|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 9(4); 2015 > Article |
Abstract
We report a rare case of anterior cervical disc herniation associated with dysphagia. A 32-year-old man presented with complaints of dysphagia and concomitant pain in the right arm resistant to conservative therapy. On physical examination with respect to the muscle strength, the right shoulder abduction and flexion of the forearm were 3/5. Lateral X-ray revealed calcified osteophytes at the anterior C4-5 level. Magnetic resonance imaging showed soft disc herniation involving the right C6 root at the C5-6 level and anterior herniation of the C4-5 cervical disc. Anterior discectomies for C4-5 and C5-6 levels stabilized and ameliorated the dysphagia and pain. Cervical disc herniation usually presents with radicular findings. However, dysphagia may be an uncommon presentation. Anterior cervical disc herniation should be considered in a patient presenting with dysphagia.
Posterior or posterolateral cervical disc herniation is a common disease that usually presents with radicular signs [1]. Sometimes, signs due to myelopathy can be detected [2]. Anterior cervical disc herniation is a rare condition [3456]. This condition can cause dysphagia due to pressure on the posterior aspect of the esophagus. Cases of dysphagia caused by hypertrophic anterior cervical osteophytes have been increasing in number in the literature in recent years [78910]. Dysphagia caused by neurological disorders is mostly seen in patients suffering from diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) [11].
We describe a case of anterior cervical disc herniation presenting with dysphagia in this report.
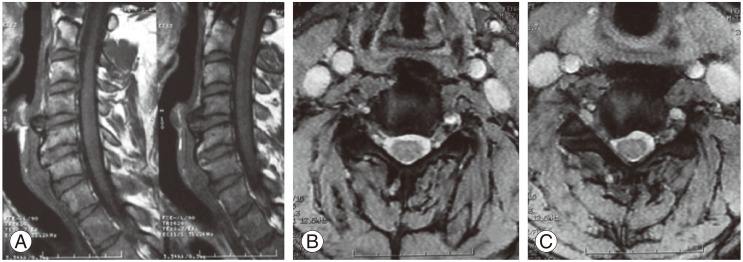
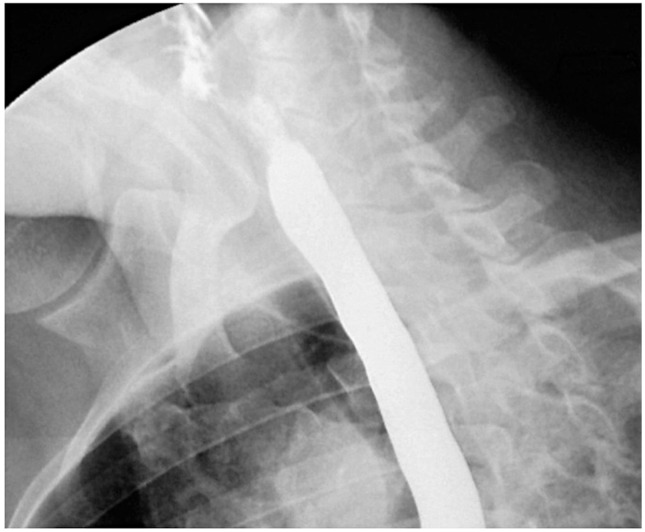
A 32-year-old male was admitted with complaints of dysphagia and radicular pain in the right arm. He was suffering from dysphagia for two years and was treated conservatively at internal medicine clinics. His complaints were initially limited to a sensation of discomfort in his throat, which later on progressed to difficulty in swallowing liquids rather than solid foods. Four months ago, he experienced acute radicular pain in the right arm, but it persisted despite rest and analgesics. On neurological examination, right shoulder abduction and flexion of the forearm were 3/5. X-ray showed a fluffy, radiodense mass at the C4-5 level, which did not extend to the anterior longitudinal ligament (Fig. 1). Cervical magnetic resonance imaging scans revealed partially calcified and degenerated anterior disc herniation, compressing the esophagus at the C4-5 level, and soft disc herniation involving the right C6 root at the C5-6 level (Fig. 2). On esophagography, an extrinsic esophageal lesion was considered to be responsible for the obstruction of the passage at the same level with partially calcified anterior disc herniation (Fig. 3).
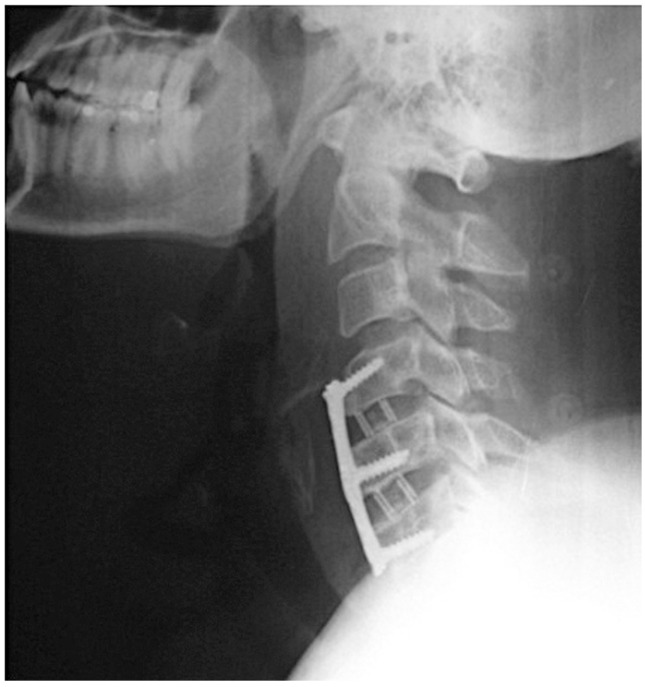
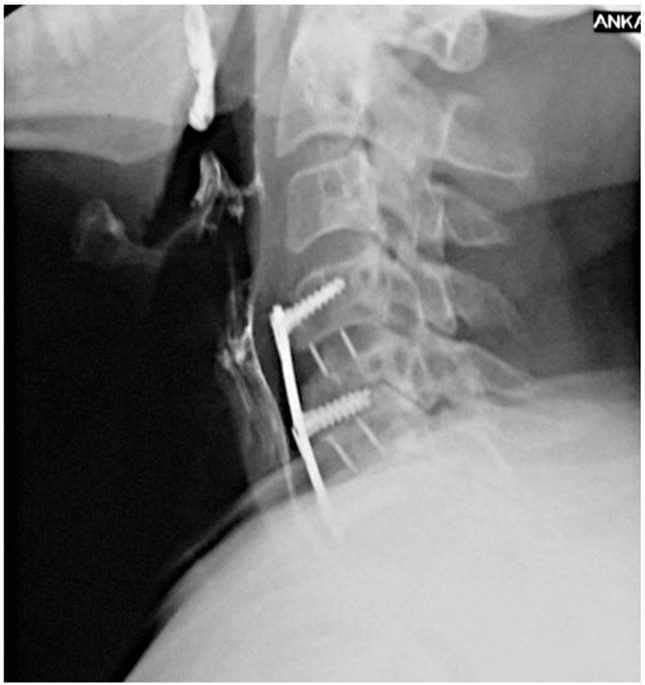
We performed anterior microdiscectomies for C4-5 and C5-6 levels and stabilized the spine with polyetheretherketone cages and plate-screw system (Fig. 4). The surgery was performed without any complications, and there were no obvious difficulty in either manipulating or dissecting the esophagus from anterior disc herniation without any fibrotic adhesions. He was mobilized on the first postoperative day and his complaints (especially dysphagia and pain) improved considerably. On follow-up examination at the second month, he was neurologically normal and dysphagia had resolved. Moreover, esophagography revealed a normal peristaltic esophagus (Fig. 5).
Dysphagia due to a neurological disorder more commonly develops due to anterior cervical osteophytes [51012]. DISH is a common cause of anterior cervical osteophyteinduced progressive dysphagia treated surgically in the literature [11131415161718].
The esophagus is fixed to the cricoid cartilage at the level of C5-6 vertebral body in the cervical area and is attached to the diaphragm in the upper thoracic area. These two areas are the regions where the esophagus can be compressed by a bony protuberance [19].
