|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 10(2); 2016 > Article |
Abstract
Purpose
To identify the characteristics of candidate indexes for early detection of surgical site infection (SSI).
Overview of Literature
SSI is a serious complication of spinal instrumentation surgery. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the welfare of the patient postoperation.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed laboratory data of patients who underwent posterior lumbar instrumentation surgery for degenerative spine disease. The sensitivity and specificity of six laboratory markers for early detection of SSI were calculated: greater elevation of the white blood cell count at day 7 than at day 4 postoperatively, greater elevation of the C-reactive protein (CRP) level at day 7 than at day 4 postoperatively, a CRP level of >10 mg/dL at 4 days postoperatively, neutrophil percentage of >75% at 4 days postoperatively, a lymphocyte percentage of <10% at 4 days postoperatively, and a lymphocyte count of <1,000/µL at 4 days postoperatively. Statistical analysis was via Fisher's exact test and a p-value of <0.05 was considered significant.
Results
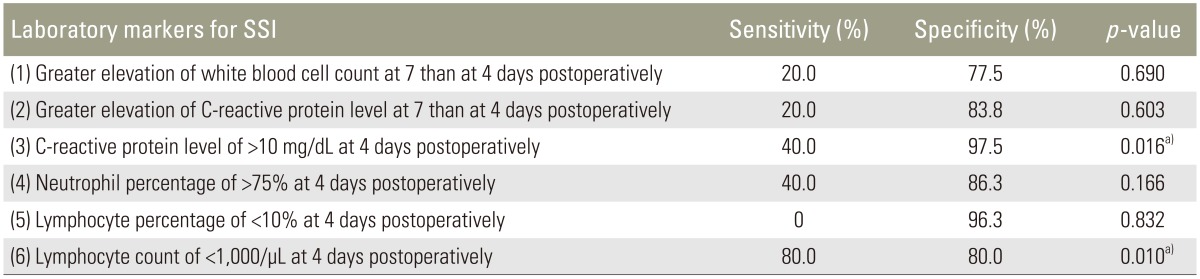
In total, 85 patients were enrolled. Of these, five patients developed deep SSI. The sensitivity and specificity of each index were as follows: index 1, 20.0% and 77.5%; index 2, 20.0% and 83.8%; index 3, 40.0% and 97.5%; index 4, 40.0% and 86.3%; index 5, 0% and 96.3%; and index 6, 80.0% and 80.0%. A significant difference was noted for indexes 3 and 6.
Conclusions
A CRP level of >10 mg/dL at 4 days postoperatively would be useful for definitive diagnosis of SSI, and a lymphocyte count of <1,000/µL at 4 days postoperatively would be a useful screening test for SSI. Although laboratory markers for early detection of SSI have been frequently reported, we believe that it is important to understand the characteristics of each index for a precise diagnosis.
The implementation of spinal instrumentation surgery has dramatically increased because of its ability to achieve strong fixation and correct deformities. However, this procedure is associated with more complications than surgeries without instrumentation and of these complications, the surgical site infection (SSI) is one of the most serious [12]. Infection rates after spinal instrumentation surgery reportedly range from 2.2% to 8.5% [3456]. Insertion of instrumentation may lead to infection if a relatively small number of bacteria adhere to the surface of the implanted device and form a glycoprotein biofilm. In general, this process is attributable to intractable infections that are resistant to antibiotics and result in increased infection rates [7]. SSI may also affect the final outcome of the surgery including the need for revision surgery, persistent pain or deformity, additional hospitalization, prolonged recovery time, and considerable added expense for treatment [891011]. Preventing SSI is important, but when an infection does occur, early diagnosis and treatment are very important to prevent worsening of the affected patient [812131415]. Diagnosis of SSI is based on the presence of systemic infection indicators such as fever type and laboratory data in combination with local findings such as tenderness, swelling, redness, and purulent discharge [121516]. Of the clinical findings associated with SSI, postoperative laboratory markers are most frequently used because of their objectivity and convenience [812131417]. There are several laboratory markers available for early detection of SSI, but clinicians often struggle to interpret them because of the different characteristics among these markers [81314]. The aim of the present study was to clarify the characteristics of each marker in allow the precise early detection of SSI.
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients who underwent posterior lumbar instrumentation surgery for degenerative spine disease from January 2003 to December 2013. The records were examined for evidence of deep SSI and laboratory data. Diagnosis of SSI was by using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria [18]. Diagnosis of deep SSI was made only if the attending surgeon diagnosed deep SSI and conducted debridement within 4 weeks. Each patient underwent single or two-segment posterior lumbar instrumentation surgery and laboratory data were collected preoperatively and at 4 and 7 days postoperatively. We excluded patients with trauma, tumors, existing infection, chronic inflammatory disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, current dialysis therapy, or