 |
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 17(4); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
To compare the radiographic risk factors for decreased cervical lordosis (CL) after laminoplasty, focusing on the difference between cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) and cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (C-OPLL).
Overview of Literature
A few reports compared the risk factors for decreased CL between CSM and C-OPLL although these two pathologies have their characteristics.
Methods
This study included 50 patients with CSM and 39 with C-OPLL who underwent multi-segment laminoplasty. Decreased CL was defined as the difference between preoperative and 2-year postoperative neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angles. Radiographic parameters included preoperative neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angles, C2ŌĆō7 sagittal vertical axis (SVA), T1 slope (T1S), dynamic extension reserve (DER), and range of motion. The radiographic risk factors were investigated for decreased CL in CSM and C-OPLL. Additionally, the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score was assessed preoperatively and 2 years postoperatively.
Results
C2ŌĆō7 SVA (p=0.018) and DER (p=0.002) were significantly correlated with decreased CL in CSM, while C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (p=0.012) and C2ŌĆō7 SVA (p=0.028) were correlated with decreased CL in C-OPLL. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that greater C2ŌĆō7 SVA (B=0.22, p=0.026) and small DER (B=ŌłÆ0.53, p=0.002) were significantly associated with decreased CL in CSM. By contrast, greater C2ŌĆō7 SVA (B=0.36, p=0.031) was significantly associated with decreased CL in C-OPLL. The JOA score significantly improved in both CSM and C-OPLL (p<0.001).
Laminoplasty is a surgical procedure that provides posterior decompression and is widely performed in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) and cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (C-OPLL) to treat compressive myelopathy [1ŌĆō3].
Laminoplasty can cause kyphotic alignment change postoperatively [4,5], although the risk is lower than that for laminectomy alone [6]. Postoperative cervical kyphosis alignment changes may occur in both patients with C-OPLL and CSM even if the patientŌĆÖs cervical alignment is lordosis preoperatively [7,8]. The posterior muscle ligament complex (PMLC) has received much attention and is damaged during laminoplasty, which can result in cervical kyphotic deformity or, more often, decreased cervical lordosis (CL) [9]. Cervical kyphotic alignment changes may limit the dorsal shift of the spinal cord, resulting in less indirect decompression in laminoplasty [10,11]. Hence, patients with kyphosis deformity, as well as patients with postoperatively decreased CL, often have poor neurological outcomes after laminoplasty. Kyphosis deformity causes axial pain due to fatigue of neck extensor muscles in addition to neurological dysfunction [12].
