 |
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 16(6); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Lumbar interbody fusion (LIF) is an excellent treatment option for a number of lumbar diseases. LIF can be performed through posterior, transforaminal, anterior, and lateral or oblique approaches. Each technique has its own pearls and pitfalls. Through LIF, segmental stabilization, neural decompression, and deformity correction can be achieved. Minimally invasive surgery has recently gained popularity and each LIF procedure can be performed using minimally invasive techniques to reduce surgery-related complications and improve early postoperative recovery. Despite advances in surgical technology, surgery-related complications after LIF, such as pseudoarthrosis, have not yet been overcome. Although autogenous iliac crest bone graft is the gold standard for spinal fusion, other bone substitutes are available to enhance fusion rate and reduce complications associated with bone harvest. This article reviews the surgical procedures and characteristics of each LIF and the osteobiologics utilized in LIF based on the available evidence.
Lumbar spinal disorders are among the most prevalent musculoskeletal disorders. Lumbar interbody fusion (LIF) is a treatment option that restores the intervertebral height, decompresses the spinal canal, stabilizes the instability, and resolves lordosis resulting from various lumbar pathologies [1]. It was introduced to overcome the low fusion rates seen after posterolateral fusion (PLF). Traditionally, LIF procedures were usually performed using anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) and posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) [1-3]. Recently, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), lateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF), and oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) gained popularity over ALIF or PLIF because these procedures can be conducted using minimally invasive techniques to reduce surgery-related complications and improve early postoperative recovery [4-6]. To date, there is no clear high-level evidence on which of the approaches is clinically the best [7,8].
Lumbar fusion surgeries have increased over the past few decades owing to improvements in surgical technique and implants [9]. Despite these advances in surgical technology, pseudoarthrosis after LIF has not yet been overcome. Recent studies showed that nonunion rates after LIF still ranged from 5.5% to 20% [10,11]. Traditionally, autogenous iliac crest bone graft (ICBG) has been accepted as the “gold standard,” but harvesting of ICBG is restricted by donor site morbidities. Currently, several alternatives to ICBG are in use to enhance bony fusion.
This review presents the surgical technique of each LIF and provides their specific advantages, disadvantages, and indications/contraindications. In addition, the current options of osteobiologics for spinal fusion are reviewed.
PLIF was first recorded in 1944 [2], and Cloward [12] developed this procedure in the 1950s. PLIF is a traditional posterior approach and the most common lumbar approach. It allows access to the posterior and anterior columns in a single incision, and it allows for bilateral decompression with excellent visualization of neural structures [13,14]. This approach allows wide posterior visualization and circumferential decompression of nerve elements. Since the spine is already exposed for decompression, no separate incision is required. Accepted indications for PLIF include symptomatic spinal stenosis, segmental instability, spondylolisthesis, pseudoarthrosis, and recurrent disc herniation (Fig. 1) [15,16]. However, PLIF has its drawbacks. PLIF inevitably causes paravertebral muscle damage due to surgical access and prolonged muscle contraction [17]. PLIF also requires more retraction of the neural elements to access the intervertebral space [18-21]. Epidural bleeding and epidural fibrosis are inevitable, and sometimes neurological impairment occurs as a result. Additionally, retraction of the dura may entail an increased risk of durotomy, particularly during revision surgery [22]. Therefore, relative contraindications for PLIF surgery include extensive epidural scarring, arachnoiditis, and active infection [15]. The PLIF procedure consists of adequate laminectomy, medial facetectomy, annulotomy, discectomy, and insertion of cages or strut bone graft.
TLIF was popularized by Harms and Rolinger as an alternative to PLIF [4,5]. The idea behind TLIF is to access the intervertebral disc space from a more lateral trajectory compared to PLIF [23]. Resection of the superior and inferior facets at the intended level of fusion is required to access the intervertebral disc [24]. Subsequent steps including discectomy, endplate preparation, and cage insertion are similar to PLIF; however, the major advantage of TLIF over PLIF is that it provides lateral access to the disc, reducing retraction of nerve elements. Therefore, TLIF may be associated with a decreased risk of incidental dural tear and neural complications when compared with PLIF [25]. TLIF can also be safely performed in the upper lumbar segment. TLIF may be a good option in revision cases because a lateral approach avoids the postoperative scar tissue of a posterior approach [26-28]. Also, TLIF preserves the interlaminar surface and facet joint on the contralateral side, allowing them to be used as an additional surface area for fusion. Compared to PLIF, TLIF can maintain biomechanical stability due to less damage to the posterior ligament complex. TLIF appears to have similar results to PLIF in biomechanical studies [29,30].
