|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 11(2); 2017 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the long-term outcomes of in situ fusion procedures for treating dysplastic spondylolisthesis.
Overview of Literature
In situ fusion performed in patients with dysplastic spondylolisthesis avoids the development of nerve complications.
Methods
In total, 12 of 28 patients who underwent in situ fusion for treating dysplastic spondylolisthesis at Chiba University Hospital from 1974 to 2004 were followed up in August 2013. Surgical complications were evaluated. Low back pain and leg pain were assessed using a visual analog scale (VAS). Vertebral alignment, including the lumbosacral angle and lumbar lordosis angle measurement on radiographic images (profile view in the neutral standing position), was evaluated during preoperative, postoperative, and final examinations.
Results
The mean follow-up duration, patient age at the final examination, and patient age at operation were 20.0±7.2, 42.3±13.3, and 22.3±11.4 years, respectively. No complications were reported. Mean VAS scores for low back pain and leg pain were significantly lower at the final examination than at the preoperative examination (p<0.05). At the preoperative, postoperative, and final examinations, the mean lumbosacral angle was 32.3°±14.2°, 33.7°±11.8°, and 36.5°±16.4°, while the mean lumbar lordosis angle was 51.0°±14.8°, 48.6°±18.8°, and 49.6°±15.5°, respectively. No significant differences were noted among these values across the different time periods (p<0.05).
Dysplastic spondylolisthesis is a rare disease characterized by the occurrence of forward subluxation of the lumbosacral joint due to dysplasia of the sacral vertebra. Dysplastic spondylolisthesis is found at the L5–S1 level and usually presents in women. Genetic predisposition is a significant causative factor [1]. Patients with dysplastic spondylolisthesis usually develop symptoms during adolescence. Typical clinical symptoms are low back pain and stiffness with hamstring shortening [2], although symptoms may also include lumbar hyperlordosis, flexed-hip and -knee walking, and toe walking [3]. Radicular pain radiating to the buttocks and thighs is not always evident as the nerves adapt to tension or compression. The radiation of pain below the knees, or cauda equina syndrome, is suggestive of high-grade spondylolisthesis [4].
The ideal mode of treatment for high-grade spondylolisthesis remains a subject of controversy. The nonsurgical management of symptomatic patients with high-grade spondylolisthesis is generally less successful than that of patients with low-grade spondylolisthesis. Although long-term natural history studies on patients with a slippage of >50% have indicated that not all outcomes are poor, majority of surgeons recommend fusion for high-grade spondylolisthesis [5].
Satisfactory clinical outcomes may be achieved in response to various surgical methods, including in situ fusion with or without postural reduction, instrumented reduction and fusion, and combined anteroposterior fusion techniques [6]. Selecting the best treatment option for a patient is based on a careful analysis of the presenting symptoms, clinical deformity, neurological function, and spinal imaging, together with the operating surgeon's preference and experience.
Modern surgical techniques and instrumentation permit the reduction or even removal of a severely slipped L5 vertebra. These procedures usually involve posterior or anteroposterior surgeries, and despite modern neurophysiological monitoring (somatosensory and motor evoked potentials), they present the possibility of treating severe neurological complications. The incidence of nerve paralysis after the surgical reduction of spondylolisthesis ranges from 20% to 40% [7]. To avoid these complications, in situ fusion has been performed at our hospital for many years, and our postoperative results have been generally excellent. The purpose of this present study was to investigate long-term outcomes after performing in situ fusion for the treatment of dysplastic spondylolisthesis.
Twenty-eight patients underwent in situ fusion at Chiba University Hospital from 1974 to 2004 for dysplastic spondylolisthesis with radiologically-demonstrated pars articularis defects and facet joint dysplasia but without any history of previous trauma or vertebral operation and without any degenerative or pathological changes. Of these 28 patients, we examined 12 who were followed up in August 2013.
All 12 patients investigated had spondylolisthetic displacement at L5 level. All patients underwent a modification of the standard in situ posterolateral fusion procedure, after wide-decompression L5 through S2 laminotomies and wide L5 foraminotomies. Furthermore, we performed sacral dome resection and interbody fusion with iliac bone grafts. We completed circumferential fusion by posterolateral bone graft placement from L5 to the sacral alae.
We then evaluated complications arising from operation and the need for further procedures. We assessed the walking ability by evaluating activities of daily living (ADLs) and low back pain and leg pain using a visual analog scale (VAS) during preoperative, postoperative, and final examinations. In addition, vertebral alignment evaluation during the preoperative, postoperative, and final examinations included measurement of the lumbosacral angle and lumbar lordosis angle using radiographic images in the profile view with the patient in the neutral standing position (Fig. 1).
The mean age of our patients was 22.3±11.4 years at the time of operation, while the mean follow-up duration was 20.0±7.2 years. At the final follow-up examination, the mean age of our patients was 42.3±13.3 years (Table 1). We did not observe any complication, such as paralysis, in any patient, and none required additional operation. Regarding ADLs, all patients could walk by themselves without the help of a walking stick.