The preoperative neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle, C2ŌĆō7 sagittal vertical axis (C2ŌĆō7 SVA), and T1 slope (T1S) are risk factors for postoperatively decreased CL [13ŌĆō16]. Additionally, the PMLC is an important factor in maintaining cervical lordotic alignment [17,18]. The dynamic extension reserve (DER), which predicts the contraction reserve of PMLC, is also reported as a risk factor for decreased CL [7]. Previous studies have analyzed the risk factors for decreased CL in CSM and C-OPLL together or analyzed them only for single pathologies although CSM and C-OPLL have characteristics for each condition and a few reports compared the risk factors for decreased CL in different CSM and C-OPLL conditions [19,20].
Here, we compared the radiographic risk factors for decreased CL focusing on the difference between CSM and C-OPLL.
This retrospective study of human patients conformed to the ethical standards of the Institutional Review Board of Chiba University Hospital (M10251), which approved the study protocol and waived the requirement for informed consent due to the retrospective nature of this study. This study included data from 177 patients with CSM and C-OPLL, and 116 and 61 patients with CSM and C-OPLL, respectively, underwent laminoplasty between October 2001 and November 2019. Data from patients who underwent multiple-segment laminoplasty with Ōēź4 levels of operated laminae were included in this study. Data from patients who had previous cervical spine surgery or a history of trauma, tumor, rheumatoid arthritis, infection, dialysis, or neurology disease, such as ParkinsonŌĆÖs disease, were excluded, as well as data from patients without preoperative extension and flexion lateral radiography and with a follow-up period of <2 years, ultimately including 89 patients with CSM or C-OPLL. The spinous processes of C7 were removed and open-door laminoplasty of C7 was performed in some patients. This study included dome-fenestrated C2 and C7 lamina in the operating segments. Our institution indicated patients with a kyphotic deformity or K-line (ŌłÆ) cervical OPLL for anterior or posterior decompression and fusion [21ŌĆō23].
Each parameter was assessed on lateral radiographs. Fig. 1 shows a summary of the radiographic parameters. The neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle was the angle formed by the endplates of C2 and C7. Decreased CL was the difference between preoperative and 2-year postoperative neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle. The C2ŌĆō7 SVA was the distance between a plumb line dropped from the center of the C2 body and the posterosuperior aspect of the C7 vertebral body. The T1S was the angle between the superior endplate of T1 and a horizontal plane on lateral radiographs. DER was the difference between the extension C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle and the neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle. Range of motion (ROM) was the difference between the extension C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle and flexion C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle. The clinical outcomes were assessed using the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score preoperatively and 2-year postoperatively in patients with CSM and C-OPLL. The recovery rate of the JOA score was calculated using the following formula: recovery rate (%)=(postoperative scoreŌĆōpreoperative score)/(17ŌĆōpreoperative score)├Ś100 [24]. JOA scores were missing in nine and eight patients with CSM and C-OPLL, respectively, 2 years after laminoplasty, and thus were excluded from clinical outcome data analysis.
