 |
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 13(3); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to compare three widely used interbody fusion approaches in regard to their ability to correct sagittal balance, including pelvic parameters.
Overview of Literature
Restoration of sagittal balance in lumbar spine surgery is associated with better postoperative outcomes. Various interbody fusion techniques can help to correct sagittal balance, with no clear consensus on which technique offers the best correction.
Methods
The charts and imaging of patients who have undergone surgery through either open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), minimally invasive TLIF (MIS TLIF), or oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) were retrospectively reviewed. The following sagittal balance parameters were measured pre- and postoperatively: segmental lordosis, lumbar lordosis, disk height, pelvic tilt, and pelvic incidence. Data on postoperative complications were gathered.
Results
Only OLIF managed to significantly improve segmental lordosis (4.4°, p<0.001) and lumbar lordosis (4.8°, p=0.049). All approaches significantly augmented disk height, with OLIF having the greatest effect (3.7°, p<0.001). No approaches were shown to significantly correct pelvic tilt. Pelvic incidence remained unchanged in all approaches. Open TLIF was the only approach with a higher rate of postoperative complications (33%, p=0.009).
Conclusions
The OLIF approach might offer greater correction of sagittal balance over open and MIS TLIF, mainly in regard to segmental lordosis, lumbar lordosis, and disk height. MIS TLIF, although offering more limited access than open TLIF, was not inferior to open TLIF in regard to sagittal balance correction. A higher rate of complications was shown for open TLIF than the other approaches, possibly due to its more invasive nature.
Sagittal balance is related to the alignment of the spine in the sagittal plane, allowing for an upright gait with a minimal use of power [1,2]. The role of the pelvis is being increasingly recognized as a central aspect of sagittal balance [3,4], and three key pelvic parameters are now commonly used to help depict sagittal balance: pelvic tilt, pelvic incidence, and sacral slope (Fig. 1). With degenerative changes and the loss of lumbar lordosis, the pelvis compensates with retroversion, increasing the pelvic tilt [5]. Postoperative failure to correct this loss of balance in the sagittal plane has been associated with persistent low back pain, residual extremity numbness, heightened adjacent level disease, and hardware failure [6-8]. Thus, establishing postoperative sagittal balance has become a main goal of surgery.
Interbody fusion techniques allow for some degree of correction in the sagittal plane without the need for more extensive osteotomies. Various approaches, such as transforaminal, anterolateral, and extreme lateral approaches augment the tools the surgeon can use to perform interbody fusion and correct sagittal balance. Open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is a mainstay approach. In recent years, however, other avenues such as minimally invasive TLIF (MIS TLIF), and lateral techniques such as oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) have gained popularity. The rationale of less-invasive approaches such as MIS TLIF and OLIF is to reduce blood loss and tissue debridement, increasing the tolerability of such surgeries [9,10].
To date, there has been no consensus as to which of these approaches offers greater sagittal balance correction [11]. Thus, the objective of this study was to compare three of the most used interbody fusion approaches to sagittal balance correction using pelvic parameters: TLIF, MIS TLIF, and OLIF.
After approval from the ethics committee of Centre Hospitalier de l'Université de Montréal (IRB approval no., 2017-6668), a retrospective analysis was conducted of a series of patients at a single institution submitted to a lumbar interbody fusion surgery using either open TLIF, MIS TLIF, or OLIF. Written informed consents were not obtained due to the retrospective and anonymized nature of the study. Technical specifications defining each of these approaches will be detailed in a later section. Inclusion criteria were as follows: surgery between February 2010 and September 2017, age older than 18 years, and preoperative lumbosciatalgia warranting intervention. Exclusion criteria were as follows: pre- or postoperative lumbar imaging not available for analysis, pre- or postoperative imaging available but of too poor quality to be analyzed, and previous lumbar instrumentation. Data were retrospectively collected from the patient’s medical files, operative reports, and imaging