Mean VAS scores were 6.8±0.8 (preoperative examination), 2.0±0.9 (postoperative examination), and 2.25±2.0 (final examination) for low back pain and 6.2±1.8 (preoperative), 2.4±1.1 (postoperative), and 1.2±0.5 (final) for leg pain. Mean VAS scores for low back pain and leg pain were significantly lower at the preoperative and final examinations than at the preoperative examination (p<0.05) (Fig. 2). Regarding vertebral alignment, the mean lumbosacral angle was 32.3±14.2° (preoperative), 33.7°±11.8° (postoperative), and 36.5°±16.4° (final), whereas the mean lumbar lordosis angle was 51.0°±14.8° (preoperative), 48.6°±18.8° (postoperative), and 49.6°±15.5° (final). There were no significant differences in the mean lumbosacral angle and lumbar lordosis angle measured at the preoperative, postoperative, and final examination (all angles, p>0.05) (Table 2).
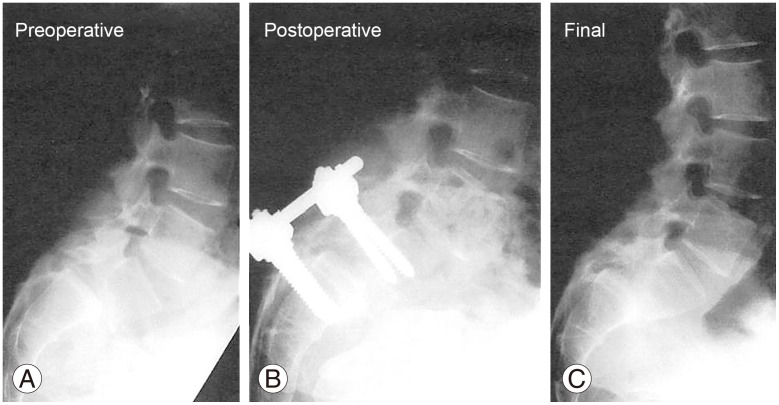
A 22-year-old woman presented with severe bilateral sciatica and a positive straight leg raise test at 30° in both legs. Forward bending was restricted in the lumbar spine. She had a high level of difficulty in performing ADLs and underwent in situ fusion. She was 39 years old at the final examination, and the duration of follow-up was 17 years. She had no low back or leg pain and could walk by herself without the help of a walking stick. Furthermore, she ran over 5 km every day. Regarding vertebral alignment, the lumbosacral angle was 49.9° (preoperative), 45.5° (postoperative), and 22.1° (final), whereas the lumbar lordosis angle was 71.1° (preoperative), 62.8° (postoperative), and 74.3° (final) (Fig. 3).
In the present study, there were no incidences of reoperation cases or perioperative complications such as nerve paralysis. Moreover, in all cases, the ADL status was good, the lower lumbar and leg pain VAS values were low at the final examination, and patient satisfaction was high. In previous studies, reposition fixation was required after in situ fusion for slip progression in the sagittal plane; false joint and cosmetic problems, among other issues, have also been reported [68]. Better alignment may provide better function. However, these operations involve an increased risk of neurological complications from screw placement and the possibility of distracting neurological elements during the corrective procedure [9]. The incidence of nerve paralysis following the surgical reduction of spondylolisthesis ranges from 20% to 40% [7]. Risk factors for nerve paralysis after surgical reduction include sacral bone posterosuperior annulus fibrosus and L5 vertebral arch and strangulation with the pedicle of the vertebral arch, posterior bone spur compression with reduction, cauda equina traction in the spinal canal, and compression by the transplanted bone. However, a follow-up study dividing patients into in situ fusion and reduction trial groups did not show significantly different clinical results between the two groups [10].
While evaluating vertebral alignment among our patients, we noted that the mean lumbosacral angle was similar to that of healthy individuals (35°), although the lumbar lordosis angle was significantly greater than that of healthy individuals (27°). This finding indicates that lumbar lordosis compensated for the kyphosis resulting from the advanced spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra. We believe that this phenomenon resulted from the relatively young age of our patients at the time of operation, and by the time of the final examination, the compensatory actions of the back muscles had allowed for over-flexure. According to previous studies on patients with abnormal vertebral alignment, lumbar flexure is important for trunk balance stability. If compensation is insufficient, trunk balance becomes difficult to maintain, and ADLs such as ambulatory ability are affected [111213]. In the present study, kyphosis created by the high-grade slip of the L5 vertebra was compensated by lumbar flexure, even 20 years postoperatively.
The clinical situation differs when operating on elderly patients with abnormal vertebral alignment. In elderly patients with spondylolisthesis, abnormal vertebral alignment progresses with age and the compensatory support mechanism capabilities, such as those of the back muscles, decrease. Consequently, at some point, the compensatory mechanism collapses and vertebral alignment cannot be maintained; subsequently, ADL-related problems, such as ambulation difficulty and back pain and leg pain, become aggravated. Therefore, further follow-up may be required in these patients. By contrast, dysplastic spondylolisthesis of L5 occurs congenitally, and compensation for abnormal alignment occurs at an early stage [1] and may vary among individuals.
Operative treatment is selected in a small number of patients with dysplastic spondylolisthesis of L5. The primary reason for this is to reduce the influence of compression by the posterior factor with separation. Therefore, unlike in cases of high-level abnormal alignment with high-grade slip, a follow-up examination without operation is indicated in most cases of dysplastic spondylolisthesis of L5 with complete separation. Currently, very few operative treatments are available for dysplastic spondylolisthesis of L5 with complete separation because of the aggravation of abnormal alignment. When treating dysplastic spondylolisthesis of L5, it is important to improve neurological symptoms in a safe manner while avoiding subsequent ADL disorders.
There were several potential limitations to our present study. Firstly, we did not perform an alignment evaluation of the entire spine. Furthermore, as the follow-up period covered a long duration, it was difficult to obtain radiography data immediately before/after operation—an issue related to the normal storage period of radiography data. Furthermore, ADL was only evaluated by walking ability or by determining whether the patient could walk without the help of a walking stick. In addition, the absence of a control group with correction/fixation may represent a limitation. Because our institution mainly conducts in situ fusion for the treatment of spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra (dysplastic type), we now plan to perform a multicenter comparative analysis of in situ fusion and correction/fixation including institutions that perform correction/fixation.
Notes
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Moke L, Debeer P, Moens P. Spondylolisthesis in twins: multifactorial etiology: a case report and review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011;36:E741–E746. PMID: 21270694.