There are various mechanisms of dysphagia caused by large osteophytes on the cervical vertebrae. Important mechanisms are direct compression of the pharynx or esophagus [20], inflammatory reactions in the paraesophageal tissues [21], cricopharyngeal spasm [22], and secondary neurological lesions such as recurrent nerve palsies resulting from hyperostosis [23]. In our case, an anterior disc herniation at the C4-5 level caused dysphagia due to esophageal compression.
Symptomatic anterior cervical disc herniations are quite rare and only a few cases have been reported so far. The previous cases of anterior cervical disc herniation presenting with dysphagia in the literature were reported by Coventry [3], Picus et al. [4], and Bernardo et al. [5]. Anterior cervical disc herniations occurred at the C7-T1 level in all of these reports (Table 1). Complaints related to dysphagia disappeared after surgery. In 2000, Andersen and Fagerlund [6] reported a case with C4-5 anterior and C5-6 posterior cervical disc herniation presenting with dysphagia, weight loss, and gait disturbance (Table 1). Our case was similar with C4-5 anterior and C5-6 posterior cervical disc herniation.
Various theories related to the mechanism of anterior vertebral osteophyte formation have been suggested [24]. According to one theory, herniated anterior cervical discs are degenerated and finally ossified. Such mechanisms of formation of anterior cervical osteophytes indicate that anterior cervical disc herniation is not uncommon. But this theory is contradictory to the fact that few cases of anterior cervical disc herniation have been reported in the literature.
The anterior mechanical compression caused by an anteriorly herniated disc causes serious complications pertained to esophagus or other neighboring structures; obviously mechanical compression may lead to progressive dysphagia starting from discomfort in the throat to serious blockage of the passage allowing only liquids to pass. Moreover, associated inflammatory reactions may also cause edema, cricopharyngeal spasm, and hoarseness [25].
Dysphagia due to cervical spinal pathologies can be managed with either conservative or surgical approaches depending on the exact cause, severity of the symptoms, and associated conditions like aspiration pneumonia [9]. Several conservative therapies have been proposed; (1) non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, (2) steroid pulses, (3) skeletal relaxants, (4) anti-reflux regimes, and (5) bisphosphonates [26]. Conservative methods were reported as the treatment method in only 20.6% of the patients [927]. However, the authors of this article believe that being unaware of the underlying external compression caused by anterior disc herniation, and performing some diagnostic or therapeutic procedures like esophagography or endoscopic balloon dilation may cause injury to the esophagus. Surgical treatment is warranted, particularly in progressive cases. Moreover, surgery is the accepted treatment option in patients who are suffering from severe and anterior discectomy aimed at fusion of the neighboring vertebra is the recommended surgical technique [2128]. Our patient's complaints disappeared after surgery, which is consistent with that in the cases reported in the literature. However, the surgery itself is not always straightforward, although there was no difficulty in approaching the compressive side in our case through the conventional anterior cervical approach. Difficulty in manipulating the esophagus because of adhesions between the prevertebral fascia and the surrounding tissues incurring esophageal injury has been reported [25]. Moreover, injury to sympathetic nerves (Horner syndrome), hoarseness due to recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, and tracheoesophageal fistula were reported as complications of this surgery [29].
Although pain, numbness, and weakness are the most common symptoms of cervical disc herniation, few case reports demonstrated an association between anterior disc herniation and dysphagia. Dysphagia may be caused by anterior cervical osteophytes without DISH and cervical disc herniation should be kept in mind in these cases.
Conflict of Interest
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Gebremariam L, Koes BW, Peul WC, Huisstede BM. Evaluation of treatment effectiveness for the herniated cervical disc: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37:E109âE118. PMID: 21587105.