files. Collected information focused on the patient’s demographic characteristics, diagnosis, pain improvement, postoperative complications within hospitalization, and pre- or postoperative sagittal balance parameters. Sagittal balance parameters were collected by a single-blinded observer from pre- and postoperative lateral lumbar spine radiographs showing at least the T12 vertebra superiorly and both femoral heads inferiorly. The studied parameters included segmental lordosis at each surgically treated level, disk height for each surgically treated level, lumbar lordosis, pelvic tilt, and pelvic incidence (Fig. 1). Segmental lordosis for a given level was defined as the angle between the superior and inferior endplates composing the disk space. Disk height was defined as the mean of the anterior and posterior heights of a given intervertebral space. Lumbar lordosis was defined as the angle between the sacral plate and the lower endplate of the T12 body. Pelvic tilt was defined as the angle between a line joining the middle of the sacral plate and the middle of the femoral heads and a descending vertical line. Pelvic incidence was defined as the angle between a line joining the middle of the sacral plate and the femoral heads and a line perpendicular to the sacral plate. All these parameters were measured for each patient pre- and postoperatively on lateral plain radiographs. To assess the clinical outcome after surgery, data on postoperative complications were collected. We defined postoperative complications as any adverse and new event occurring during hospitalization following surgery.
The statistical analysis on the collected data was conducted using IBM SPSS software ver. 24.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). A paired two-tailed Student t-test was used for a means comparison of the continuous variables, such as the pre- and postoperative differences between the five sagittal balance parameters studied. A univariate two-tailed chi-square test was used for the nominal and ordinal variables, and Fisher’s exact test was used instead, when indicated. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used when comparing means between the three studied groups. For the paired Student t-test and the ANOVA, a p-value of <0.05 was considered significant. For the chisquare test, a Bonferroni correction was used to adjust the p-value when comparing the three groups studied in regard to complication occurrence. When comparing each group with the others, a p-value <0.016 was considered significant (for a global p-value of <0.05).
Open TLIF procedures are performed with the patient lying ventrally, via a midline incision to dissect the paraspinal muscles and expose the lumbar spine. After laminectomy at the appropriate level, a unilateral facetectomy is performed to access the disk space, followed by a discectomy and placement of a lordotic 4° cage (CONCORDE; DePuy Synthes Spine, Warsaw, IN, USA). Posterolateral instrumentation with screws and rods is then used to supplement the anterior construct. MIS TLIF procedures are performed using tubular retractors to access the lumbar spine, followed by a laminectomy, facetectomy, and lordotic 4° cage placement (CONCORDE, DePuy Synthes Spine). Percutaneous screw placement follows. OLIF procedures are performed with the patient lying on their side with an incision centered between the lower rib margin and the anterosuperior iliac spine to access the lumbar spine in a retroperitoneal fashion. After discectomy, a lordotic 7.5° cage (COUGAR, DePuy Synthes Spine) is placed in the intervertebral space. A second-stage surgery is performed either the same day or in the following days. As needed, laminectomy and Smith–Peterson osteotomy are performed to add more correction to the sagittal alignment. Furthermore, if the patient presents severe spinal stenosis, only posterior laminectomy is performed to decompress the neural elements. If the surgery is performed for foraminal stenosis without any severe central stenosis and if the sagittal alignment is corrected via only the oblique approach, then a posterior laminectomy is not performed, and only percutaneous posterior fixation is achieved. Fig. 2 depicts an illustrative case of an OLIF procedure.
