 |
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 17(5); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to identify the clinicoradiological risk factors associated with the inability to achieve minimum clinically important difference (MCID) on the modified Japanese Orthopaedic Association (mJOA) Scale in operated cases of cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM).
Overview of Literature
Only a few studies have evaluated the outcomes of surgery performed for CSM using MCID on the mJOA scale.
Methods
We analyzed 124 operated CSM cases from March 2019 to April 2021 for preoperative clinical features, cervical sagittal radiographic parameters, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) signal intensities (SI). The risk factors associated with missing the MCID (poor outcome) on mJOA at the final follow-up were identified using binary logistic regression. Multivariate analysis was used to find significant risk factors, and odds ratios (OR) were computed.
Results
A total of 110 men (89.2%) and 14 women (10.8%) with an average age of 53.5±13.2 years were included in the analysis. During the last follow-up, 89 cases (72.1%) achieved MCID (meaningful gains following surgery) while 35 (27.9%) could not. The final model identified the following parameters as significant risk factors for poor outcome: increased duration of symptoms (OR, 6.77; p=0.001), lower preoperative mJOA scale (OR, 0.75; p=0.029), the presence of multilevel T2-weighted (T2W) MRI SI (OR, 4.79; p=0.004), and larger change in cervical sagittal vertical axis (ΔcSVA) (OR, 1.06; p=0.013). Also, an increase in cSVA postoperatively correlated with a reduced functional recovery rate (r=−0.4, p<0.001).
As the global population ages, spine physicians will be seeing an increased number of degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM) cases in the coming times [1]. In 20%–60% of patients with symptoms of cervical myelopathy, clinical deterioration is expected unless the compression is reversed [2]. It is, thus, imperative to reverse the stenosis before irreversible changes in the spinal cord set in. Surgery is performed in cases of moderate to severe myelopathy but a dilemma over treatment strategy exists in patients with mild myelopathic symptoms. Due to increasing epidemiological relevance and the large disease burden of cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM), it seems intuitive to elucidate the predictors of neurological recovery after surgery. These parameters assist the surgeon in decision-making and managing the expectations of patients regarding the surgery outcomes. Previous studies on outcome predictors in patients with CSM have either focused on preoperative clinical factors [3–6] or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) changes [7,8]. In recent years, few studies highlighting the influence of cervical sagittal alignment have also come to the forefront [9–12]. In most of these studies, measurement scales for outcome assessment included the modified Japanese Orthopaedic Association (mJOA) scale, Nurick grade, Visual Analog Scale (VAS), and the Neck Disability Index (NDI) among others [8–12]. Whether the change in these functional scores truly translates into clinically meaningful gains for the individual remains unclear.
Outcome studies relying on patient-reported outcome measurements to assess treatment effects have a drawback. The extent of improvement in the numerical scores of these questionnaires lacks a direct clinical meaning. Because of this, the concept of a minimum clinically important difference (MCID) has been used to measure the critical threshold needed to achieve clinically relevant treatment effectiveness. The newly introduced, validated paradigm, MCID is defined as the measure of minimum change in a measurement that a patient would identify as meaningful. This enables the assessment of disease severity and objectively determines an individual patient’s improvement after surgery [13]. Although some high-quality studies on predictors of functional recovery in CSM patients exist in the literature, only a few have done this evaluation using MCID of mJOA scale. This study aimed to robustly assess risk factors across three domains, namely, preoperative clinical features, radiographic cervical sagittal parameters, and MRI parameters associated with the inability to achieve MCID of mJOA scale postoperatively in a surgical cohort of CSM patients at a minimum of 1-year follow-up.
This study was approved by the by the Ethics Review Board of Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, India (EC/2/19/2008). Informed consent was obtained from all the patients included in the study. In our institution, data of consecutively operated cases of DCM from March 2019 to April 2021 was retrospectively analyzed. Inclusion criterion included cases of symptomatic DCM with at least one clinical sign of myelopathy and an MRI evidence of cervical cord compression with no history of previous cervical surgery and a complete set of records (clinical, preoperative radiographs, and MRI images) including cervical lateral radiographs having properly visible endplates up to the C7 vertebra. Of the 168 cases that were initially selected, 44 were excluded based on the exclusion criterion (Fig. 1). Thus, 124 cases (n=124) of CSM, with a minimum 1-year follow-up, were available for final evaluation and were analyzed for preoperative clinical features, lateral cervical sagittal parameters, and preoperative MRI signal intensities (SI) (both qualitative and quantitative). Clinical factors included age, duration of symptoms, comorbidities, presence or absence of spasticity, smoking habits, and preoperative myelopathy severity.