2. Park SJ, Kim SB, Kim MK, Lee SH, Oh IH. Clinical features and surgical results of cervical myelopathy caused by soft disc herniation. Korean J Spine 2013;10:138â143. PMID: 24757475.



3. Coventry MB. Calcification in a cervical disc with anterior protrusion and dysphagia: case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1970;52:1463â1466. PMID: 5469200.


4. Picus D, McClennan BL, Balfe DM, Roper CL, Berrigan T. "Discphagia": a case report. Gastrointest Radiol 1984;9:5â7. PMID: 6724240.


5. Bernardo KL, Grubb RL, Coxe WS, Roper CL. Anterior cervical disc herniation: case report. J Neurosurg 1988;69:134â136. PMID: 3379468.


6. Andersen PM, Fagerlund M. Vertebrogenic dysphagia and gait disturbance mimicking motor neuron disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2000;69:560â561. PMID: 10990527.



7. Zhang C, Ruan D, He Q, Wen T, Yang P. Progressive dysphagia and neck pain due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: a case report and literature review. Clin Interv Aging 2014;9:553â557. PMID: 24729695.



8. Hwang JS, Chough CK, Joo WI. Giant anterior cervical osteophyte leading to Dysphagia. Korean J Spine 2013;10:200â202. PMID: 24757489.



9. Song AR, Yang HS, Byun E, Kim Y, Park KH, Kim KL. Surgical treatments on patients with anterior cervical hyperostosis-derived Dysphagia. Ann Rehabil Med 2012;36:729â734. PMID: 23185741.



10. Miyamoto K, Sugiyama S, Hosoe H, Iinuma N, Suzuki Y, Shimizu K. Postsurgical recurrence of osteophytes causing dysphagia in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Eur Spine J 2009;18:1652â1658. PMID: 19714374.



11. Calisaneller T, Ozdemir O, Tosun E, Altinors N. Dysphagia due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2005;147:1203â1206. PMID: 16044355.


12. Brandenberg G, Leibrock LG. Dysphagia and dysphonia secondary to anterior cervical osteophytes. Neurosurgery 1986;18:90â93. PMID: 3945383.


13. Burkus JK. Esophageal obstruction secondary to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Orthopedics 1988;11:717â720. PMID: 3261010.