A total of 170 patients met the inclusion criteria. Of these, 21 had to be excluded due to unavailability of pre- or postoperative plain radiographs, and one patient had to be excluded due to poor-quality radiographs. The remaining 148 patients were included for the analysis. Of these, 45 (30%) had surgeries via open TLIF, 65 (44%) via MIS TLIF, and 38 (26 %) via OLIF. The mean age at surgery was 62 years, and the population was comprised of 61 men (41%) and 87 women (59%). No statistical differences were found between groups in regard to age or sex (p=0.917 and p=0.919, respectively). Spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis were the two most common diagnoses (67% and 51% of patients, respectively). Spondylolisthesis was more common among patients having MIS TLIF (80%) than TLIF (47%) or OLIF (68 %, p<0.001). Spinal stenosis was less common in patients having OLIF (29%) than TLIF (58%) or MIS TLIF (60%, p=0.002). A total of 256 levels were surgically treated in all patients, with a mean of 1.7 levels per patient. The average number of levels on which surgery was performed per patient was lower for MIS TLIF (1.3) compared with OLIF (2.1) and TLIF (2.1). The level of most surgeries was L4–L5 (46%) followed by L5–S1 (26%). No statistical differences were found between the three approaches in regard to the proportion of L4–L5 levels surgically treated (p=0.752). There was significantly less intervention on the L5–S1 space in the OLIF (19%) group compared with the TLIF (33%) and MIS TLIF (27%) groups. Details regarding the baseline characteristics of the population can be found in Table 1.
Plain lateral radiographs used to measure sagittal balance parameters were taken 8 months prior to and 10 days after surgery, on average. No statistically significant differences were found between groups in regard to baseline pelvic tilt and pelvic incidence (p=0.076 and p=0.517, respectively). At baseline, patients in the OLIF group had a smaller disk height than those in the MIS TLIF and TLIF groups (5.8 9 mm versus 8.8 mm and 8. 4 mm, respectively, p<0.001). Preoperative lumbar and focal lordosis were the lowest in the OLIF group and the highest in the TLIF group (focal lordosis 5.97° and 9.46°, respectively, p=0.01; lumbar lordosis 43.39° and 53.45°, respectively; p=0.015). Preoperative sagittal balance parameters for each group are summarized in Table 1.
For all patients, the mean preoperative segmental lordosis was 7.7°, and the mean postoperative segmental lordosis was 9.5° (p=0.003). Regarding the performance of each approach, only OLIF managed to significantly augment the segmental lordosis of surgically treated levels postoperatively (4.4° correction, p<0.001). For all patients, the mean preoperative disk height was 7.7 mm, and the mean postoperative disk height was 9.8 mm (p<0.001). In regard to the approach used, each one managed to statistically significantly augment disk height, with OLIF having the greatest impact (0.9 mm, 1. 7 mm, and 3.7 mm of correction for TLIF, MIS TLIF, and OLIF, with p=0.009, p<0.001, and p<0.001, respectively). For all patients, the mean preoperative lumbar lordosis was 48.26°, and the mean postoperative lumbar lordosis was 48.28° (p=0.99). Assessing each approach, only OLIF managed to significantly correct lumbar lordosis (4.8° correction, p=0.049), whereas MIS TLIF did not affect it (0.9° correction, p=0.65) and TLIF negatively corrected it (-5.2° correction, p=0.011). The mean preoperative pelvic tilt for all patients was 21.1 9°, whereas the mean postoperative pelvic tilt was 21.21° (p=0.9). No approach managed to significantly reduce the pelvic tilt; however, the open TLIF was significantly associated with an augmented postoperative−pelvic tilt (3.1° of augmentation, p=0.03). The mean preoperative pelvic incidence for all patients was 57.44°, and the mean postoperative pelvic incidence was 57.8 5° (p=0.7). No approaches were associated with a significant change in pelvic tilt. Table 2 summarizes the degree of correction provided for all the sagittal balance parameters for every approach.
Due to the anatomical and biomechanical differences of the L5–S1 segment in regard to other lumbar segments [12,13], a subgroup analysis limited to this segment was performed. In this group, no approach significantly corrected segmental lordosis, and only OLIF and MIS TLIF augmented disk height (2.7 mm correction, p<0.001; 1.34 mm correction, p=0.029, respectively). No approach positively changed lumbar lordosis, pelvic tilt, or pelvic incidence. However, for these three parameters, the analysis was limited to patients who underwent surgery solely on the L5–S1 level, greatly limiting the number of patients in each group. Table 3 summarizes the findings of the subgroup analysis.