Since Foley et al. [31,32] introduced TLIF using minimally invasive surgery (MIS) to reduce approach-related complications, the MIS technique has gained popularity as it has led to better outcomes due to reduced blood loss and muscle damage, shorter operation time, and earlier recovery after surgery compared to the conventional open technique (Fig. 2) [25,33-39]. Patient selection for TLIF is similar to that for PLIF. Indications for TLIF include spinal stenosis, segmental instability, spondylolisthesis, pseudoarthrosis, and recurrent disc herniation. Contraindications are arachnoiditis, epidural scarring, active infection, and severe osteoporosis. Furthermore, conjoined nerve roots are a relative contraindication as they may preclude access to the intervertebral disc.
Recently, endoscopic LIF has been attempted [40], and the basic principles of endoscopic LIF are the same as TLIF [41]. TLIF can be conducted using biportal endoscopic systems with two channels: one working and one endoscopic channel. The next step is similar to TLIF in that discectomy and endplate preparation are conducted through the endoscopic system. Although evidence of the pros and cons relating to surgical outcomes and complications is still lacking, published studies have shown promising postoperative outcomes [42-44]. There are, however, unavoidable obstacles such as a learning curve to overcome [42,45-47].
ALIF allows a less traumatic approach compared to the posterior approach, resulting in less pain and a shorter hospital stay [48-50]. The direct visualization of the intervertebral disc allows complete discectomy for a larger interbody cage. Large interbody devices offer significant biomechanical advantages over other LIFs [51]. Placing more lordotic cages in the lower lumbar spine may increase the chances of achieving sagittal alignment [52-56]. Also, ALIF can yield higher fusion rates and preserve the posterior structures, including back muscles and ligaments [57,58].
The anterior approach is an excellent approach for the L5–S1 level. A thorough preoperative evaluation is required before considering ALIF. A careful review of the vascular structures along with the lumbar spine by preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and/or computed tomography scan is recommended to assess the region of interest (Fig. 3) [59-61]. Generally, the retroperitoneal approach is preferred, because transperitoneal access is associated with high rates of ileus, internal organ injury, and retrograde ejaculation and is restricted in the L5–S1 segment. Because the vena cava is more vulnerable than the aorta, the usual access is from the patient’s left side. By careful examination with gentle finger dissection, the arcuate line and the transverse fascia are seen and separated from the abdominal wall. After the transverse fascia is incised, all the peritoneal components are swept anteriorly to access the retroperitoneal space through a gentle dissection. The reference points are usually the round psoas muscle and the left common iliac artery. The next landmark is the sacral promontory. The superior hypogastric plexus exits in front of the L5–S1 disc and can be damaged by unipolar electrocautery, resulting in autonomic dysfunction. Injury to the superior hypogastric plexus may develop, leading to a high rate of retrograde ejaculation in men (up to 45%) [62-64]. There is a risk of damage to the abdominal organs and ureters, and postoperative hernias may occur [65]. Large vessel manipulation may result in deep vein thrombosis and/or direct injury [65]. Surgical indications for ALIF include sagittal plane deformities, degenerative disc disease, pseudarthrosis, and postoperative spondylodiscitis. Contraindications include severe obesity, previous abdominal surgery or radiation therapy, and severe aortic disease.
First described by Ozgur et al. [66] in 2006, LLIF is considered a safe and effective alternative to ALIF or PLIF. LLIF can minimize approach-related morbidity such as soft tissue damage, blood loss, and length of hospital stay, with better clinical and radiological results compared to a traditional open approach [67-69]. LLIF begins with the patient in either a left or right lateral decubitus position. After a lateral incision is made, the abdominal muscles are bluntly dissected. After reaching the retroperitoneum, care must be taken not to injure important nerves, including the intercostal nerve, the subiliac nerve, the iliac inguinal nerve, and the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Intraoperative nerve monitoring is helpful in preventing damage to the lumbar plexus within the psoas [70]. After the placement of sequential dilators and a tubular retractor on the psoas muscle, a classic discectomy and cage insertion are performed with fluoroscopy.