Sagittal parameters were measured in standard lateral radiographs of the cervical spine taken in a neutral position with the upper extremities positioned at the side of the body while maintaining a horizontal gaze [14,15]. Parameters measured included the following: (1) C2–C7 lordosis (CL, in degrees)—the Cobb angle between the lower endplates of the C2 and C7 vertebral body. The symbol “+” denoted lordosis, while “−” denoted kyphotic alignment. (2) C2–C7 sagittal vertical axis (cSVA, in mm)—the distance from the posterosuperior corner of C7 to a vertical line from the center of the C2 vertebra (the anterior shift of plumbline was assigned “+,” while the posterior shift was “−”). (3) C7 slope (C7S, in degrees)—the angle between the upper endplate of the C7 vertebral and the horizontal body. Patients’ demographics were recorded, and the measurements were done using Surgimap ver. 2.3.2 (Nemaris Inc., New York, NY, USA) application by two spine surgeons on two separate occasions, and the mean of measurements was further analyzed. These assessors were blinded to the outcomes of the patients.
For qualitative assessment of sagittal MRI, distinct patterns at the area of greatest cord compression were enumerated as suggested in the literature [7,16], namely, single-level T2-weighted (T2W) SI (diffuse or sharp) (Fig. 3A, B), multilevel T2W SI changes (sharp and/or diffuse) (Fig. 3C), and hypointense T1W SI (Fig. 3D). The single level was defined as hyperintense SI (diffuse, Fig. 3A or sharp, Fig. 3B), accompanied by cord compression present at one disc level only; multilevel (>1 level) was defined as one with a focal area of hyperintense signal located at the most compressed level along with an area of high SI that exists at other compressed levels (sharp and/or diffuse type).
As done in previous studies, quantitative analysis of T2W sagittal MRI was performed using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) [11,12]. SI ratio was defined as the ratio of intensity at the area of greatest cord SI change (Fig. 4A) and the cerebrospinal fluid behind the spinal cord at C2 (Fig. 4B), calculated with 100-pixel circles at both places.
Another quantitative measure for cord compression found in T1W axial MRI was the compression ratio (CR) as previously described [5]. CR was defined as the ratio of the smallest sagittal diameter of the cord and the broadest transverse diameter of the cord taken at the same level. All MRI assessments were performed by two spine surgeons independently, and the assessors were blinded to the outcome of the patients.
All patients underwent cervical decompression surgeries, performed by three senior spine surgeons from the orthospine department at our institute. The choice of anterior or posterior surgery was the surgeon’s discretion. The number of levels involved, neck pain, cervical alignment, the presence or absence of retrovertebral compression, and the patient’s surgical capacity were the factors considered in decision-making. Anterior surgeries included anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) and anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion, while posterior surgeries included cervical laminectomy with or without lateral mass fixation and laminoplasty. In a few cases, combined anterior and posterior surgery was performed.
The surgery outcome was assessed using the mJOA scale and its corresponding MCID along with Nurick grading at the last follow-up. The functional recovery rate for the mJOA scale (mJOArr) was calculated using Hirabayashi’s method [17].
All patients were divided based on their preoperative myelopathy severity: mild, moderate, and severe groups. Change in the mJOA score at the last follow-up was used as the primary outcome measure. The MCID for each group was based on the preoperative myelopathy severity. For patients with mild disease (mJOA score of ≥15), MCID was one point increment in the preoperative mJOA score; for those with moderate disease (mJOA score of 12–14), MCID was increased by two points; and for severe myelopathy (mJOA score of <12), MCID chosen was increased by three points [13]. A change in the mJOA scale greater than or equal to the MCID of that group was defined as an “optimal” outcome.
Patients were then grouped into two categories: cases of those who achieved MCID on mJOA (good outcome) and cases of those who could not achieve MCID on mJOA (poor outcome) at the last follow-up assessment. Cases were followed at baseline, postoperatively at 1 year and at the last follow-up. Variables associated with the two groups were compared using statistical analysis, and risk factors associated with poor outcome were identified. Patients with a minimum 1-year follow-up were considered for evaluation. Short follow-up duration was used to avoid complications including adjacent segment pathologies or pseudoarthrosis (usually occurring by 2–3 years post-surgery) which may affect the results.