The surgical procedure for multiple-segment laminoplasty was as follows. The multifidus and semispinalis muscles were detached from both sides of the spinous processes, thereby exposing the laminae from the cranial C3 (or 4) to the caudal C6 (or 7). The semispinalis cervicis muscle was preserved as much as possible during surgery, while a minimal detachment of the semispinalis cervicis from the inferior border of the C2 spinous process base was necessary to secure the surgical field in certain cases where C3 laminoplasty was performed. The spinous process at C3 (or C4) to C6 (or C7) was removed. Bilateral gutters were made at the medial border of the facet joint using a high-speed air-burr drill, a hole was drilled on the left lamina, and the left side lamina was opened. The spinous process or the hydroxyapatite spacers were used to keep the laminae open. Spinous processes were used instead of hydroxyapatite spacers in some cases, depending on the surgeonŌĆÖs preference. Small bone chips made from the spinous processes were placed on the hinged side. Inferior lamina at C2 or superior lamina at C7 were fenestrated for patients who had stenosis to the C2ŌĆō3 or C6ŌĆō7 levels, respectively.
JMP ver. 15.00 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used for all statistical analyses. Unpaired t-test, paired t-test, chi-square tests, or Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to examine the demographic, radiographic parameters, and clinical outcomes between CSM and C-OPLL. The Pearson correlation coefficients were used to assess correlations between dependent variables (decrease in CL) and independent variables (neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle, C2ŌĆōC7 SVA, T1S, DER, and ROM). Stepwise multivariate linear regression was performed with a forward stepwise procedure, removing terms with p-values of Ōēź0.2, to identify the preoperative risk factors of radiographic parameters for decreased CL between patients with CSM and C-OPLL. All p-values of <0.05 were considered significant.
Table 1 shows the demographics of 89 patients. Data from 50 patients with CSM and 39 patients with C-OPLL were analyzed. No significant differences were found in age, sex, the number of operative segments, and the proportion of cases with removed C7 spinous processes. Table 2 shows the radiographic parameters and clinical outcomes. No significant differences were found in preoperative neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle, C2ŌĆō7 SVA, or T1S between patients with CSM and C-OPLL. The DER (p=0.006) and ROM (p=0.002) in patients with C-OPLL were significantly lower than those in patients with CSM. The mean preoperative neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle was 15.3┬░┬▒9.5┬░ in patients with CSM and 12.0┬░┬▒6.6┬░ in patients with C-OPLL, with no significant differences between the patients (p=0.062). The mean 2-year postoperative neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle was 11.4┬░┬▒13.3┬░ in patients with CSM and 5.4┬░┬▒13.2┬░ in patients with C-OPLL. The 2-year postoperative neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle in patients with C-OPLL was significantly lower than that in patients with CSM (p=0.036). The mean decreased CL was 3.9┬░┬▒9.6┬░ in patients with CSM and 6.5┬░┬▒9.7┬░ in patients with C-OPLL, with no significant differences between the patients (p=0.195). Preoperative and 2-year postoperative JOA score and the recovery rate of the JOA score revealed no statistically significant difference between patients with CSM and C-OPLL. The JOA score significantly improved after laminoplasty in patients with both CSM and C-OPLL (p<0.001). Table 3 summarizes the Pearson correlation coefficients. C2ŌĆō7 SVA (r=0.334, p=0.018) had a weak positive correlation and DER (r=ŌłÆ0.436, p=0.002) had a moderate negative correlation with decreased CL in patients with CSM. C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (r=ŌłÆ0.398, p=0.012) has a weak negative correlation and C2ŌĆō7 SVA (r=0.352, p=0.028) has a weak positive correlation with decreased CL in patients with C-OPLL. Multivariate linear regression for the risk factors for decreased CL in patients with CSM or C-OPLL is shown in Tables 4 and 5, respectively. Multivariate linear regression analysis revealed that greater C2ŌĆō7 SVA (B=0.22, p=0.026) and smaller DER (B=ŌłÆ0.53, p=0,002) in patients with CSM were significantly associated with a higher postoperatively decreased CL. By contrast, greater C2ŌĆō7 SVA (B=0.36, p=0.031) was significantly associated with higher postoperatively decreased CL in patients with C-OPLL. Figs. 2 and 3 show representative cases in patients with CSM or C-OPLL, respectively.
The present study compared the radiographic risk factors for decreased CL focusing on the difference between CSM and C-OPLL. Large C2ŌĆō7 SVA was associated with a postoperatively decreased CL both in patients with CSM and C-OPLL, but DER was associated with decreased CL only in patients with CSM. Risk factors for decreased CL after laminoplasty slightly differed depending on the CSM or C-OPLL etiology.
Our study revealed that C2ŌĆō7 SVA was associated with postoperatively decreased CL both in patients with CSM and C-OPLL. Cervical sagittal balance, which is assessed by the cervical SVA, has recently been identified as a significant factor in clinical outcomes after cervical surgery [25]. Additionally, cervical SVA has been reported as a risk factor for decreased CL. Zhang et al. [14] revealed that cervical alignment was compromised after laminoplasty in patients with CSM, and the degree of decreased CL was associated with preoperative C2ŌĆō7 SVA. Sakai et al. [26] identified the center of gravity of the head-C7 SVA and advanced age as preoperative risk factors for postoperative kyphotic deformity after laminoplasty in patients with CSM and recommended that enhancing muscle strength of cervical extension muscles is necessary to maintain CL. Patients with drop head syndrome have an increased offset of the gravity axis of the head from the trunk, which may result in an increase of 10 pounds of stress on neck extensors for