Indications for LLIF include degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, and scoliosis. LLIF is especially effective in revision cases where there is adjacent segment pathology or postlaminectomy syndrome [71,72]. Correction of sagittal as well as coronal deformities can be achieved using lordotic and big cages [72-76]. Furthermore, LLIF has been demonstrated to restore foraminal height and central canal surface through indirect decompression [76-79]. However, LLIF has disadvantages, including damage to the psoas, internal organs, or lumbar plexus [72,80]. Postoperative groin or thigh pain, hip flexion weakness, and paresthesia may also occur on the approach side [72,80]. Contraindications are adhesive retroperitoneal situations that inhibit safe access, including a history of previous retroperitoneal surgery, infection, or radiation therapy. This approach is contraindicated on L5–S1 discs because the iliac wing obstructs the true lateral accessibility.
OLIF, also called anterior-to-psoas or prepsoas, had been developed to overcome LLIF’s limitations. Access to discs between the psoas muscle and the major abdominal vessels reduces the risk of injury to the muscles and lumbar plexus (Fig. 4). Thus, postoperative groin or thigh pain can be avoided and neuromonitoring is not required [81]. Meta-analysis found that the risk of anterior thigh pain, ipsilateral hip flexor weakness, and lumbar plexus injury were decreased with OLIF compared to LLIF [80,82,83]. However, the risk of large vessel damage may increase due to its proximity [80,83]. Another disadvantage of OLIF is the risk of sympathetic damage due to the presence of the sympathetic chain in the working window [80,83].
Indications and contraindications of OLIF are the same as for LLIF. The L5–S1 space cannot be accessed by LLIF, but OLIF can target L5–S1; however, access above L2–L3 using OLIF is difficult due to the ribs. The surgeon’s view is much more advantageous in OLIF; while LLIF only allows the surgeon to see the surgical field vertically. Typical indications for OLIF include degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, discitis, and pseudarthrosis from L2–L3 to L5–S1. Contraindications include a history of previous retroperitoneal surgery, radiation therapy, or infection. The surgical procedure is similar to LLIF. A skin incision is made around the anterior edge of the disc. After the placement of sequential dilators and a tubular retractor in the bare area between the aorta and the psoas muscle, a classic discectomy and cage insertion are performed with the orthogonal maneuver.
Autogenous and allogeneic bone grafts can be used for spinal fusion, but autogenous ICBG is considered the gold standard due to its osteogenic, osteoinductive, and osteoconductive properties.
Autograft is the gold standard, but has limitations, as the amount of bone obtained through decompression is limited and additional incisions for ICBG harvesting due to donor site morbidity increase complications such as donor site pain, increased blood loss, and increased operation time [84-86]. These drawbacks have created a need to reduce the use of ICBG and find alternative sources of graft material. Consequently, the use of ICBG has declined consistently and efforts have been made to find cost-effective alternatives to ICBG. Osteobiologics are bone substitutes that promote bone healing and are increasingly being used in spinal surgery. The use of osteobiologics is believed to reduce complications and improve fusion rates [87]. Currently, common options for osteobiologics include allografts, bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), and stem cell-based therapy. In this review, we will briefly discuss the properties, efficacy, and future applications of various osteobiologics.
Allograft bone is sourced from cadavers and is readily available. Generally, an allograft can act as an osteoconductive and weakly osteoinductive scaffold; however, it has no osteogenic potential because it has no viable cells. Nevertheless, previous studies have shown that allograft is a reasonable alternative to autograft. A recent systematic review by Liao et al. [88] showed that fusion rates between allograft and autograft in patients who underwent lumbar fusion were not significantly different. Although several studies have demonstrated similar fusion rates between the two, a randomized clinical trial (RCT) found autograft showed a relatively shorter time to complete fusion [89]. Gao et al. [90] reported that allograft alone yielded a lower fusion rate compared to allograft with autogenous bone marrow and allograft with BMP in their LLIF series. The use of allografts to supplement local autogenous bone can produce similar results to ICBG. For this reason, allografts generally act as autograft extenders rather than alone in posterior spinal fusion.
Demineralized bone matrices (DBMs) are acid-extractive allogeneic bone grafts, leaving behind the organic matrix of type 1 collagen, non-collagenous proteins, and growth factors. DBMs are commercially available in various forms, from putty or paste to injectable gel. They are less osteoconductive and non-osteogenic than mineralized allografts but retain more osteoinductivity and are also used as autograft extenders. In an RCT by Kang et al. [91], fusion rates at 2-year follow-up were 92% and 86% for autograft and DBM, respectively. Kim et al. [92] reported fusion rates using autograft and DBM were 62.2% and 52% at the second year, respectively. However, previous studies supported that fusion rate with DBM increased when supplemented with autografts [93,94]. DBM is a reasonable substitute as an autograft extender in spinal fusion, but there is currently little or no evidence that DBM is a good stand-alone osteobiologic.