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Continuous variables were described using means, standard deviations, median, and interquartile range. Categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and percentages. Quantitative data was first tested for its normality and homogeneity of variance, and according to different situations, different tests were used. For the continuous variable for linear regression, the Shapiro-Wilk test of normality was used. Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test was performed initially to evaluate the association between variables and surgical outcomes. To evaluate for statistical significance, stepwise logistic regression was used which involved adding or removing potential independent variables in succession and after each iteration testing. Subsignificant thresholds with p<0.15 rather than a strict p<0.05 were used to finalize the risk factors to be examined for the multivariate model. This provided the benefit of including possible confounders that did not meet the threshold of significance but still were clinically important. Then, using binary logistic regression, the influence of these variables on the odds ratio (OR) of the observed event of interest was analyzed (i.e., inability to achieve the MCID on the mJOA scale). In the multivariate analysis, a p-value of <0.05 was considered to be significant. Linear regression analysis was used to find the relationship between functional recovery rate (mJOArr) and radiographic cervical sagittal parameters. The interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility were assessed using the intraclass correlation coefficient at 95% confidence interval.
The study included 110 men (89.2%) and 14 women (10.8%), with an average age of 61.5±13.2 years (range, 26–81 years). The mean duration of symptoms was 5.8±4.6 months (range, 1–24 months). The mean baseline mJOA score was 11.67±2.1 (range, 4–15 points), with 19 cases of mild myelopathy, 45 cases of moderate disease, and 60 cases of severe myelopathy. Approximately 72.1% of surgical patients with CSM exhibited optimum results with meaningful gains in neurological function following surgery. This included 17/19 cases (89.3%) of mild myelopathy achieving MCID. At the last follow-up, the mean increase in the mJOA scale was 3.18±0.46 points, while the mean decrease in the Nurick score was 1.4±0.32 points. The demographic data of the cohort is presented in Table 1. The changes in the parameters from baseline to the last follow-up are presented in Table 2. Interrater correlation coefficient was high for the quantitative MRI evaluation (Table 1). A high interrater correlation was noted for sagittal cervical parameter measurements (Table 2). Significant correlations were observed between preoperative cSVA and preoperative myelopathy severity (r=−0.23, p≤0.04), and functional recovery rate (mJOArr) and postoperative cSVA (r=−0.4, p<0.001) at the last follow-up. Using linear regression, with mJOArr as dependent variable and postoperative cSVA as independent variable, the following regression equation was formulated: y=−0.86x+71.4 (r=−0.4, p<0.001).
Based on univariate analysis, the MCID (poor outcome) was not achieved on the mJOA scale due to the following significant risk factors: higher age (OR, 2.25; p=0.023), increased duration of symptoms (OR, 7.61; p<0.001), higher comorbidities (OR, 6.56; p=0.006), higher preoperative severity (OR, 3.35; p=0.005), posterior approach (OR, 6.44; p=0.001), greater number of levels involved (OR, 12.0; p=0.019), presence of multilevel T2W SI MRI changes (OR, 5.50; p<0.001), hypointense T1W SI (OR, 6.29; p=0.004), postoperative cSVA >40 mm (OR, 4.63; p=0.002), and higher ΔcSVA (OR, 8.4; p=0.006) (Table 3).
In the final model, four parameters were identified which were found to be significantly associated with missing the MCID for mJOA at the final follow-up. The odds of missing the MCID (1) increased by more than 6 times as the duration of symptoms increased (i.e., moved from <6 months to >6 months duration), (2) increases by approximately 25% when patient had increased preoperative myelopathy severity (i.e., preoperative mJOA is below 12 than at or above it), (3) increases by more than 4 times in the presence of multilevel T2W MRI SI changes, and (4) increases by 1.06 times as change in cSVA increases postoperatively from below 0 to between 0 and 20 mm and then >20 mm (Table 4).
This study aimed to identify the parameters associated with poor functional outcome post-surgery for CSM. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that has assessed parameters pertaining to clinical features and MRI and X-ray measurements all done in a single analysis using severity-based MCID on mJOA scale as measuring index. After reviewing a wide range of literature in similar studies, the clinical parameters in the evaluation and cutoffs for the variables used in the study were selected [3–12].