every 2.54 cm (1 inch) that the head slips forward [27]. Invasion in the PMLC in laminoplasty may lead to decreased CL because C2ŌĆō7 SVA increases and the head and neck tilt forward, which increases the muscle strength required to maintain lordosis. Our present study revealed that the preoperative C2ŌĆō7 SVA was positively associated with decreased CL after laminoplasty in patients with CSM as it was in previous reports, and C2ŌĆō7 SVA has a positive association with decreased CL in patients with C-OPLL. Therefore, a large cervical SVA is considered a risk factor for decreased CL after laminoplasty both in patients with CSM and C-OPLL.
DER was acknowledged as a risk factor for decreased CL only in patients with CSM in the present study. The difference between the position with neck extension and the neutral position can be regarded as the contraction reserve of PMLC during dynamic movement of the cervical spine [8]. Lee et al. [7]. reported that DER had a clear negative correlation with decreased CL after laminoplasty, and postoperative kyphosis deformity did not occur in patients with >14┬░ of extension ability. DER can be restricted by a bony structure, such as a facet joint and the spinous process, although DER was reported as a reliable parameter for predicting significant angular kyphosis deformity. Jeon et al. [20] investigated preoperative radiological parameters predicting kyphosis deformity after laminoplasty between patients with CSM or C-OPLL and revealed that the DER had an association with decreased CL after laminoplasty in patients with CSM, but DER did not have a clear association with decreased CL in patients with C-OPLL. The present study revealed that DER was associated with postoperatively decreased CL in patients with CSM, but was not associated with decreased CL in patients with C-OPLL. The risk factors for kyphosis deformity have differed between CSM and C-OPLL, because of a less flexible spine in patients with multiple OPLL [19]. The present study revealed significantly lower ROM in patients with C-OPLL than those with CSM, and extension may be restricted due to the inflexibility of the spine. This suggests that DER predicts the contraction reserve of PMLC in patients with CSM, whereas DER is restricted in patients with cervical OPLL due to poor spinal flexibility and does not reflect the contraction reserve of PMLC.
T1S has been identified as an important risk factor for kyphotic alignment change after laminoplasty both in patients with CSM and C-OPLL [9,15,28,29]. A greater effort by the PMLC may be required to maintain a horizontal gaze in patients with a large T1S to maintain the lordosis of the cervical spine. Patients with a large T1S are at increased risk of kyphosis alignment change due to posterior structural damage after laminoplasty. By contrast, studies are reporting no significant association between a large T1S and decreased CL after laminoplasty [7,28]. Therefore, the role of T1S as a predictor of postoperative kyphosis remains unclear. Preoperative T1S was not associated with decreased CL following laminoplasty in our analysis both in patients with CSM and C-OPLL.