BMPs, first isolated by Urist [95] in 1965, are growth factors of the transforming growth factor-β family with osteogenic capabilities. So far, more than 20 subtypes of BMPs are known but BMP-2, BMP-4, and BMP-7 are the most studied. BMPs are widely used in various medical areas, and recombinant human BMP-2 (rhBMP-2) is the one most widely used for spinal fusion. Since the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of ALIF in 2002, improved fusion rates have been demonstrated in many studies [96,97]. Early RCTs even showed an increased fusion rate and decreased complications compared to ICBG [96,97]. Recently, the off-label use of rhBMP-2 has widely expanded into posterior lumbar fusion and cervical fusion, as well as ALIF. Numerus studies have shown successful fusion rates with rhBMP-2 in PLIF, TLIF, and PLF. In an RCT of 463 patients who underwent PLF, the rhBMP-2 group showed a significantly higher fusion rate at 2 years and a less reoperation rate compared to the ICBG group [98]. A systematic review found that fusion rates with rhBMP-2 use are statistically significantly improved in ALIF and PLF, but not in PLIF or TLIF [99]. However, the same authors also cautiously concluded that the results could be biased due to the heterogeneity of dosing and surgical procedures.
Potentially serious adverse outcomes have been reported with rhBMP-2 use. In cervical fusion, serious complications such as airway edema and dysphagia have led to an FDA-issued warning [100,101]. Other concerns in lumbar fusion include retrograde ejaculation, seroma formation, radiculitis, ectopic ossification, and vertebral osteolysis [101]. Crandall et al. [102] in a 5-year follow-up of 509 TLIF patients with rhBMP-2, however, reported that BMP-related complication rates were rare (seroma in 0.4% and ectopic bone growth in 0.6%). Another critical concern is the possible association between rhBMP-2 and tumorigenesis [103], although insufficient conclusions were drawn on meta-analysis [104,105]. Further research is needed to find safe and effective doses of rhBMP-2.
The use of stem cells in tissue regeneration is rapidly expanding and osteogenic stem cells are thought to have the potential to bring about bony fusion. Among various stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), which can differentiate into osteoprogenitor cells and osteoblasts, are the most likely candidate substitute for bone. Recent preclinical and clinical trials using MSC-based therapy for spinal fusion demonstrated that MSC could be a viable option for utilization in spinal fusion [106,107]. One study using autogenous MSC from the iliac crest reported a fusion rate of 95.1% when used together with porous tricalcium phosphate for posterior spinal fusion [108]. A recent RCT of 24 patients who underwent 1-to-3 lumbar posterior fusions compared the fusion rates between ICBG and allografts with bone marrow aspirates containing autogenous stem cells. This study showed no significant difference in the fusion rate between the two groups [109]. However, bone marrow aspirates yield only 0.001% to 0.01% MSC [110]. While stem cell use is promising in spinal fusion, there are still limitations to overcome.
LIF has already proven to be an excellent surgical technique for a variety of lumbar diseases. With the continuous development of surgical techniques and cage design, several LIF procedures are now available, and each has its own characteristics. The optimal surgical procedure and implant should be selected according to the anatomical, pathological, and surgical conditions. The most important surgical goal is bony fusion and avoidance of complications; however, successful fusion remains a major challenge to spinal surgeons. Future studies are needed to improve fusion rates and reduce adverse effects with the development of more effective osteogenic factors.
Notes
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: YHK, KYH, KWK; data curation: HYP, JK, SIK; formal analysis: YSK, JHS; methodology: YSK, KWR, JBP, JHS; project administration: YSK, YHK; writing–original draft: YHK, SIK; writing–review & editing: YYK, JSL, SJL; and final approval of the manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1.
A 61-year-old male patient underwent posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) for recurrent disc herniation at L4–L5. Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (A) and X-ray (B). (C) Postoperative X-ray shows placement of PLIF cages and pedicle screws/rods.
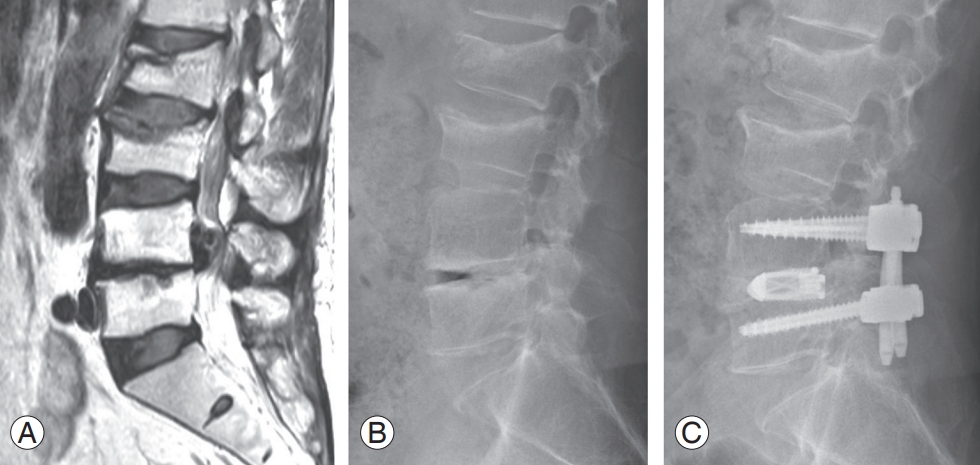
Fig. 2.
A 67-year-old female patient underwent minimally invasive surgery-transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis and right foraminal stenosis at L4–L5. Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (A) and X-ray (B). Postoperative MRI (C) and X-ray (D) show foraminal decompression and placement of cages and pedicle screws/rods.