The total complication rate for our population was 20% (30 patients). The most common complications were new onset of paresthesia (4.1%), increased sciatic pain (4.1%), and surgical site infections (4.7%). Only the open TLIF approach was associated with a significantly higher rate of complications (33%, p=0.009) compared with the rest of the population. The complication rates of MIS TLIF (14%) and OLIF (16 %) did not significantly differ from the rest of the patients (p=0.09 and p=0.4, respectively). Table 4 summarizes the complication rate in regard to each approach, and Table 5 summarizes the main complications. Pain improvement at the time of discharge was achieved for 78% of the patients. None of the approaches had a higher rate of pain improvement than the others in our analysis (p=0.81), and none of the postoperative sagittal balance parameters were associated with pain improvement on discharge (p=0.29, p=0.38, p=0.29, p=0.73, and p=0.34 for pelvic tilt, pelvic incidence, focal lordosis, lumbar lordosis, and disk height, respectively).
Sagittal parameters of the lumbar spine can be divided into those linked to the curvature of the spine, such as lumbar and segmental lordosis, and those involving the sacrum and pelvis, such as pelvic parameters. There is a direct correlation between lumbar lordosis and the sacral slope, which in turn is known to be related to the pelvic tilt [1 4]. This interdependence of pelvic parameters shows that correction of a single parameter might influence the others and help improve global balance.
The importance of sagittal balance correction, particularly in regard to pelvic parameters, is currently gaining more and more recognition, with restoration of sagittal balance being associated with overall better postoperative outcomes [7,15]. Current literature on the capacity of interbody fusion techniques to re-establish sagittal balance reports a variable degree of success for the various approaches. Ohtori et al. [16] found that OLIF significantly improved lumbar lordosis, pelvic tilt, and sacral slope; and Jin et al. [17] reported a significant increase in segmental lordosis and disk height with OLIF. Sembrano et al. [18] reported on the success of anterior interbody fusion (ALIF), TLIF, and lateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF) to improve segmental lordosis and disk height, with TLIF being the technique with the most modest gain in segmental lordosis (1.9° versus 3.8° and 3.2° for ALIF and LLIF, respectively). Open TLIF has been reported to significantly improve pelvic tilt, sacral slope, and lordosis by some [19,20] and not by others [21]. Sparse data exist regarding MIS TLIF and sagittal balance correction, with some studies reporting success in improving segmental lordosis and pelvic tilt, although the minimally invasive nature of the approach has raised controversy regarding its capacity to do so [22-24].
Few studies compare the results in regard to sagittal balance correction for more than one interbody fusion approach. A trend among those comparative studies is the superiority of anterior and lateral approaches over TLIF in regard to correction of segmental lordosis and disk height [25]. Our results are similar, given that OLIF was the only approach to significantly improve segmental and overall lumbar lordosis as well as being the approach with the highest gain in regard to disk height. The easier access to the anterior column offered by OLIF and the higher lordotic angle of the cages used could partly explain these results. Regarding pelvic parameters, our population can be regarded as having a high pelvic tilt (mean preoperative pelvic tilt of 21.19°) in regard to normal values adjusted for our population’s age (15°–18°) [26]. This is not surprising, given that loss of sagittal balance is part of the degenerative process leading to the symptomatic presurgical state these patients are in. Unfortunately, none of the approaches was able to significantly reduce the pelvic tilt. OLIF did however come close to a significant result (p=0.06). What is surprising is that the open TLIF approach significantly increased the pelvic tilt, negatively impacting sagittal balance. Even MIS TLIF, potentially viewed as inferior to open TLIF in its capacity to correct sagittal balance, did not show such a result. A possible reason for the low impact of all the approaches on the pelvic parameters is that the average number of surgically treated levels was low (mean=1.7), with more extensive surgeries having greater chance to change the pelvic parameters and sagittal balance [22]. As expected, none of the approaches had an effect on pelvic incidence, given it represents a fixed parameter.