We acknowledge several limitations in the present study. First, this was a retrospective study and did not investigate clinical measurements of neck pain such as the visual analog scale or the neck disability index. Second, a whole sagittal radiograph was not performed and the relationship between the decreased CL after laminoplasty and thoracolumbar or spine-pelvic parameters could not be investigated. However, this study demonstrated different risk factors for decreased CL after laminoplasty in patients with CSM and C-OPLL. Our study is valuable for understanding the risk factors for decreased CL after laminoplasty in different conditions between patients with CSM and C-OPLL.
C2ŌĆō7 SVA is associated with postoperatively decreases CL both in patients with CSM and C-OPLL, but DER was only associated with patients with CSM. Risk factors for decreased CL after laminoplasty slightly differed depending on CSM or C-OPLL etiology. This suggests that DER predicts the contraction reserve of PMLC in patients with CSM, whereas DER is restricted in patients with cervical OPLL due to poor spinal flexibility and does not reflect the contraction reserve of PMLC.
Notes
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: SM; methodology: TI, SM; validation: TI, SM; formal analysis: TI; investigation: TI; project administration: SM, TF, SO; writingŌĆōoriginal draft: TI; writingŌĆōreview & editing: SM, TF, SO, AY, MM, YS, YN, JM, YS, KI, SO, YE; supervision: TF, SO; and final approval of the manuscript: all authors.
Fig.┬Ā1
Measurement of parameters in cervical spine lateral radiographs, including neutral (A), extension (B), and flexion radiographs (C). ╬▒: neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (A), double-headed arrow: C2ŌĆō7 sagittal vertical axis (A), ╬▓: T1 slope (A). ╬│: extension C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (B). ╬┤: flexion C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (C). Dynamic extension reserve was defined as ╬│ŌĆō╬▒. Range of motion was defined ╬│ŌĆō╬┤.
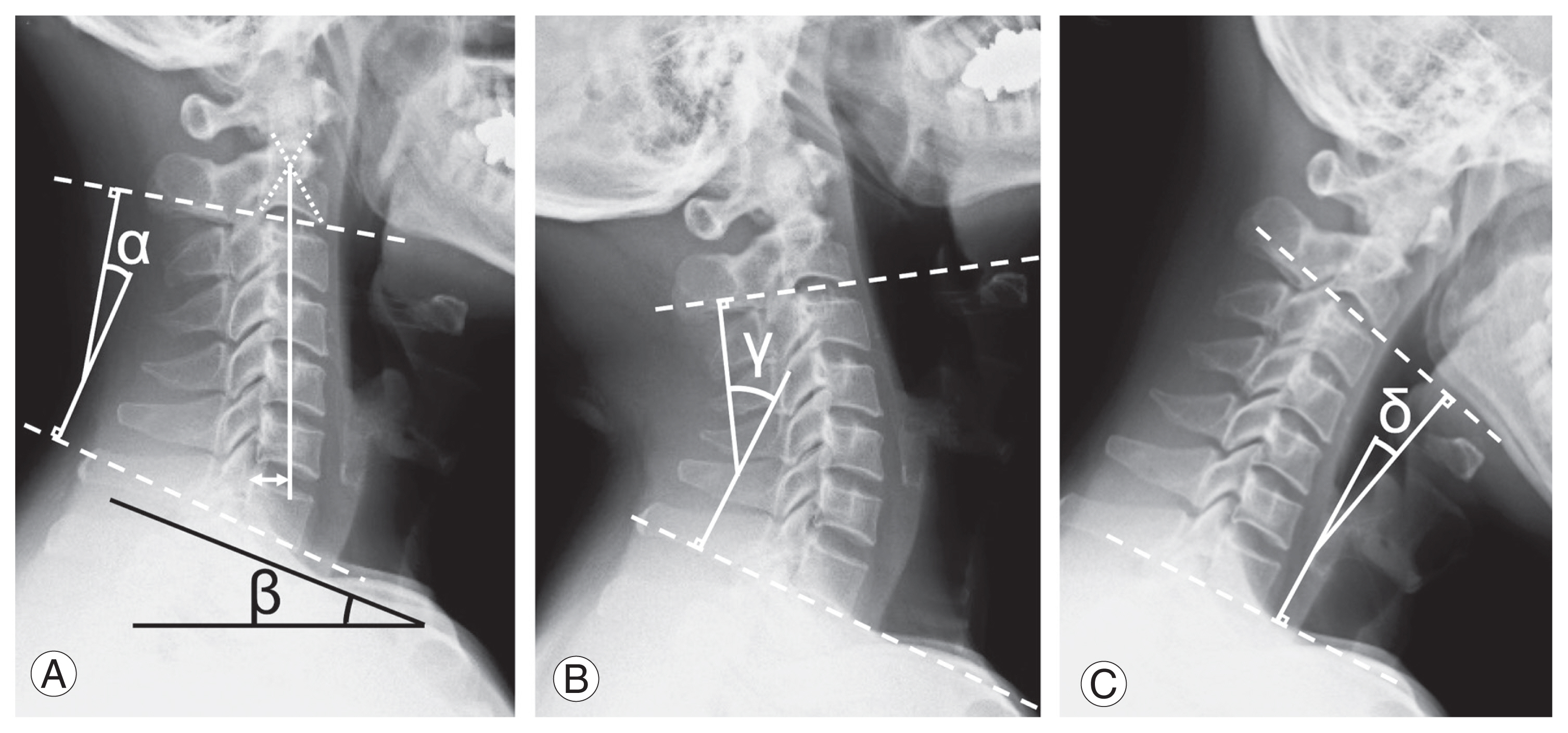
Fig.┬Ā2
An 81-year-old man with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Preoperative lateral neutral (A) and extension (B) and flexion (C) radiographs demonstrated that neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle was 2.4┬░, C2ŌĆō7 sagittal vertical axis was 37 mm, T1 slope was 23.4┬░, dynamic extension reserve was 6.0┬░, and range of motion was 27.9┬░. After a 2-year follow-up of laminoplasty at the C3ŌĆōC6 level, the neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle changed ŌłÆ19.5┬░. Decrease in cervical lordosis was 21.9┬░ (D).
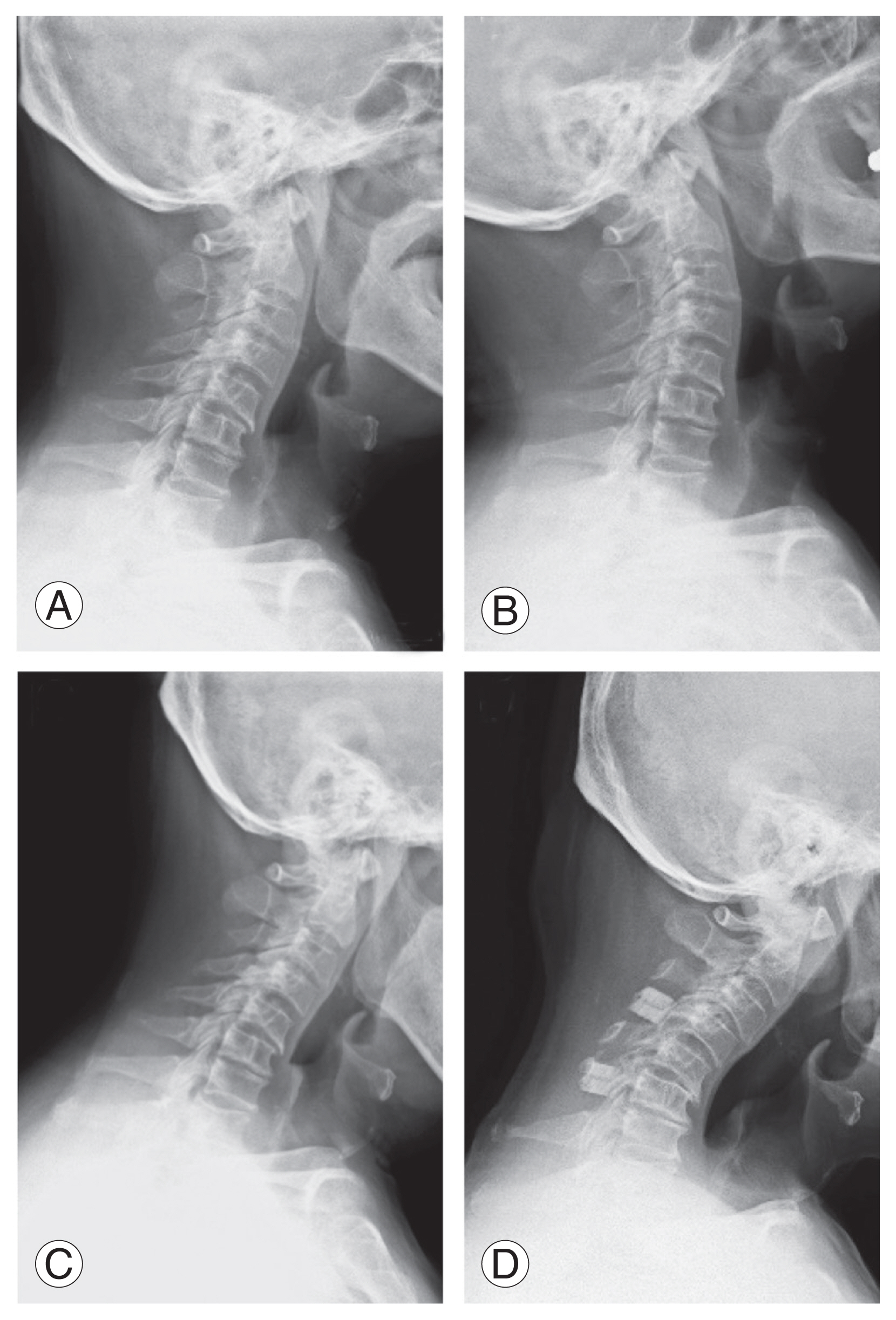
Fig.┬Ā3
An 81-year-old man with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL). OPLL type was continuous. Preoperative lateral neutral (A) and extension (B) and flexion (C) radiographs demonstrated that neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle was 8.0┬░, C2ŌĆō7 sagittal vertical axis was 42 mm, T1 slope was 23.4┬░, dynamic extension reserve was 5.0┬░, and range of motion was 23.2┬░. After a 2-year follow-up of laminoplasty at the C3ŌĆōC6 levels, the neutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle changed ŌłÆ9.0┬░. Decrease in cervical lordosis was 17.0┬░ (D).