The true benefit of surgery must be assessed as a change in function on an individual basis. Additionally, the benefit that a patient experiences after surgery is dependent on his or her preoperative myelopathy severity. Alternatively, the same change in the mJOA score after surgery may not correspond to the same “benefit” in two patients who were at different stages of preoperative severity spectrum. To overcome this inherent shortcoming in the mJOA scale, Tetreault et al. [13] developed that an increment in the mJOA score that would translate into substantial benefit postoperatively should be one point, 2 points, and three points for mild, moderate, and severe cases, respectively. This demarcation allows clinicians to individualize the improvements achieved after an intervention. Achieving or the inability to achieve this change formed the basis of an assessment.
This analysis showed that 72.1% of surgical patients with CSM exhibited optimum results with meaningful gains in neurological function following surgery, underscoring the efficacy of intervention in these cases. Notably, 17/19 (89.3% cases) with mild myelopathy achieved MCID highlighting the benefits of surgical intervention in these mild severity cases. The four parameters that were significantly associated with poor clinical outcome (i.e., inability to achieve MCID) included greater duration of symptoms, higher preoperative myelopathy severity, multilevel T2W MRI SI, and a larger shift in the cSVA post-surgery. A longer duration of symptoms may correspond to more advanced degeneration and, thus, higher structural and histological damage in the cord including cystic necrosis, cavitation, and syrinx formation [7]. Similar to our findings, Tetreault et al. [18] have found duration of symptoms to be a significant risk factor for achieving MCID over mJOA (relative risk, 0.943; p=0.0003). Similarly, our model predicts cases of preoperative mJOA <12 as having 25% lower odds of achieving MCID. Gao et al. [19] also reported 4.85 times higher chances of recovery rate being <50% in patients with preoperative Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) scales of ≤9 than those with JOA scales of >9, while Shin et al. [20] reported decreased odds of recovering greater than 75% on the JOA score (OR, 1.34; p<0.036) in patients with lower baseline JOA score. It is postulated that the higher the preoperative severity, the more advanced the degenerative changes and the higher the cord damage.
Even though many previous reports suggested that both preoperative severity and duration of symptoms can be used to predict outcomes, some reports were unable to establish the duration of symptoms [21,22] or preoperative severity [18,23] as an independent predictor of postoperative outcome. The authors believe that the threshold at which these factors become significant enough to impact the outcome may require further probing, and further studies are recommended to evaluate the relationship between surgical outcomes with baseline severity and duration of symptoms.
Multilevel T2W SI changes were observed to show more than 4 times higher odds of poor outcome. DCM was postulated to be a multilevel pathology with varying degree of cord compression occurring at different levels [7]. T2W SI changes at multiple levels would correspond to higher cord damage with more extensive histological changes. Several authors have evaluated the impact of preoperative MRI changes on the outcome of surgery in CSM cases. In their review on the different classifications of T2W SI changes, Vedantam and Rajshekhar [16] reported that both sharp, intense T2 SI and multilevel T2 SI are associated with poorer surgical results (class II evidence). In a systematic review of 14 studies evaluating the characteristics of MRI SI changes in DCM, Karpova et al. [7] concluded that the presence of SI changes on T2W MRI, whether single or multilevel, and its brightness and presence in both T1 and T2W have predictive values pertaining to outcomes.
Previously published literature on the influence of sagittal alignment on surgical outcomes in CS has focused more on cervical kyphosis rather than on sagittal imbalance [10,24]. Our analysis shows that cSVA is more closely associated with outcome in the CSM than in C2–C7 Cobb. Also, as we progress from lordotic to neutral and toward kyphotic alignment, the increasing cSVA (sagittal imbalance) correlates negatively with the functional outcome and positively with myelopathy severity (decreasing preoperative mJOA score). In the univariate analysis, the odds of not achieving MCID was observed to be 2.5 times higher when postoperative cSVA was at or >40 mm than if it was below it (OR, 2.66; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.54–4.59; p<0.001). While in our final model, a larger increase in cSVA (higher ΔcSVA) postoperatively was found to be associated with poorer functional outcomes (OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.01–1.11; p<0.013). The influence of sagittal malalignment and its impact on the spinal cord have been analyzed using biomechanical studies. In a kyphotic deformity, anteriorly placed vertebral bodies and disc-osteophyte complexes “drape” the cord which leads to anterior cord pathology. The increased longitudinal cord tension and the progressive structural cord changes manifest into clinical myelopathy [25,26].