Fig. 3.
Computed tomography angiography is helpful to assess vascular anatomy for anterior lumbar interbody fusion.

Fig. 4.
A 70-year-old female patient underwent minimally invasive surgery-oblique lumbar interbody fusion for foraminal stenosis at L3–L4 and L4–L5. (A) On preoperative magnetic resonance imaging, the bare window (red arrow) between the aorta and the psoas muscle should be confirmed. (B) Preoperative X-ray. (C) Postoperative X-ray shows restoration of disc heights and placement of cages and pedicle screws/rods.

References
1. de Kunder SL, Rijkers K, Caelers IJ, de Bie RA, Koehler PJ, van Santbrink H. Lumbar interbody fusion: a historical overview and a future perspective. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018;43:1161–8.

2. Briggs H, Milligan PR. Chip fusion of the low back following exploration of the spinal canal. J Bone Joint Surg 1944;26:125–30.
3. Steffee AD, Sitkowski DJ. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion and plates. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1988;227:99–102.


4. Oppenheimer JH, DeCastro I, McDonnell DE. Minimally invasive spine technology and minimally invasive spine surgery: a historical review. Neurosurg Focus 2009;27:E9.



5. Harms J, Rolinger H. A one-stager procedure in operative treatment of spondylolistheses: dorsal traction-reposition and anterior fusion. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 1982;120:343–7.


6. Eck JC, Hodges S, Humphreys SC. Minimally invasive lumbar spinal fusion. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2007;15:321–9.


7. Verma R, Virk S, Qureshi S. Interbody fusions in the lumbar spine: a review. HSS J 2020;16:162–7.




8. Lenz M, Mohamud K, Bredow J, Oikonomidis S, Eysel P, Scheyerer MJ. Comparison of different approaches in lumbosacral spinal fusion surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Spine J 2022;16:141–9.




9. Deyo RA, Mirza SK, Martin BI, Kreuter W, Goodman DC, Jarvik JG. Trends, major medical complications, and charges associated with surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis in older adults. JAMA 2010;303:1259–65.



10. Noshchenko A, Lindley EM, Burger EL, Cain CM, Patel VV. What is the clinical relevance of radiographic nonunion after single-level lumbar interbody arthrodesis in degenerative disc disease?: a meta-analysis of the YODA project database. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016;41:9–17.

11. Meng B, Bunch J, Burton D, Wang J. Lumbar interbody fusion: recent advances in surgical techniques and bone healing strategies. Eur Spine J 2021;30:22–33.



12. Cloward RB. The treatment of ruptured lumbar intervertebral discs by vertebral body fusion. I. Indications, operative technique, after care. J Neurosurg 1953;10:154–68.

13. Lestini WF, Fulghum JS, Whitehurst LA. Lumbar spinal fusion: advantages of posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Surg Technol Int 1994;3:577–90.

14. Kim KT, Lee SH, Lee YH, Bae SC, Suk KS. Clinical outcomes of 3 fusion methods through the posterior approach in the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:1351–8.


15. Mobbs RJ, Phan K, Malham G, Seex K, Rao PJ. Lumbar interbody fusion: techniques, indications and comparison of interbody fusion options including PLIF, TLIF, MI-TLIF, OLIF/ATP, LLIF and ALIF. J Spine Surg 2015;1:2–18.


16. DiPaola CP, Molinari RW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2008;16:130–9.


17. Fan SW, Hu ZJ, Fang XQ, Zhao FD, Huang Y, Yu HJ. Comparison of paraspinal muscle injury in one-level lumbar posterior inter-body fusion: modified minimally invasive and traditional open approaches. Orthop Surg 2010;2:194–200.



18. Okuda S, Miyauchi A, Oda T, Haku T, Yamamoto T, Iwasaki M. Surgical complications of posterior lumbar interbody fusion with total facetectomy in 251 patients. J Neurosurg Spine 2006;4:304–9.


19. Krishna M, Pollock RD, Bhatia C. Incidence, etiology, classification, and management of neuralgia after posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery in 226 patients. Spine J 2008;8:374–9.


20. Humphreys SC, Hodges SD, Patwardhan AG, Eck JC, Murphy RB, Covington LA. Comparison of posterior and transforaminal approaches to lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:567–71.


21. Zhang Q, Yuan Z, Zhou M, Liu H, Xu Y, Ren Y. A comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a literature review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2014;15:367.




22. Molinari RW, Gerlinger T. Functional outcomes of instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion in active-duty US servicemen: a comparison with nonoperative management. Spine J 2001;1:215–24.

23. Lee MJ, Mok J, Patel P. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: traditional open versus minimally invasive techniques. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2018;26:124–31.


24. Youn YH, Cho KJ, Na Y, Kim JS. Global sagittal alignment and clinical outcomes after 1-3 short-segment lumbar fusion in degenerative spinal diseases. Asian Spine J 2022;16:551–9.




25. de Kunder SL, van Kuijk SM, Rijkers K, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J 2017;17:1712–21.


26. AlShazli AB, Amer AY, Sultan AM, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the surgical management of post-discectomy syndrome. Asian Spine J 2020;14:148–56.




27. Hammad A, Wirries A, Ardeshiri A, Nikiforov O, Geiger F. Open versus minimally invasive TLIF: literature review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 2019;14:229.




28. Khechen B, Haws BE, Patel DV, et al. Comparison of postoperative outcomes between primary MIS TLIF and MIS TLIF with revision decompression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2019;44:150–6.


29. Xu H, Tang H, Guan X, et al. Biomechanical comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion by finite element analysis. Neurosurgery 2013;72(1 Suppl Operative): 21–6.



30. Sim HB, Murovic JA, Cho BY, Lim TJ, Park J. Biomechanical comparison of single-level posterior versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusions with bilateral pedicle screw fixation: segmental stability and the effects on adjacent motion segments. J Neurosurg Spine 2010;12:700–8.