The subgroup analysis of the L5–S1 level was similar to the overall analysis in regard to segmental lordosis and disk height, but with less statistical significance, which can be expected due to the lower number of patients included. None of the approaches positively changed lumbar lordosis, pelvic tilt, or pelvic incidence. Conclusions regarding these three parameters should be made cautiously. Given that these parameters encompass the whole lumbar spine, patients surgically treated on levels other than L5–S1 were excluded from the analysis, leaving very few patients in some groups (e.g., two patients in the OLIF group). Also, the impact on spinal alignment was minimized because only one level was surgically treateGiven the more restricted access, concerns have been raised about the capacity of MIS TLIF to offer adequate correction of sagittal balance [22,27,28] ; and, to date, it has not been directly compared with open TLIF in that regard. In the current study, MIS TLIF is not inferior to open TLIF in regard to sagittal balance correction, and it has fewer complications. The higher complication rate of open TLIF, also reported by others [29], could partially be explained by more extensive tissue debridement, heightening the susceptibility to infection [30]. The threshold used for complications in the current study is also very low, encompassing both minor and major complications. This might have contributed to the high level of complications reported in the TLIF group.
The current study presents various limitations. Due to its retrospective nature, it is subject to selection bias. This can be exemplified, for example, by the fact that the MIS TLIF group had fewer levels surgically treated per patient than the other two groups, potentially minimizing its effect on global sagittal alignment parameters such as lumbar lordosis and pelvic tilt. Also, OLIF patients were more severely imbalanced at baseline in regard of focal lordosis, lumbar lordosis, and disk height. This imbalance is reflected in the higher level of kyphosis and scoliosis diagnosed in this surgical group. The effect of this difference on the OLIF group is difficult to predict, given that more imbalanced cases could lead to balance correction being a more central aspect of the surgery, which at the same time could make sagittal balance correction more difficult. Another limitation is the relatively small sample that limits the validity of the drawn conclusions. The sagittal balance evaluation is restricted to the parameters chosen, given that other parameters such as the sagittal vertical axis were not accounted for. This study also focuses on short-term outcomes, with no long-term radiological follow-up to confirm whether the results were sustained. The clinical outcomes are limited to the hospitalization period and were not the focus of the current study.
The current study retrospectively compares the degree of sagittal balance correction of three different interbody fusion techniques. Among these approaches, OLIF provided the best results in regard to focal lordosis, lumbar lordosis, and disk height, with a near-significant impact on pelvic tilt. The MIS TLIF technique was not inferior to open TLIF in regard to sagittal balance correction, and both MIS TLIF and OLIF had a lower postoperative complication rate than open TLIF. Future studies involving long-term radiological and clinical follow-up in a prospective fashion could provide a better understanding of the performance of the various interbody fusion techniques in regard to sagittal balance and clinical outcome.
Fig. 1.
Sagittal balance parameters measured on lateral X-rays pre- and postoperatively. (A) focal lordosis; (B) disk height; (C) pelvic incidence; and (D) pelvic tilt. DH, disk height; FL, focal lordosis; PI, pelvic incidence; PT, pelvic tilt.
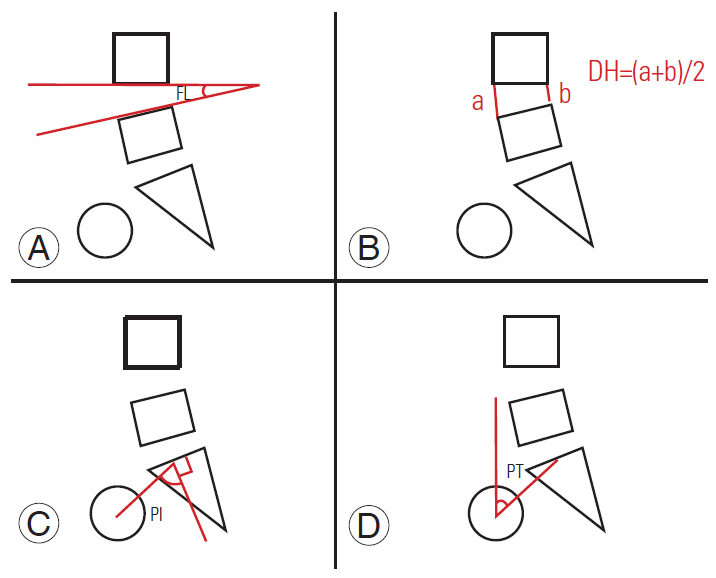
Fig. 2.
Illustrative case of an oblique lumbar interbody fusion procedure. Preoperative sagittal T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showing L4–L5 degenerative changes (A) and sagittal computed tomography scan showing grade 1 spondylolisthesis of L4 over L5 (B). Postoperative sagittal (C) and coronal (D) lumbar X-rays showing correction of the spondylolisthesis and improvement of sagittal balance following L4–L5 cage placement and fixation. Insert: preoperative fluoroscopy imaging during placement of the cage in the L4–L5 disk space.
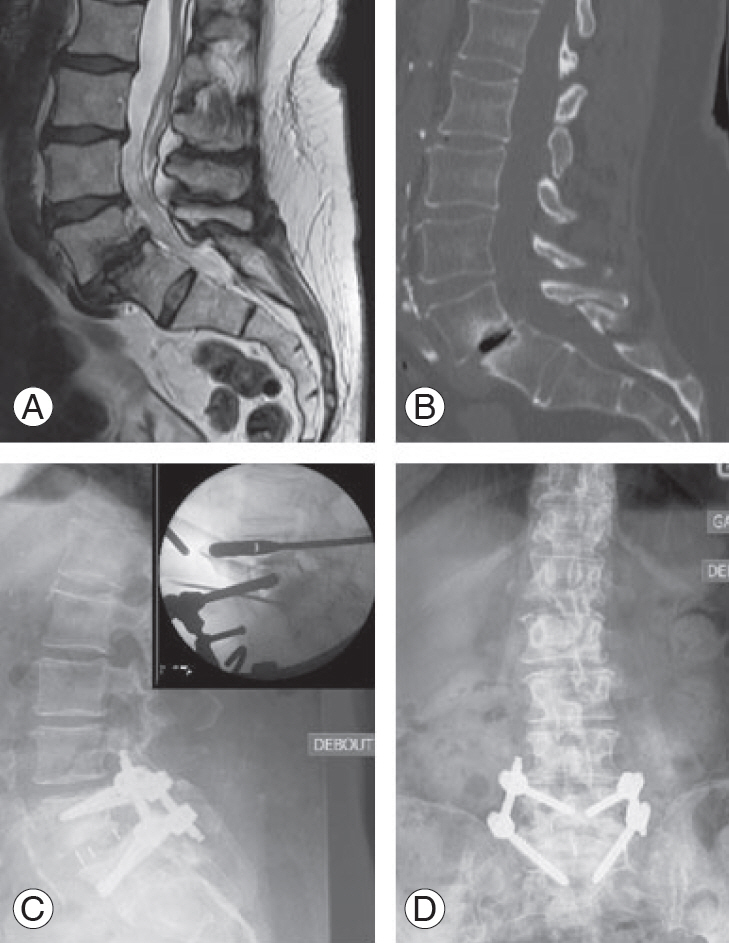
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the population for each approach
Table 2.
Sagittal balance parameters change (postoperatively minus preoperatively) for each surgical approach
Table 3.
Subgroup analysis of the L5–S1 Level
Table 4.
Complication rate according to the different approaches
| Approach | Complication rate (%) | Univariate analysis (p-value) |
|---|---|---|
| TLIF | 33 | 0.009 |
| Minimally invasive TLIF | 14 | 0.09 |
| Oblique lumbar interbody fusion | 16 | 0.4 |
| Total | 20 | - |
Table 5.
Main complications according to each approach
References
1. Bayerl SH, Pohlmann F, Finger T, et al. The sagittal balance does not influence the 1 year clinical outcome of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis without obvious instability after microsurgical decompression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:1014–21.


2. Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J. Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:346–53.


3. Dubousset J, Charpak G, Dorion I, et al. A new 2D and 3D imaging approach to musculoskeletal physiology and pathology with low-dose radiation and the standing position: the EOS system. Bull Acad Natl Med 2005;189:287–97.

4. Mehta VA, Amin A, Omeis I, Gokaslan ZL, Gottfried ON. Implications of spinopelvic alignment for the spine surgeon. Neurosurgery 2012;70:707–21.



5. Costanzo G, Zoccali C, Maykowski P, Walter CM, Skoch J, Baaj AA. The role of minimally invasive lateral lumbar interbody fusion in sagittal balance correction and spinal deformity. Eur Spine J 2014;23 Suppl 6:699–704.


6. Mac-Thiong JM, Transfeldt EE, Mehbod AA, et al. Can c7 plumbline and gravity line predict health related quality of life in adult scoliosis? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:E519–27.


7. Videbaek TS, Bunger CE, Henriksen M, Neils E, Christensen FB. Sagittal spinal balance after lumbar spinal fusion: the impact of anterior column support results from a randomized clinical trial with an eight-to thirteen-year radiographic follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011;36:183–91.


8. Aoki Y, Nakajima A, Takahashi H, et al. Influence of pelvic incidence-lumbar lordosis mismatch on surgical outcomes of short-segment transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2015;16:213.