a preoperative C-reactive protein (CRP) level of >2 mg/dL and previous surgery of the lumbar spine. All enrolled patients were categorized into two groups: an SSI group and a non-SSI group. The data of 85 patients were evaluated. Of these patients, five developed deep SSI. We collected laboratory data regarding the CRP level, white blood cell (WBC) count, and WBC differential (neutrophil and lymphocyte percentages) preoperatively and at 4 and 7 days postoperatively. The CRP level was measured using the latex agglutination method, and an automatic cell counter was used to determine the WBC count. Neutrophil and lymphocyte counts were calculated from the WBC count and WBC differential percentages. Data on the operating time and intraoperative blood loss were also collected.
Six laboratory markers for early detection of SSI were part of the review (Table 1) [12131719]: (1) higher WBC count at day 7 than at day 4 postoperatively, (2) greater level of serum CRP at day 7 than at day 4 postoperatively, (3) a CRP level of >10 mg/dL at 4 days postoperatively, (4) a neutrophil percentage of >75% at 4 days postoperatively, (5) a lymphocyte percentage of <10% at 4 days postoperatively, and (6) a lymphocyte count of <1,000/µL at 4 days postoperatively. We calculated the sensitivity and specificity of each index, and statistical analysis was performed with Fisher's exact probability test. Quantitative data such as age, operating time, and intraoperative blood loss were analyzed with Mann–Whitney's U test, and the number of fusion segments was analyzed with Student's t test. Qualitative data such as sex were analyzed using Fisher's exact probability test. All statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS for Windows, ver. 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk NY, USA). A p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
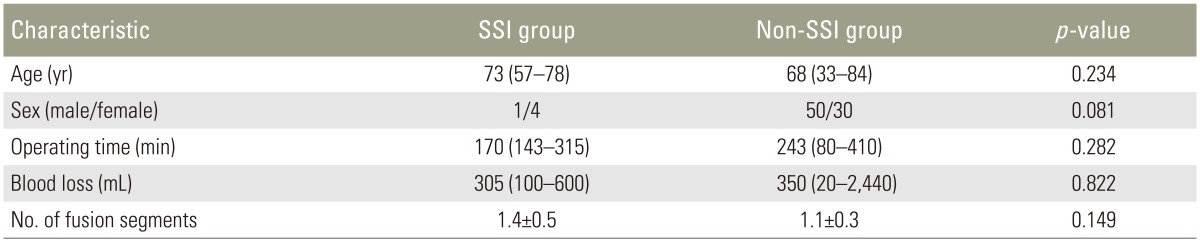
The data of 85 patients were evaluated in this study. Five patients who developed deep SSI were enrolled in the SSI group, and 80 patients were enrolled in the non-SSI group. The SSI group comprised 1 man and 4 women, and the non-SSI group comprised 50 men and 30 women. The median age at surgery was 73 and 68 years in the SSI and non-SSI groups, respectively. The median operating time was 170 minutes (range, 143–315 minutes) and 243 minutes (range, 80–410 minutes), and the median intraoperative blood loss volume was 305 mL (range, 100–600 mL) and 350 mL (range, 20–2440 mL) in the SSI and non-SSI groups, respectively. The mean±standard deviation number of fusion segments was 1.4±0.5 and 1.1±0.3 in the SSI and non-SSI groups, respectively. There were no significant differences in age, sex, operating time, intraoperative blood loss, or the number of fusion segments between the two groups (Tables 2, 3). The sensitivity and specificity of each laboratory marker were as follows: (1) greater WBC count at day 7 than at day 4 postoperatively, 20.0% and 77.5%; (2) greater elevation of CRP level at day 7 than at day 4 postoperatively, 20.0% and 83.8%; (3) CRP level of >10 mg/dL at day 4 postoperatively, 40.0% and 97.5%; (4) neutrophil percentage of >75% at day 4 postoperatively, 40.0% and 86.3%; (5) lymphocyte percentage of <10% at day 4 postoperatively, 0.0% and 96.3%; and (6) lymphocyte count of <1,000/µL at day 4 postoperatively, 80.0% and 80.0%. From our analysis there was a statistically significant difference for indexes (3) and (6) (CRP level of >10 mg/dL and lymphocyte count of <1,000/µL both at day 4 postoperatively) (Table 4).
The objective of SSI treatment after spinal instrumentation surgery is not only to resolve infection, but also to maintain spinal stability. Ishii et al. [20] reported that patients who developed SSI and were able to retain their implants were diagnosed at an early stage. They concluded that early diagnosis at a low intensity of infection may reduce the need for implant removal. Early diagnosis of SSI may be made from fever type and laboratory markers in combination with local findings such as tenderness, swelling, redness, having a sensation of heat and purulent discharge [8121314]. As moist healing, which promotes healing by closing a surgical wound with a wound-covering material, has become mainstream in recent years, the ability to observe a surgical wound directly has decreased and the risk of delayed diagnosis of an SSI complication has increased. Therefore, laboratory markers as indicators of SSI are very useful. The most widely implemented laboratory markers are the CRP level and WBC count, which can easily be measured by most institutions.