31. Foley KT, Lefkowitz MA. Advances in minimally invasive spine surgery. Clin Neurosurg 2002;49:499–517.

32. Foley KT, Holly LT, Schwender JD. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003;28(15 Suppl): S26–35.


33. Champagne PO, Walsh C, Diabira J, et al. Sagittal balance correction following lumbar interbody fusion: a comparison of the three approaches. Asian Spine J 2019;13:450–8.




34. Kim CH, Easley K, Lee JS, et al. Comparison of minimally invasive versus open transforaminal interbody lumbar fusion. Global Spine J 2020;10(2 Suppl): 143S150S.




35. Terman SW, Yee TJ, Lau D, Khan AA, La Marca F, Park P. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: comparison of clinical outcomes among obese patients. J Neurosurg Spine 2014;20:644–52.


36. Wong AP, Smith ZA, Stadler JA, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MI-TLIF): surgical technique, long-term 4-year prospective outcomes, and complications compared with an open TLIF cohort. Neurosurg Clin N Am 2014;25:279–304.

37. Tian NF, Wu YS, Zhang XL, Xu HZ, Chi YL, Mao FM. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a meta-analysis based on the current evidence. Eur Spine J 2013;22:1741–9.




38. Vazan M, Gempt J, Meyer B, Buchmann N, Ryang YM. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a technical description and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2017;159:1137–46.



39. Patel MR, Jacob KC, Zamanian C, et al. Single-level anterior lumbar interbody fusion versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion at L5/S1 for an obese population. Asian Spine J 2022 Aug 23 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.31616/asj.2022.0071

40. Kim JE, Choi DJ, Park EJ, et al. Biportal endoscopic spinal surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Asian Spine J 2019;13:334–42.




41. Kapetanakis S, Gkantsinikoudis N, Thomaidis T, Charitoudis G, Theodosiadis P. The role of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic surgery in lateral recess stenosis in elderly patients. Asian Spine J 2019;13:638–47.




43. Heo DH, Son SK, Eum JH, Park CK. Fully endoscopic lumbar interbody fusion using a percutaneous unilateral biportal endoscopic technique: technical note and preliminary clinical results. Neurosurg Focus 2017;43:E8.



44. Lee SH, Erken HY, Bae J. Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic lumbar interbody fusion: clinical and radiological results of mean 46-month follow-up. Biomed Res Int 2017;2017:3731983.




45. Choi DJ, Choi CM, Jung JT, Lee SJ, Kim YS. Learning curve associated with complications in biportal endoscopic spinal surgery: challenges and strategies. Asian Spine J 2016;10:624–9.



46. Yang J, Guo C, Kong Q, et al. Learning curve and clinical outcomes of percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Int Orthop 2020;44:309–17.



47. Kolcun JP, Brusko GD, Basil GW, Epstein R, Wang MY. Endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion without general anesthesia: operative and clinical outcomes in 100 consecutive patients with a minimum 1-year follow-up. Neurosurg Focus 2019;46:E14.

48. Bassani R, Morselli C, Querenghi AM, Nuara A, Sconfienza LM, Peretti GM. Functional and radiological outcome of anterior retroperitoneal versus posterior transforaminal interbody fusion in the management of single-level lumbar degenerative disease. Neurosurg Focus 2020;49:E2.

49. Allain J, Dufour T. Anterior lumbar fusion techniques: ALIF, OLIF, DLIF, LLIF, IXLIF. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2020;106:S149–57.


50. Upadhyayula PS, Curtis EI, Yue JK, Sidhu N, Ciacci JD. Anterior versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: perioperative risk factors and 30-day outcomes. Int J Spine Surg 2018;12:533–42.



51. Xu DS, Walker CT, Godzik J, Turner JD, Smith W, Uribe JS. Minimally invasive anterior, lateral, and oblique lumbar interbody fusion: a literature review. Ann Transl Med 2018;6:104.



52. Teng I, Han J, Phan K, Mobbs R. A meta-analysis comparing ALIF, PLIF, TLIF and LLIF. J Clin Neurosci 2017;44:11–7.


53. Lee N, Kim KN, Yi S, et al. Comparison of outcomes of anterior, posterior, and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion surgery at a single lumbar level with degenerative spinal disease. World Neurosurg 2017;101:216–26.


54. Cho JY, Goh TS, Son SM, Kim DS, Lee JS. Comparison of anterior approach and posterior approach to instrumented interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis: a meta-analysis. World Neurosurg 2019;129:e286–93.


55. Anand N, Alayan A, Agrawal A, Kahwaty S, Nomoto E, Khandehroo B. Analysis of spino-pelvic parameters and segmental lordosis with L5-S1 oblique lateral interbody fusion at the bottom of a long construct in circumferential minimally invasive surgical correction of adult spinal deformity. World Neurosurg 2019;130:e1077–83.


56. Watkins RG, Hanna R, Chang D, Watkins RG. Sagittal alignment after lumbar interbody fusion: comparing anterior, lateral, and transforaminal approaches. J Spinal Disord Tech 2014;27:253–6.