Another analysis by Fan et al. [27], evaluating 89 cases of ACDF in multilevel CSM, found that cervical sagittal parameters were closely related with the clinical outcome. They observed lower preoperative JOA scale, longer duration of symptoms, smaller change in Cobb angle, and larger change in cSVA after surgery were independent risk factors for poor outcomes. Similar to this analysis, Tetreault et al. [18] found that 70% of patients in their prospective cohort of DCM patients, who were surgically treated, achieved MCID for mJOA at the end of a 2-year follow-up. They concluded that the variables associated with achieving MCID included younger aged patients, smaller duration of myelopathy symptoms, nonsmokers, and absence of significant gait impairment at presentation.
Another important correlation was between mJOArr and postoperative cSVA (r=−0.4, p<0.001). The relationship between the two variables was governed by the equation y=−0.86x+71.4, with y being the dependent variable mJOArr and x being the postoperative cSVA. This would mean that every 10 mm increase in postoperative cSVA, the functional recovery rate would decrease by 8.6%. Thus, increasing sagittal imbalance deteriorates functional outcomes irrespective of the nature of surgery performed. In our analysis, preoperative cSVA was also found to be significantly correlated with preoperative myelopathy severity (r=−0.23, p≤0.04). The weak correlation could be explained due to the smaller number of kyphotic cases in our cohort (14/124 [12.3%] overall).
Several authors studying the impact of sagittal alignment on myelopathy severity and outcomes found similar observations [9,10,28]. Pinter et al. [29] recently published their results while analyzing the impact of cervical sagittal alignment on NDI and VAS scores after posterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery. They reported that preoperative cSVA <40 mm had a larger improvement VAS neck pain scores at 3 months and greater improvements in NDI scores at 1 year postoperatively than those patients with cSVA ≥40 mm. Patients with a decrease in cSVA (ΔcSVA) by 5 mm postoperatively were also observed to have lower NDI scores at 3 months postoperatively when compared with patients whose cSVA increased or remained unchanged, though this observation did not hold when the comparison was done at 1-year follow-up [29]. These studies emphasize the influence of sagittal parameters on clinical outcomes and the need to consider these factors during surgery.
This study has several limitations. Firstly, the analysis was done on patients with CSM who belonged to a predecided surgical cohort. Selection bias would have excluded cases who were not subjected to surgery. These would be either cases of very mild disease or cases of overtly severe disease unlikely to benefit from surgery. Also, risk of bias may exist due to confounding risk factors associated with the type of surgery performed. The retrospective nature of analysis is another limitation, but blinding was ensured wherever possible to reduce biases in assessment. Lastly, a smaller subset of kyphotic patients in the cohort (12.3%) might have contributed to weaker correlations in the analysis.
Approximately 72.1% of surgical patients with CSM exhibited optimum results with meaningful gains in neurological function following surgery emphasizing the efficacy of intervention in these cases. However, poorer results are found in patients with longer duration of symptoms, higher baseline severity in the presence of multilevel T2W MRI SI, and a larger increase in sagittal imbalance at the last follow-up. Among the cervical sagittal parameters, cSVA is more closely associated with functional outcome and baseline severity than C2–C7 Cobb. Cervical sagittal imbalance must be considered when performing decompressive surgery in cases of CSM.
Notes
Author Contributions
Conception and design: Varun Khanna; data acquisition: Varun Khanna; analysis of data: Varun Khanna, Rupinder Chahal, Gayatri Vishwakarma; drafting of the manuscript: Varun Khanna; critical revision: Varun Khanna, Rupinder Chahal; obtaining funding: Shankar Acharya, Kashmiri Lal Kalra; administrative support: Shankar Acharya, Rupinder Chahal, Kashmiri Lal Kalra; supervision: Shankar Acharya, Kashmiri Lal Kalra; and final approval of the manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1
Flowchart depicting the methodology of the study. DCM, degenerative cervical myelopathy; OPLL, ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament; MCID, minimum clinically important difference; SVA, sagittal vertical axis; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
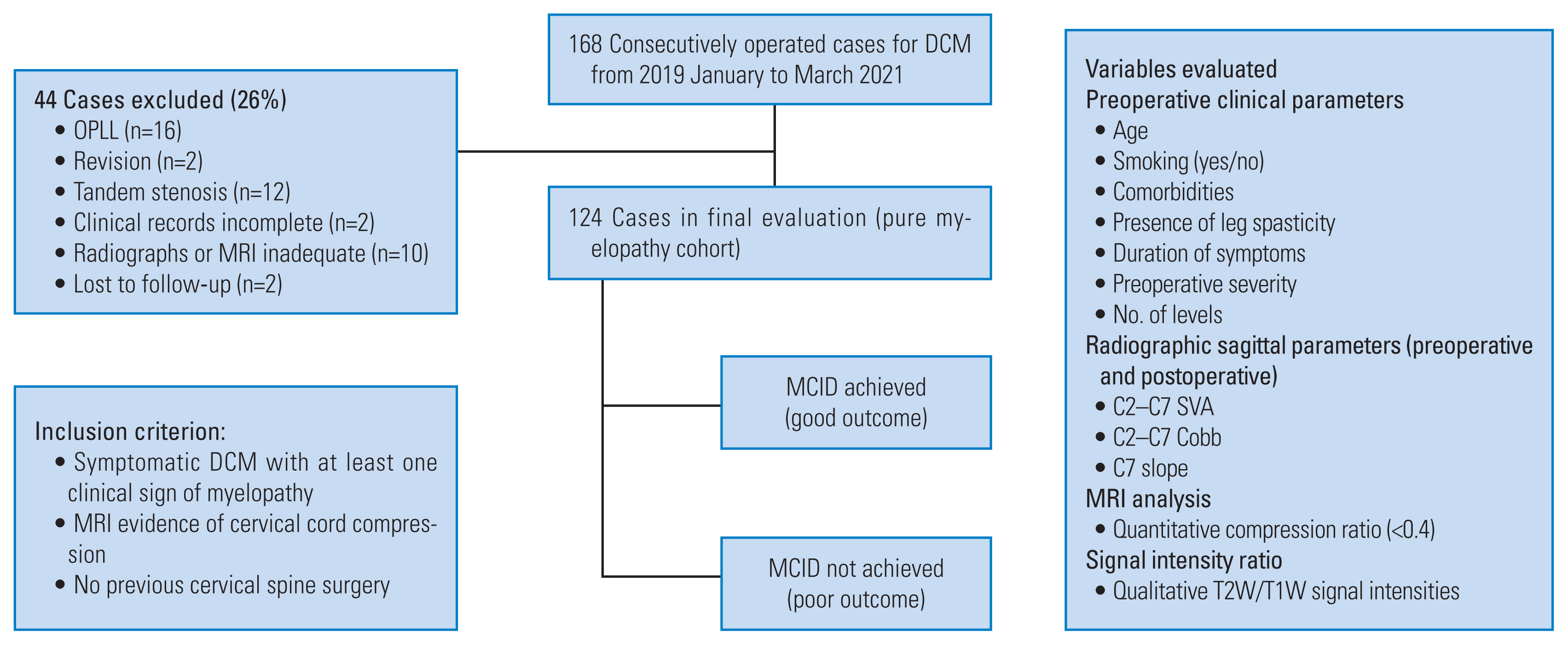
Fig. 2
Lateral cervical radiograph with sagittal parameters that were evaluated in the study. cSVA, cervical sagittal vertical axis.