2. Cavalier R, Herman MJ, Cheung EV, Pizzutillo PD. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents: I. Diagnosis, natural history, and nonsurgical management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2006;14:417–424. PMID: 16822889.


3. Demchenko OV, Kolesnichenko VA. Mechanisms of incidence and specifics of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis course in vertebral osteochondropathy. Klin Khir 2000;(3): 35–37.
4. Al-Khawashki H, Wasef Al-Sebai M. Combined dysplastic and isthmic spondylolisthesis: possible etiology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:E542–E546. PMID: 11725254.


5. Moshirfar A, Khanna AJ, Kebaish KM. Treatment of symptomatic spondyloptosis in an adult previously treated with in situ fusion and instrumentation by L5 vertebrectomy and L4-S1 instrumented reduction. Spine J 2007;7:100–105. PMID: 17197342.


6. Boos N, Marchesi D, Zuber K, Aebi M. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by reduction and pedicular fixation: a 4-6-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993;18:1655–1661. PMID: 8235846.


7. Poussa M, Remes V, Lamberg T, et al. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis in adolescence with reduction or fusion in situ: long-term clinical, radiologic, and functional outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:583–590. PMID: 16508556.


8. Bradford DS, Boachie-Adjei O. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by anterior and posterior reduction and stabilization: a long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1990;72:1060–1066. PMID: 2384506.


9. Matthiass HH, Heine J. The surgical reduction of spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1986;(203): 34–44.

10. Poussa M, Schlenzka D, Seitsalo S, Ylikoski M, Hurri H, Osterman K. Surgical treatment of severe isthmic spondylolisthesis in adolescents. Reduction or fusion in situ. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993;18:894–901. PMID: 8316890.


11. Hasday CA, Passoff TL, Perry J. Gait abnormalities arising from latrogenic loss of lumbar lordosis secondary to Harrington instrumentation in lumbar fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1983;8:501–511. PMID: 6648700.


12. Itoi E. Roentgenographic analysis of posture in spinal osteoporotics. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1991;16:750–756. PMID: 1833827.