Table┬Ā1
Demographic data in patients with CSM and C-OPLL
Table┬Ā2
Radiographic parameters and clinical outcomes in CSM and C-OPLL
| Variable | CSM | C-OPLL | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiographic parameters | |||
| ŌĆāNo. of patients | 50 | 39 | |
| ŌĆāPreoperative | |||
| ŌĆāŌĆāNeutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (┬░) | 15.3┬▒9.5 | 12.0┬▒6.6 | 0.062 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāC2ŌĆō7 SVA (┬░) | 24.9┬▒12.5 | 27.1┬▒12.8 | 0.423 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāT1 slope (┬░) | 25.6┬▒8.3 | 25.2┬▒7.7 | 0.778 |
| ŌĆāŌĆāDynamic extension reserve (┬░) | 11.9┬▒7.2 | 8.1┬▒5.0 | 0.006* |
| ŌĆāŌĆāROM (┬░) | 34.0┬▒12.2 | 26.5┬▒8.4 | 0.002* |
| ŌĆā2-Year postoperative | |||
| ŌĆāŌĆāNeutral C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (┬░) | 11.4┬▒13.3 | 5.4┬▒13.2 | 0.036* |
| ŌĆāDecrease in cervical lordosis (┬░) | 3.9┬▒9.6 | 6.5┬▒9.7 | 0.195 |
| Clinical outcomes | |||
| ŌĆāNo. of patients | 41 | 31 | |
| ŌĆāJOA score (points) | |||
| ŌĆāŌĆāPreoperative | 8.6 (4 to 14) | 9.5 (3 to 14) | 0.182 |
| ŌĆāŌĆā2-Year postoperative | 12.8 (6 to 16.5) | 13.2 (5.5 to 17) | 0.615 |
| ŌĆāThe recovery rate of the JOA score (%) | 47.3 (ŌłÆ30.8 to 95.8) | 46.0 (ŌłÆ27.8 to 100) | 0.996 |
| ŌĆāp-value preoperative/2-year postoperative | <0.001* | <0.001* | |
Values are presented as number, mean┬▒standard deviation, or mean (range). Only patients for whom data were available preoperative and 2-year postoperative were included in the clinical outcomes data analysis. p-values represent differences between CSM and C-OPLL.
Table┬Ā3
Correlation analysis of relationships between postoperative decrease in cervical lordosis and risk factors in patients with CSM and C-OPLL
| Variable | CSM | C-OPLL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| r | p-value | 95% CI | r | p-value | 95% CI | |
| C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (┬░) | 0.030 | 0.838 | ŌłÆ0.029 to 0.306 | ŌłÆ0.398 | 0.012* | ŌłÆ0.634 to ŌłÆ0.094 |
|
|
||||||
| C2ŌĆō7 SVA (┬░) | 0.334 | 0.018* | 0.062 to 0.561 | 0.352 | 0.028* | 0.042 to 0.601 |
|
|
||||||
| T1 slope (┬░) | 0.227 | 0.113 | ŌłÆ0.056 to 0.475 | ŌłÆ0.129 | 0.439 | ŌłÆ0.431 to 0.199 |
|
|
||||||
| Dynamic extension reserve (┬░) | ŌłÆ0.436 | 0.002* | ŌłÆ0.637 to ŌłÆ0.180 | ŌłÆ0.158 | 0.335 | ŌłÆ0.451 to 0.165 |
|
|
||||||
| ROM (┬░) | ŌłÆ0.180 | 0.211 | ŌłÆ0.437 to 0.103 | ŌłÆ0.313 | 0.052 | ŌłÆ0.572 to 0.002 |
Table┬Ā4
Multivariate linear regression analysis of relationships between decrease in cervical lordosis and preoperative radiographic parameters in CSM
| Variable | Unstandardized coefficients | Standardized coefficients | t-value | p-value | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| B | SE | ╬▓ | ||||
| C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (┬░) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
|
|
||||||
| C2ŌĆō7 SVA (┬░) | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.29 | 2.30 | 0.026* | 0.027 to 0.288 |
|
|
||||||
| T1 slope (┬░) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
|
|
||||||
| Dynamic extension reserve (┬░) | ŌłÆ0.53 | 0.10 | ŌłÆ0.40 | ŌłÆ3.22 | 0.002* | ŌłÆ0.865 to ŌłÆ0.199 |
|
|
||||||
| ROM (┬░) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Table┬Ā5
Multivariate linear regression analysis of relationships between decrease in cervical lordosis and preoperative radiographic parameters in C-OPLL
| Variable | Unstandardized coefficients | Standardized coefficients | t-value | p-value | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| B | SE | ╬▓ | ||||
| C2ŌĆō7 Cobb angle (┬░) | ŌłÆ0.22 | 0.30 | ŌłÆ0.48 | ŌłÆ0.72 | 0.476 | ŌłÆ0.822 to 0.392 |
|
|
||||||
| C2ŌĆō7 SVA (┬░) | 0.36 | 0.16 | 0.29 | 2.25 | 0.031* | 0.034 to 0.677 |
|
|
||||||
| T1 slope (┬░) | ŌłÆ0.40 | 0.29 | ŌłÆ0.32 | ŌłÆ1.37 | 0.180 | ŌłÆ0.986 to 0.192 |
|
|
||||||
| Dynamic extension reserve (┬░) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
|
|
||||||
| ROM (┬░) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
References
1. Bajamal AH, Kim SH, Arifianto MR, et al. Posterior surgical techniques for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: WFNS Spine Committee recommendations. Neurospine 2019;16:421ŌĆō34.