Fig. 3
Different patterns of magnetic resonance imaging signal intensity (SI) (with level of compression marked) that were evaluated for qualitative assessment. Single level T2 weighted (T2W) hyperintense SI: (A) diffuse type (white arrowhead) and (B) sharp type (white arrow). (C) multilevel T2W SI changes (sharp and/or diffuse) (white and black arrowheads). (D) Hypointense T1W SI (white arrow).
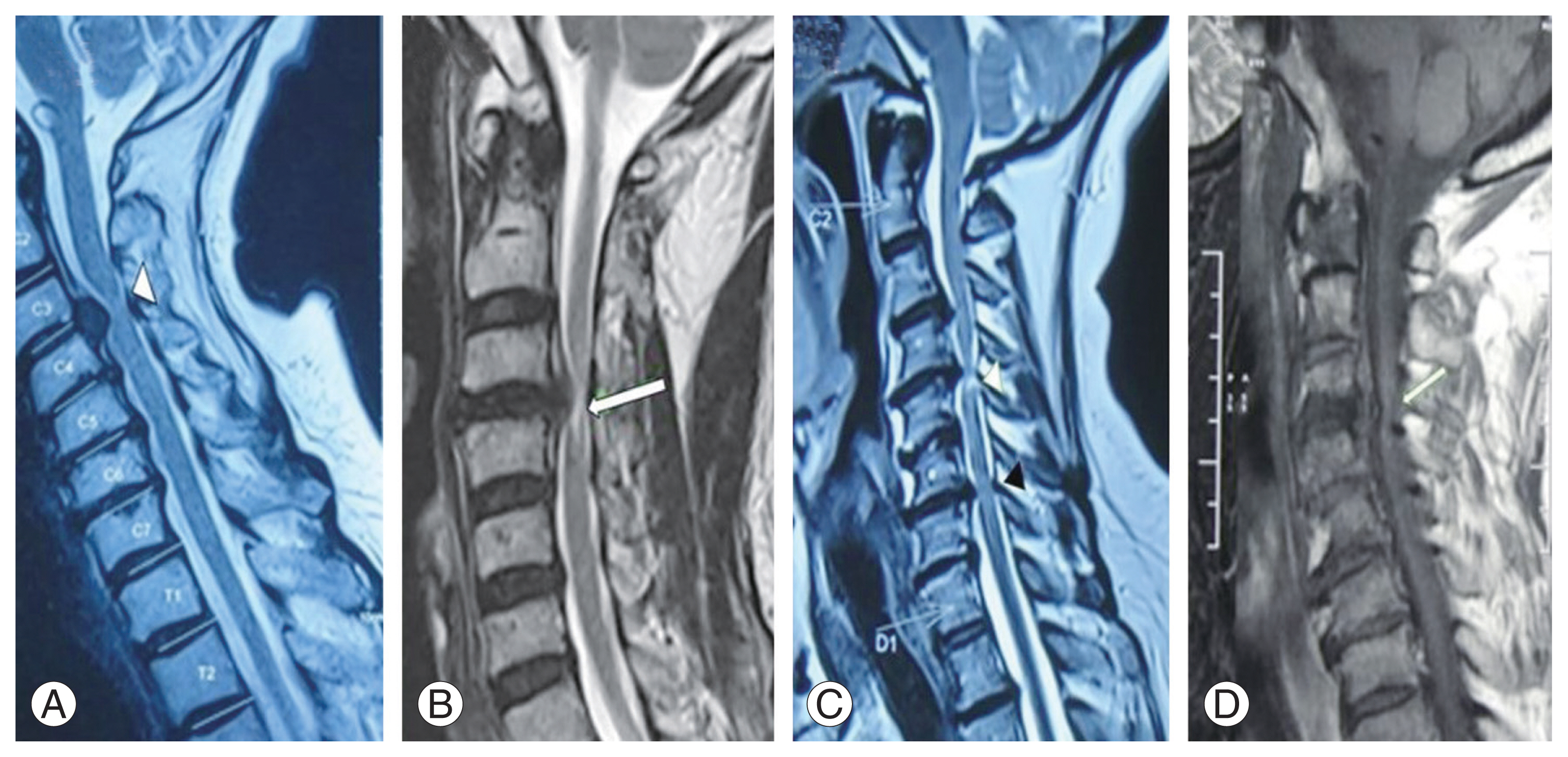
Fig. 4
Quantitative assessment of magnetic resonance imaging using signal intensity ratio. (A, B) It is defined as ratio of intensity at the area of greatest cord signal intensity change (A) and the cerebrospinal fluid behind the spinal cord at C2 (B), calculated with 100-pixel circles at both places.