57. Sihvonen T, Herno A, Paljarvi L, Airaksinen O, Partanen J, Tapaninaho A. Local denervation atrophy of paraspinal muscles in postoperative failed back syndrome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993;18:575–81.


58. Phan K, Thayaparan GK, Mobbs RJ. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Neurosurg 2015;29:705–11.


59. Choi J, Rhee I, Ruparel S. Assessment of great vessels for anterior access of L5/S1 using patient positioning. Asian Spine J 2020;14:438–44.




60. Baker JF, Chan JC, Moon BG, Robertson PA. Relationship of aortic bifurcation with sacropelvic anatomy: application to anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Anat 2021;34:550–5.



61. Liu L, Liang Y, Zhou Q, et al. Study on the anatomy of the lumbosacral anterior great vessels pertinent to L5/S1 anterior interbody surgery with computer tomography angiography. Acta Orthop Belg 2014;80:537–43.

62. Lindley EM, McBeth ZL, Henry SE, et al. Retrograde ejaculation after anterior lumbar spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37:1785–9.


63. Comer GC, Smith MW, Hurwitz EL, Mitsunaga KA, Kessler R, Carragee EJ. Retrograde ejaculation after anterior lumbar interbody fusion with and without bone morphogenetic protein-2 augmentation: a 10-year cohort controlled study. Spine J 2012;12:881–90.


64. Bateman DK, Millhouse PW, Shahi N, et al. Anterior lumbar spine surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of associated complications. Spine J 2015;15:1118–32.


65. Manunga J, Alcala C, Smith J, et al. Technical approach, outcomes, and exposure-related complications in patients undergoing anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Vasc Surg 2021;73:992–8.


66. Ozgur BM, Aryan HE, Pimenta L, Taylor WR. Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF): a novel surgical technique for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J 2006;6:435–43.


67. Nakashima H, Kanemura T, Satake K, et al. Comparative radiographic outcomes of lateral and posterior lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of degenerative lumbar kyphosis. Asian Spine J 2019;13:395–402.




68. Nakashima H, Kanemura T, Satake K, et al. Changes in sagittal alignment following short-level lumbar interbody fusion: comparison between posterior and lateral lumbar interbody fusions. Asian Spine J 2019;13:904–12.




69. Derman PB, Albert TJ. Interbody fusion techniques in the surgical management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2017;10:530–8.




70. Riley MR, Doan AT, Vogel RW, Aguirre AO, Pieri KS, Scheid EH. Use of motor evoked potentials during lateral lumbar interbody fusion reduces postoperative deficits. Spine J 2018;18:1763–78.


71. Kudo Y, Okano I, Toyone T, et al. Lateral lumbar interbody fusion in revision surgery for restenosis after posterior decompression. Neurosurg Focus 2020;49:E11.

72. Park HY, Kim YH, Ha KY, et al. Minimally invasive lateral lumbar interbody fusion for clinical adjacent segment pathology: a comparative study with conventional posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Spine Surg 2019;32:E426–33.

73. Iwamae M, Matsumura A, Namikawa T, et al. Surgical outcomes of multilevel posterior lumbar interbody fusion versus lateral lumbar interbody fusion for the correction of adult spinal deformity: a comparative clinical study. Asian Spine J 2020;14:421–9.




74. Nakashima H, Kanemura T, Satake K, et al. Factors affecting postoperative sagittal alignment after lateral lumbar interbody fusion in adult spinal deformity: posterior osteotomy, anterior longitudinal ligament rupture, and endplate injury. Asian Spine J 2019;13:738–45.




75. Laws CJ, Coughlin DG, Lotz JC, Serhan HA, Hu SS. Direct lateral approach to lumbar fusion is a biomechanically equivalent alternative to the anterior approach: an in vitro study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37:819–25.

77. Rabau O, Navarro-Ramirez R, Aziz M, et al. Lateral lumbar interbody fusion (LLIF): an update. Global Spine J 2020;10(2 Suppl): 17S–21S.




78. Yingsakmongkol W, Jitpakdee K, Varakornpipat P, et al. Clinical and radiographic comparisons among minimally invasive lumbar interbody fusion: a comparison with three-way matching. Asian Spine J 2022;16:712–22.




79. Yingsakmongkol W, Jitpakdee K, Varakornpipat P, et al. Clinical and radiographic comparisons among minimally invasive lumbar interbody fusion: a comparison with three-way matching. Asian Spine J 2022;16:712–22.




80. Walker CT, Farber SH, Cole TS, et al. Complications for minimally invasive lateral interbody arthrodesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing prepsoas and transpsoas approaches. J Neurosurg Spine 2019;30:446–60.


81. Guerin P, Obeid I, Bourghli A, et al. The lumbosacral plexus: anatomic considerations for minimally invasive retroperitoneal transpsoas approach. Surg Radiol Anat 2012;34:151–7.



82. Kim WJ, Lee JW, Kim SM, et al. Precautions for combined anterior and posterior long-level fusion for adult spinal deformity: perioperative surgical complications related to the anterior procedure (oblique lumbar interbody fusion). Asian Spine J 2019;13:823–31.