In the present study, we reviewed six laboratory markers related to the CRP level and WBC count for early detection of SSI, as previously reported [12131719]. CRP has been reported to be the most sensitive inflammatory marker [141721222324] and is induced by interleukin-6 and synthesized by hepatocytes. Besides the level of inflammation, CRP can also reflect surgical injury [2526]. Thelander and Larsson [14] and Larsson et al. [22] were the first to report changes in the CRP level after posterior lumbar instrumentation surgery. The CRP level tended to peak after postoperative day 3. However, Takahashi et al. [17] reported that the CRP level peaked on day 2 postoperatively and Aono et al. [13] reported that it peaked at day 4 postoperatively. With the postoperative CRP peak ranging from day 2 to day 4, all four groups agreed that renewed elevation of the CRP level or an increase in the CRP level after the peak day may indicate an onset of postoperative SSI [121327].
Takahashi et al. [1217] reported that the WBC count and WBC differential were useful for early detection of SSI following spinal instrumentation surgery. Furthermore, the change in the WBC count over time, especially the neutrophil count, served as a useful marker of postoperative progress. Takahashi et al. [17] reported that a second increase in the neutrophil and WBC counts several days after surgery was one of the most important signs of bacterial infection. They concluded that a renewed elevation of the WBC and neutrophil counts after postoperative days 4 to 7 and a neutrophil percentage of >75% after postoperative day 4 may be critical signs of infection [1217]. However, the numbers of lymphocytes, which are involved in nonspecific biophylaxis, often decrease after invasion regardless of noninfectious or infectious invasion. Takahashi et al. [1217] demonstrated that in patients with infection, the percentage and number of lymphocytes significantly decreased on day 4 postoperatively. This represents immune depression, indicating the possibility of a predominance of anti-inflammatory cytokines and an attendant compensatory anti-inflammatory reaction syndrome [2829]. In this condition, patients are more susceptible to infection and often develop postoperative infections. The authors concluded that postoperative lymphopenia (≤10% or 1,000/µL) after day 4 indicates possible SSI [1217].
In reference to these reports, we calculated the sensitivity and specificity of six laboratory markers for early detection of SSI. Two laboratory markers were found to be statistically significant. The first index was having a CRP level of >10 mg/dL at day 4 postoperatively, and the other index was noting a lymphocyte count of <1,000/µL at day 4 postoperatively. The sensitivity and specificity of the CRP level were 40.0% and 97.5%, and those of the lymphocyte count were 80.0% and 80.0%, respectively. So, Index 3 would be useful for a definitive diagnosis of SSI based on its high specificity and Index 6 could be a screening test (i.e., early detection) based on its high sensitivity.
Our study has several limitations. First, it was a retrospective study. As a result, there may have been an inherent bias associated with patient selection and any incomplete patient information. Patients who did not meet the SSI criteria were placed in a non-SSI group, which may have resulted in a notable underestimation of the actual number of patients with SSI. Another limitation is the comparatively small number of patients with SSI might have resulted in a type 2 error. Only indexes 3 and 6 were considered statistically significant; however, if the number of patients with SSI had been larger, another index may have been found to be statistically significant. A prospective study and larger cohort may eliminate these problems. Although many authors have evaluated laboratory markers for early detection of SSI, we believe that it is important to understand the characteristics of each index to precisely diagnose SSI.
We calculated the sensitivity and specificity of various laboratory markers to characterize the predicting capability of each index. "A CRP level of >10 mg/dL at 4 days postoperatively" would be useful as a definitive diagnosis of SSI based on its high specificity. "A lymphocyte count of <1,000/µL at 4 days postoperatively" could be an early detection sign based on its high sensitivity for SSI.
Conflict of Interest
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Olsen MA, Nepple JJ, Riew KD, et al. Risk factors for surgical site infection following orthopaedic spinal operations. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90:62–69. PMID: 18171958.