Table 1
Demographics data of the patient population
Table 2
Changes in parameters from baseline to last follow-up
Table 3
Univariate analyses evaluating the association between various parameters and missing MCID on the mJOA scale at last follow-up following surgery
Table 4
Multivariate analyses evaluating the association between various parameters and missing MCID on the mJOA scale at last follow-up following surgery
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Duration of symptoms | 6.77 (2.29–19.98) | 0.001* |
| Preoperative myelopathy severity | 0.75 (0.57–0.97) | 0.029* |
| Multilevel T2W MRI SI | 4.79 (1.63–14.05) | 0.004* |
| ΔcSVA | 1.06 (1.01–1.11) | 0.013* |
References
1. Fehlings MG, Tetreault L, Nater A, et al. The aging of the global population: the changing epidemiology of disease and spinal disorders. Neurosurgery 2015;77(Suppl 4): S1–5.

2. Karadimas SK, Erwin WM, Ely CG, Dettori JR, Fehlings MG. Pathophysiology and natural history of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38(22 Suppl 1): S21–36.


3. Tetreault LA, Nouri A, Singh A, Fawcett M, Fehlings MG. Predictors of outcome in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy undergoing surgical treatment: a survey of members from AOSpine International. World Neurosurg 2014;81:623–33.


4. Gembruch O, Jabbarli R, Rashidi A, et al. Surgery for degenerative cervical myelopathy: what really counts? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2021;46:294–9.