14. Curtis JR, Lander PH, Moreland LW. Swallowing difficulties from "DISH-phagia". J Rheumatol 2004;31:2526â2527. PMID: 15570664.

15. Ebo DG, Uytterhaegen PJ, Lagae PL, Vander Mijnsbrugge AM, Goffin J. Choking, sore throat with referred otalgia and dysphagia in a patient with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Acta Clin Belg 2005;60:98â101. PMID: 16082996.


16. Epstein NE. Simultaneous cervical diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament resulting in dysphagia or myelopathy in two geriatric North Americans. Surg Neurol 2000;53:427â431. PMID: 10874140.


17. Foshang TH, Mestan MA, Riggs LJ. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a case of dysphagia. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 2002;25:71â76. PMID: 11898021.


18. Ogul H, Tuncer K, Mutlu V, Gedikli Y, Kantarci M. Giant anterior cervical osteophytes leading to dysphagia in a patient with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Spine J 2014;14:2265PMID: 24747268.


19. Yutan E, Daras M, Koppel BS. Dysphagia due to cervical osteophytes. Clin Imaging 2001;25:262â264. PMID: 11566087.


20. Resnick D, Niwayama G. Radiographic and pathologic features of spinal involvement in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Radiology 1976;119:559â568. PMID: 935390.


21. Akhtar S, O'Flynn PE, Kelly A, Valentine PM. The management of dysphasia in skeletal hyperostosis. J Laryngol Otol 2000;114:154â157. PMID: 10748839.


22. Oga M, Mashima T, Iwakuma T, Sugioka Y. Dysphagia complications in ankylosing spinal hyperostosis and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: oentgenographic findings of the developmental process of cervical osteophytes causing dysphagia. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993;18:391â394. PMID: 8475444.


23. Clemente Coehlo P, Cansado Carvalho JP, Melo Gomes JA. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis with dysphagia: a neurological mechanism? Clin Exp Rheumatol 1995;13:268PMID: 7656477.

24. Lipson SJ, Muir H. Vertebral osteophyte formation in experimental disc degeneration: morphologic and proteoglycan changes over time. Arthritis Rheum 1980;23:319â324. PMID: 7362683.


25. Papadopoulos SM, Chen JC, Feldenzer JA, Bucci MN, McGillicuddy JE. Anterior cervical osteophytes as a cause of progressive dysphagia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1989;101:63â65. PMID: 2603770.


26. Fulton JD. Analgesic use of etidronate in Forrestier's disease. Lancet 1992;340:1287PMID: 1279336.

27. Verlaan JJ, Boswijk PF, de Ru JA, Dhert WJ, Oner FC. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: an underestimated cause of dysphagia and airway obstruction. Spine J 2011;11:1058â1067. PMID: 22015236.


28. Krause P, Castro WH. Cervical hyperostosis: a rare cause of dysphagia. Case description and bibliographical survey. Eur Spine J 1994;3:56â58. PMID: 7874543.


29. Oppenlander ME, Orringer DA, La Marca F, et al. Dysphagia due to anterior cervical hyperosteophytosis. Surg Neurol 2009;72:266â270. PMID: 19147185.


Fig. 1
Preoperative lateral (A) and anteroposterior (B) X-rays showing anterior cervical osteophytes at the C4-5 level. The mass did not extend to the anterior longitudinal ligament.
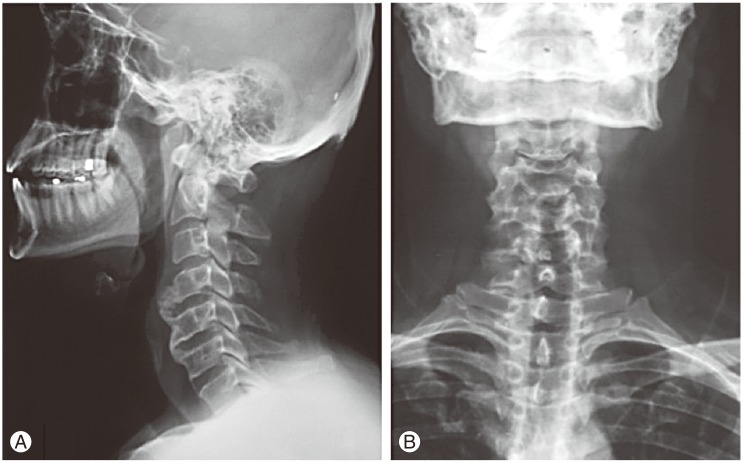
Fig. 2
Magnetic resonance imaging; (A) sagittal and (B, C) axial views. Anterior C4-5 disc herniation causing compression of the esophagus. Right-sided C5-6 disc herniation with root compression.