13. Lord MJ, Small JM, Dinsay JM, Watkins RG. Lumbar lordosis. Effects of sitting and standing. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:2571–2574. PMID: 9383867.


Fig. 1
Evaluation of vertebral alignment at the preoperative, postoperative, and final examinations including the measurement of (1) lumbosacral angle and (2) lumbar lordosis angle on lumbosacral spine radiographic images (profile view with the patient in the neutral standing position).
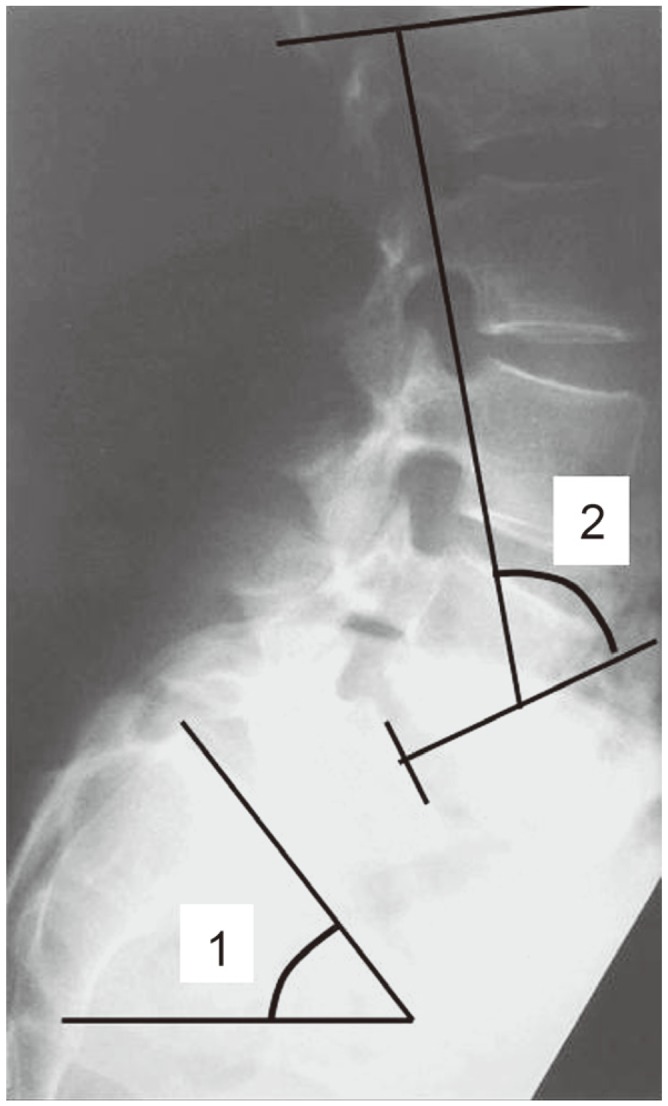
Fig. 2
Evaluation of mean visual analog scale at the preoperative, postoperative, and final examinations.
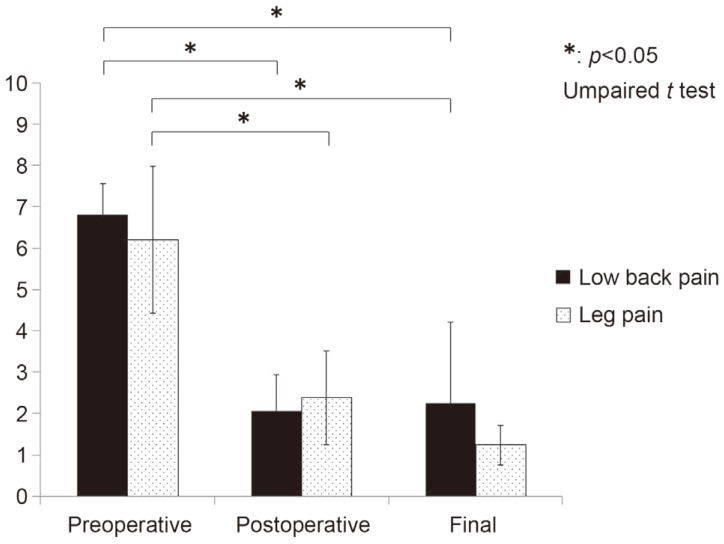
Fig. 3
(A–C) Lumbosacral spine radiographic images acquired at the preoperative, postoperative, and final examinations in the sample case.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles in ASJ
-
Decompression without Fusion for Low-Grade Degenerative Spondylolisthesis2016 February;10(1)