5. Fujiwara K, Yonenobu K, Ebara S, Yamashita K, Ono K. The prognosis of surgery for cervical compression myelopathy: an analysis of the factors involved. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1989;71:393–8.



6. Tetreault L, Palubiski LM, Kryshtalskyj M, et al. Significant predictors of outcome following surgery for the treatment of degenerative cervical myelopathy: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurg Clin N Am 2018;29:115–27.

7. Karpova A, Arun R, Cadotte DW, et al. Assessment of spinal cord compression by magnetic resonance imaging: can it predict surgical outcomes in degenerative compressive myelopathy?: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:1409–21.


8. Arvin B, Kalsi-Ryan S, Mercier D, Furlan JC, Massicotte EM, Fehlings MG. Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging is associated with baseline neurological status and can predict postoperative recovery in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:1170–6.


9. Tang JA, Scheer JK, Smith JS, et al. The impact of standing regional cervical sagittal alignment on outcomes in posterior cervical fusion surgery. Neurosurgery 2012;71:662–9.



10. Roguski M, Benzel EC, Curran JN, et al. Postoperative cervical sagittal imbalance negatively affects outcomes after surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014;39:2070–7.



11. Mohanty C, Massicotte EM, Fehlings MG, Shamji MF. Association of preoperative cervical spine alignment with spinal cord magnetic resonance imaging hyperintensity and myelopathy severity: analysis of a series of 124 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:11–6.

12. Shamji MF, Mohanty C, Massicotte EM, Fehlings MG. The association of cervical spine alignment with neurologic recovery in a prospective cohort of patients with surgical myelopathy: analysis of a series of 124 cases. World Neurosurg 2016;86:112–9.


13. Tetreault L, Nouri A, Kopjar B, Cote P, Fehlings MG. The minimum clinically important difference of the modified Japanese Orthopaedic Association Scale in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:1653–9.


14. Ling FP, Chevillotte T, Leglise A, Thompson W, Bouthors C, Le Huec JC. Which parameters are relevant in sagittal balance analysis of the cervical spine?: a literature review. Eur Spine J 2018;27(Suppl 1): 8–15.



15. Ye IB, Tang R, Cheung ZB, White SJ, Cho SK. Can C7 slope be used as a substitute for T1 slope?: a radiographic analysis. Global Spine J 2020;10:148–52.




16. Vedantam A, Rajshekhar V. Does the type of T2-weighted hyperintensity influence surgical outcome in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy?: a review. Eur Spine J 2013;22:96–106.




17. Hirabayashi K, Miyakawa J, Satomi K, Maruyama T, Wakano K. Operative results and postoperative progression of ossification among patients with ossification of cervical posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1981;6:354–64.


18. Tetreault L, Wilson JR, Kotter MR, et al. Predicting the minimum clinically important difference in patients undergoing surgery for the treatment of degenerative cervical myelopathy. Neurosurg Focus 2016;40:E14.

19. Gao R, Yang L, Chen H, Liu Y, Liang L, Yuan W. Long term results of anterior corpectomy and fusion for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. PLoS One 2012;7:e34811.



20. Shin JW, Jin SW, Kim SH, et al. Predictors of outcome in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy undergoing unilateral open-door laminoplasty. Korean J Spine 2015;12:261–6.



21. Karpova A, Arun R, Davis AM, et al. Predictors of surgical outcome in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:392–400.


22. Furlan JC, Kalsi-Ryan S, Kailaya-Vasan A, Massicotte EM, Fehlings MG. Functional and clinical outcomes following surgical treatment in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a prospective study of 81 cases. J Neurosurg Spine 2011;14:348–55.


23. Uchida K, Nakajima H, Takeura N, et al. Prognostic value of changes in spinal cord signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy. Spine J 2014;14:1601–10.


24. Buell TJ, Buchholz AL, Quinn JC, Shaffrey CI, Smith JS. Importance of sagittal alignment of the cervical spine in the management of degenerative cervical myelopathy. Neurosurg Clin N Am 2018;29:69–82.


25. Chavanne A, Pettigrew DB, Holtz JR, Dollin N, Kuntz C 4th. Spinal cord intramedullary pressure in cervical kyphotic deformity: a cadaveric study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011;36:1619–26.

26. Shimizu K, Nakamura M, Nishikawa Y, Hijikata S, Chiba K, Toyama Y. Spinal kyphosis causes demyelination and neuronal loss in the spinal cord: a new model of kyphotic deformity using juvenile Japanese small game fowls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:2388–92.

27. Fan XW, Wang ZW, Gao XD, Ding WY, Yang DL. The change of cervical sagittal parameters plays an important role in clinical outcomes of cervical spondylotic myelopathy after multi-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Orthop Surg Res 2019;14:429.




- TOOLS