2. Shimokawa N, Sato H, Matsumoto H, Takami T. Review of radiological parameters, imaging characteristics, and their effect on optimal treatment approaches and surgical outcomes for cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Neurospine 2019;16:506ŌĆō16.




3. Head J, Rymarczuk G, Stricsek G, et al. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: surgical approaches and associated complications. Neurospine 2019;16:517ŌĆō29.




4. Woods BI, Hohl J, Lee J, Donaldson W 3rd, Kang J. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2011;469:688ŌĆō95.



5. Redaelli A, Pun A, Berjano P,Sagittal alignment of the cervical spine. Itshayek E, editors. Nontraumatic cervical myelopathy: pathologies, surgical techniques, and nuances. New York (NY): Nova Science Publishers; 2020. p.93ŌĆō108.
6. Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Nakanisi K. Analysis of the cervical spine alignment following laminoplasty and laminectomy. Spinal Cord 1999;37:20ŌĆō4.



7. Lee SH, Son DW, Lee JS, Sung SK, Lee SW, Song GS. Does extension dysfunction affect postoperative loss of cervical lordosis in patients who undergo laminoplasty? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2019;44:E456ŌĆō64.


8. Sharma R, Borkar S, Katiyar V, et al. Interplay of dynamic extension reserve and T1 slope in determining the loss of cervical lordosis following laminoplasty: a novel classification system. World Neurosurg 2020;136:e33ŌĆō40.


9. Kim B, Yoon DH, Ha Y, et al. Relationship between T1 slope and loss of lordosis after laminoplasty in patients with cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine J 2016;16:219ŌĆō25.


10. Hirai T, Kawabata S, Enomoto M, et al. Presence of anterior compression of the spinal cord after laminoplasty inhibits upper extremity motor recovery in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37:377ŌĆō84.


11. Sodeyama T, Goto S, Mochizuki M, Takahashi J, Moriya H. Effect of decompression enlargement laminoplasty for posterior shifting of the spinal cord. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1999;24:1527ŌĆō32.


13. Lee SH, Son DW, Lee JS, et al. Differences in cervical sagittal alignment changes in patients undergoing laminoplasty and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Neurospine 2018;15:91ŌĆō100.




14. Zhang JT, Li JQ, Niu RJ, Liu Z, Tong T, Shen Y. Predictors of cervical lordosis loss after laminoplasty in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur Spine J 2017;26:1205ŌĆō10.



15. Kim TH, Lee SY, Kim YC, Park MS, Kim SW. T1 slope as a predictor of kyphotic alignment change after laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:E992ŌĆō7.


16. Miyazaki M, Ishihara T, Notani N, Kanezaki S, Tsumura H. Relationship of T1 slope with loss of lordosis and surgical outcomes after laminoplasty for cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2018;164:19ŌĆō24.


17. Nolan JP Jr, Sherk HH. Biomechanical evaluation of the extensor musculature of the cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1988;13:9ŌĆō11.


18. Machino M, Yukawa Y, Hida T, et al. Cervical alignment and range of motion after laminoplasty: radiographical data from more than 500 cases with cervical spondylotic myelopathy and a review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37:E1243ŌĆō50.

19. Matsuoka Y, Endo K, Nishimura H, et al. Cervical kyphotic deformity after laminoplasty in patients with cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament with normal sagittal spinal alignment. Spine Surg Relat Res 2018;2:210ŌĆō4.



20. Jeon H, Kim HC, Kim TW, et al. Prediction of angular kyphosis after cervical laminoplasty using radiologic measurements. J Clin Neurosci 2021;85:13ŌĆō9.


21. Fujiyoshi T, Yamazaki M, Kawabe J, et al. A new concept for making decisions regarding the surgical approach for cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: the K-line. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:E990ŌĆō3.

22. Furuya T, Maki S, Miyamoto T, et al. Mid-term surgical outcome of posterior decompression with instrumented fusion in patients with K-line (ŌłÆ) type cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament with a 5-year minimum follow-up. Clin Spine Surg 2020;33:333ŌĆō8.


23. Koda M, Mochizuki M, Konishi H, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes between laminoplasty, posterior decompression with instrumented fusion, and anterior decompression with fusion for K-line (ŌłÆ) cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Eur Spine J 2016;25:2294ŌĆō301.



24. Hirabayashi K, Miyakawa J, Satomi K, Maruyama T, Wakano K. Operative results and postoperative progression of ossification among patients with ossification of cervical posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1981;6:354ŌĆō64.


25. Tang JA, Scheer JK, Smith JS, et al. The impact of standing regional cervical sagittal alignment on outcomes in posterior cervical fusion surgery. Neurosurgery 2012;71:662ŌĆō9.



26. Sakai K, Yoshii T, Hirai T, et al. Cervical sagittal imbalance is a predictor of kyphotic deformity after laminoplasty in cervical spondylotic myelopathy patients without preoperative kyphotic alignment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016;41:299ŌĆō305.