2. Fang A, Hu SS, Endres N, Bradford DS. Risk factors for infection after spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:1460–1465. PMID: 15959380.


3. Collins I, Wilson-MacDonald J, Chami G, et al. The diagnosis and management of infection following instrumented spinal fusion. Eur Spine J 2008;17:445–450. PMID: 18075763.


4. Ho C, Skaggs DL, Weiss JM, Tolo VT. Management of infection after instrumented posterior spine fusion in pediatric scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:2739–2744. PMID: 18007254.


5. Pull ter Gunne AF, Mohamed AS, Skolasky RL, van Laarhoven CJ, Cohen DB. The presentation, incidence, etiology, and treatment of surgical site infections after spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:1323–1328. PMID: 20150831.


6. Schimmel JJ, Horsting PP, de Kleuver M, Wonders G, van Limbeek J. Risk factors for deep surgical site infections after spinal fusion. Eur Spine J 2010;19:1711–1719. PMID: 20445999.



7. Dougherty SH, Simmons RL. Infections in bionic man: the pathobiology of infections in prosthetic devices--Part I. Curr Probl Surg 1982;19:217–264. PMID: 7083896.


8. Mok JM, Guillaume TJ, Talu U, et al. Clinical outcome of deep wound infection after instrumented posterior spinal fusion: a matched cohort analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:578–583. PMID: 19240667.


9. Bible JE, Biswas D, Devin CJ. Postoperative infections of the spine. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2011;40:E264–E271. PMID: 22268020.

10. Gerometta A, Rodriguez Olaverri JC, Bitan F. Infections in spinal instrumentation. Int Orthop 2012;36:457–464. PMID: 22218913.



11. Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong KL, et al. Infection risk for primary and revision instrumented lumbar spine fusion in the Medicare population. J Neurosurg Spine 2012;17:342–347. PMID: 22920611.


12. Takahashi J, Shono Y, Hirabayashi H, et al. Usefulness of white blood cell differential for early diagnosis of surgical wound infection following spinal instrumentation surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:1020–1025. PMID: 16641779.


13. Aono H, Ohwada T, Kaneko N, Fuji T, Iwasaki M. The post-operative changes in the level of inflammatory markers after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2007;89:1478–1481. PMID: 17998185.


14. Thelander U, Larsson S. Quantitation of C-reactive protein levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rate after spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1992;17:400–404. PMID: 1579874.


15. Mangram AJ, Horan TC, Pearson ML, Silver LC, Jarvis WR. Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Guideline for prevention of surgical site infection, 1999. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1999;20:250–278. PMID: 10219875.


16. Taylor S, Pearce P, McKenzie M, Taylor GD. Wound infection in total joint arthroplasty: effect of extended wound surveillance on wound infection rates. Can J Surg 1994;37:217–220. PMID: 8199939.

17. Takahashi J, Ebara S, Kamimura M, et al. Early-phase enhanced inflammatory reaction after spinal instrumentation surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:1698–1704. PMID: 11474357.


18. Horan TC, Gaynes RP, Martone WJ, Jarvis WR, Emori TG. CDC definitions of nosocomial surgical site infections, 1992: a modification of CDC definitions of surgical wound infections. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1992;13:606–608. PMID: 1334988.


19. Deguchi M, Shinjo R, Yoshioka Y, Seki H. The usefulness of serum amyloid A as a postoperative inflammatory marker after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2010;92:555–559. PMID: 20357334.


20. Ishii M, Iwasaki M, Ohwada T, et al. Postoperative deep surgical-site infection after instrumented spinal surgery: a multicenter study. Global Spine J 2013;3:95–102. PMID: 24436857.



21. Aalto K, Osterman K, Peltola H, Rasanen J. Changes in erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1984;(184): 118–120. PMID: 6705332.


22. Larsson S, Thelander U, Friberg S. C-reactive protein (CRP) levels after elective orthopedic surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1992;(275): 237–242. PMID: 1735220.

23. Shih LY, Wu JJ, Yang DJ. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein values in patients with total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1987;(225): 238–246. PMID: 3677512.

24. Bottner F, Wegner A, Winkelmann W, Becker K, Erren M, Gotze C. Interleukin-6, procalcitonin and TNF-alpha: markers of peri-prosthetic infection following total joint replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2007;89:94–99. PMID: 17259424.


25. Ganter U, Arcone R, Toniatti C, Morrone G, Ciliberto G. Dual control of C-reactive protein gene expression by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. EMBO J 1989;8:3773–3779. PMID: 2555173.



26. Tillett WS, Francis T. Serological reactions in pneumonia with a non-protein somatic fraction of pneumococcus. J Exp Med 1930;52:561–571. PMID: 19869788.



27. Kang BU, Lee SH, Ahn Y, Choi WC, Choi YG. Surgical site infection in spinal surgery: detection and management based on serial C-reactive protein measurements. J Neurosurg Spine 2010;13:158–164. PMID: 20672950.


28. Bone RC. Sir Isaac Newton, sepsis, SIRS, and CARS. Crit Care Med 1996;24:1125–1128. PMID: 8674323.


29. Takahashi J, Ebara S, Kamimura M, et al. Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine increases after spinal instrumentation surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech 2002;15:294–300. PMID: 12177545.