9. Khoury NN, Champagne PO, Kotowski M, Raymond J, Roy D, Weill A. Unexpected complications with head and neck hydrogel microsphere particle embolization: a case series and a technical note. Interv Neuroradiol 2017;23:107–11.


10. Blizzard DJ, Gallizzi MA, Sheets C, et al. Sagittal balance correction in lateral interbody fusion for degenerative scoliosis. Int J Spine Surg 2016;10:29.



11. Bae J, Theologis AA, Strom R, et al. Comparative analysis of 3 surgical strategies for adult spinal deformity with mild to moderate sagittal imbalance. J Neurosurg Spine 2018;28:40–9.


12. Lawton CD, Smith ZA, Nixon AT, et al. The effect of surgical level on self-reported clinical outcomes after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: L4-L5 versus L5-S1. World Neurosurg 2014;81:177–82.


13. Okoro T, Sell P. A short report comparing outcomes between L4/L5 and L5/S1 single-level discectomy surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech 2010;23:40–2.


14. Roussouly P, Pinheiro-Franco JL. Sagittal parameters of the spine: biomechanical approach. Eur Spine J 2011;20 Suppl 5:578–85.


15. Shin MH, Ryu KS, Hur JW, Kim JS, Park CK. Comparative study of lumbopelvic sagittal alignment between patients with and without sacroiliac joint pain after lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:E1334–41.


16. Ohtori S, Mannoji C, Orita S, et al. Mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerated lumbar spinal kyphoscoliosis. Asian Spine J 2015;9:565–72.



17. Jin C, Jaiswal MS, Jeun SS, Ryu KS, Hur JW, Kim JS. Outcomes of oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease in patients under or over 65 years of age. J Orthop Surg Res 2018;13:38.



18. Sembrano JN, Yson SC, Horazdovsky RD, Santos ER, Polly DW Jr. Radiographic comparison of lateral lumbar interbody fusion versus traditional fusion approaches: analysis of sagittal contour change. Int J Spine Surg 2015;9:16.



19. Feng Y, Chen L, Gu Y, Zhang ZM, Yang HL, Tang TS. Influence of the posterior lumbar interbody fusion on the sagittal spino-pelvic parameters in isthmic L5-S1 spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 2014;27:E20–5.


20. Ould-Slimane M, Lenoir T, Dauzac C, et al. Influence of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion procedures on spinal and pelvic parameters of sagittal balance. Eur Spine J 2012;21:1200–6.


21. Recnik G, Kosak R, Vengust R. Influencing segmental balance in isthmic spondylolisthesis using transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech 2013;26:246–51.


22. Massie LW, Zakaria HM, Schultz LR, Basheer A, Buraimoh MA, Chang V. Assessment of radiographic and clinical outcomes of an articulating expandable interbody cage in minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Focus 2018;44:E8.

23. Barbagallo GM, Piccini M, Alobaid A, Al-Mutair A, Albanese V, Certo F. Bilateral tubular minimally invasive surgery for low-dysplastic lumbosacral lytic spondylolisthesis (LDLLS): analysis of a series focusing on postoperative sagittal balance and review of the literature. Eur Spine J 2014;23 Suppl 6:705–13.


24. Rajakumar DV, Hari A, Krishna M, Sharma A, Reddy M. Complete anatomic reduction and monosegmental fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis of grade II and higher: use of the minimally invasive “rocking” technique. Neurosurg Focus 2017;43:E12.

25. Hsieh PC, Koski TR, O’Shaughnessy BA, et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion in comparison with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: implications for the restoration of foraminal height, local disc angle, lumbar lordosis, and sagittal balance. J Neurosurg Spine 2007;7:379–86.


26. Asai Y, Tsutsui S, Oka H, et al. Sagittal spino-pelvic alignment in adults: the Wakayama Spine Study. PLoS One 2017;12:e0178697.



27. Fan G, Zhang H, Guan X, et al. Patient-reported and radiographic outcomes of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis with or without reduction: a comparative study. J Clin Neurosci 2016;33:111–8.


28. Hawasli AH, Khalifeh JM, Chatrath A, Yarbrough CK, Ray WZ. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with expandable versus static interbody devices: radiographic assessment of sagittal segmental and pelvic parameters. Neurosurg Focus 2017;43:E10.







