zanirato A, et al. Fusion rate and influence of surgery-related factors in lumbar interbody arthrodesis for degenerative spine diseases: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Musculoskelet Surg 2020;104:1–15.



8. Kim DH, Hwang RW, Lee GH, et al. Comparing rates of early pedicle screw loosening in posterolateral lumbar fusion with and without transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J 2020;20:1438–45.


9. Campbell RC, Mobbs RJ, Lu VM, Xu J, Rao PJ, Phan K. Posterolateral fusion versus interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Global Spine J 2017;7:482–90.




10. Heggeness MH, Esses SI. Classification of pseudarthroses of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1991;16(8 Suppl): S449–54.


11. Etminan M, Girardi FP, Khan SN, Cammisa FP Jr. Revision strategies for lumbar pseudarthrosis. Orthop Clin North Am 2002;33:381–92.


12. Heggeness MH, Esses SI, Mody DR. A histologic study of lumbar pseudarthrosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993;18:1016–20.


14. Ushirozako H, Hasegawa T, Ebata S, et al. Weekly teriparatide administration and preoperative anterior slippage of the cranial vertebra next to fusion segment < 2 mm promote osseous union after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2019;44:E288–97.


15. Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, McEnery KW, Baldus C, Blanke K. Anterior fresh frozen structural allografts in the thoracic and lumbar spine: do they work if combined with posterior fusion and instrumentation in adult patients with kyphosis or anterior column defects? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:1410–8.

16. Resnick D, Niwayama G. Radiographic and pathologic features of spinal involvement in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Radiology 1976;119:559–68.


17. Han SH, Hyun SJ, Jahng TA, Kim KJ. A comparative radiographic analysis of fusion rate between L4–5 and L5-S1 in a single level posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Korean J Spine 2015;12:60–7.



18. Mori K, Kasahara T, Mimura T, Nishizawa K, Nakamura A, Imai S. Prevalence of thoracic diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) in Japanese: results of chest CT-based cross-sectional study. J Orthop Sci 2017;22:38–42.


19. Kiss C, Szilagyi M, Paksy A, Poor G. Risk factors for diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a case-control study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002;41:27–30.


20. Sencan D, Elden H, Nacitarhan V, Sencan M, Kaptanoglu E. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in patients with diabetes mellitus. Rheumatol Int 2005;25:518–21.



21. Denko CW, Malemud CJ. Body mass index and blood glucose: correlations with serum insulin, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Rheumatol Int 2006;26:292–7.



22. Glassman SD, Alegre G, Carreon L, Dimar JR, Johnson JR. Perioperative complications of lumbar instrumentation and fusion in patients with diabetes mellitus. Spine J 2003;3:496–501.


23. Glassman SD, Anagnost SC, Parker A, Burke D, Johnson JR, Dimar JR. The effect of cigarette smoking and smoking cessation on spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:2608–15.


24. Panjabi MM, Oxland TR, Yamamoto I, Crisco JJ. Mechanical behavior of the human lumbar and lumbosacral spine as shown by three-dimensional load-displacement curves. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1994;76:413–24.


26. Otsuki B, Fujibayashi S, Takemoto M, Kimura H, Shimizu T, Matsuda S. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a risk factor for further surgery in short-segment lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J 2015;24:2514–9.



27. Borkowski SL, Tamrazian E, Bowen RE, Scaduto AA, Ebramzadeh E, Sangiorgio SN. Challenging the conventional standard for thoracic spine range of motion: a systematic review. JBJS Rev 2016;4:e51–511.

28. Wood KB, Li W, Lebl DR, Ploumis A. Management of thoracolumbar spine fractures. Spine J 2014;14:145–64.