83. Spiessberger A, Arvind V, Dietz N, et al. A comparison of complications and clinical and radiologic outcome between the mini-open prepsoas and miniopen transpsoas approaches for lumbar interbody fusion: a meta-analysis. Clin Spine Surg 2020;33:271–9.

84. Robertson PA, Wray AC. Natural history of posterior iliac crest bone graft donation for spinal surgery: a prospective analysis of morbidity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:1473–6.

85. Kannan A, Dodwad SN, Hsu WK. Biologics in spine arthrodesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 2015;28:163–70.


86. Lementowski PW, Lucas P, Taddonio RF. Acute and chronic complications of intracortical iliac crest bone grafting versus the traditional corticocancellous technique for spinal fusion surgery. Orthopedics 2010;33:1–8.

87. Golubovsky JL, Ejikeme T, Winkelman R, Steinmetz MP. Osteobiologics. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2021;21(Suppl 1): S2–9.



88. Liao Z, Wang CH, Cui WL. Comparison of allograft and autograft in lumbar fusion for lumbar degenerative diseases: a systematic review. J Invest Surg 2016;29:373–82.


89. Putzier M, Strube P, Funk JF, et al. Allogenic versus autologous cancellous bone in lumbar segmental spondylodesis: a randomized prospective study. Eur Spine J 2009;18:687–95.




90. Gao Y, Li J, Cui H, et al. Comparison of intervertebral fusion rates of different bone graft materials in extreme lateral interbody fusion. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e17685.



91. Kang J, An H, Hilibrand A, Yoon ST, Kavanagh E, Boden S. Grafton and local bone have comparable outcomes to iliac crest bone in instrumented single-level lumbar fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37:1083–91.


92. Kim DH, Lee N, Shin DA, Yi S, Kim KN, Ha Y. Matched comparison of fusion rates between hydroxyapatite demineralized bone matrix and autograft in lumbar interbody fusion. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2016;59:363–7.



93. Schizas C, Triantafyllopoulos D, Kosmopoulos V, Tzinieris N, Stafylas K. Posterolateral lumbar spine fusion using a novel demineralized bone matrix: a controlled case pilot study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2008;128:621–5.



94. Epstein NE, Epstein JA. SF-36 outcomes and fusion rates after multilevel laminectomies and 1 and 2-level instrumented posterolateral fusions using lamina autograft and demineralized bone matrix. J Spinal Disord Tech 2007;20:139–45.


96. Burkus JK, Gornet MF, Dickman CA, Zdeblick TA. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion using rhBMP-2 with tapered interbody cages. J Spinal Disord Tech 2002;15:337–49.


97. Slosar PJ, Josey R, Reynolds J. Accelerating lumbar fusions by combining rhBMP-2 with allograft bone: a prospective analysis of interbody fusion rates and clinical outcomes. Spine J 2007;7:301–7.


98. Dimar JR, Glassman SD, Burkus JK, Pryor PW, Hardacker JW, Carreon LY. Clinical and radiographic analysis of an optimized rhBMP-2 formulation as an autograft replacement in posterolateral lumbar spine arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009;91:1377–86.


99. Galimberti F, Lubelski D, Healy AT, et al. A systematic review of lumbar fusion rates with and without the use of rhBMP-2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:1132–9.


100. Carragee EJ, Hurwitz EL, Weiner BK. A critical review of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 trials in spinal surgery: emerging safety concerns and lessons learned. Spine J 2011;11:471–91.


101. Tannoury CA, An HS. Complications with the use of bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) in spine surgery. Spine J 2014;14:552–9.


102. Crandall DG, Revella J, Patterson J, Huish E, Chang M, McLemore R. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with rhBMP-2 in spinal deformity, spondylolisthesis, and degenerative disease: part 2: BMP dosage-related complications and long-term outcomes in 509 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:1137–45.

103. Poon B, Kha T, Tran S, Dass CR. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and bone therapy: successes and pitfalls. J Pharm Pharmacol 2016;68:139–47.



104. Fu R, Selph S, McDonagh M, et al. Effectiveness and harms of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in spine fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2013;158:890–902.


105. Simmonds MC, Brown JV, Heirs MK, et al. Safety and effectiveness of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 for spinal fusion: a meta-analysis of individual-participant data. Ann Intern Med 2013;158:877–89.


106. Skovrlj B, Guzman JZ, Al Maaieh M, Cho SK, Iatridis JC, Qureshi SA. Cellular bone matrices: viable stem cell-containing bone graft substitutes. Spine J 2014;14:2763–72.



107. Blanco JF, Villaron EM, Pescador D, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stromal cells embedded in tricalcium phosphate for posterolateral spinal fusion: results of a prospective phase I/II clinical trial with long-term follow-up. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019;10:63.




108. Gan Y, Dai K, Zhang P, Tang T, Zhu Z, Lu J. The clinical use of enriched bone marrow stem cells combined with porous beta-tricalcium phosphate in posterior spinal fusion. Biomaterials 2008;29:3973–82.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles in ASJ






