|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 17(1); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
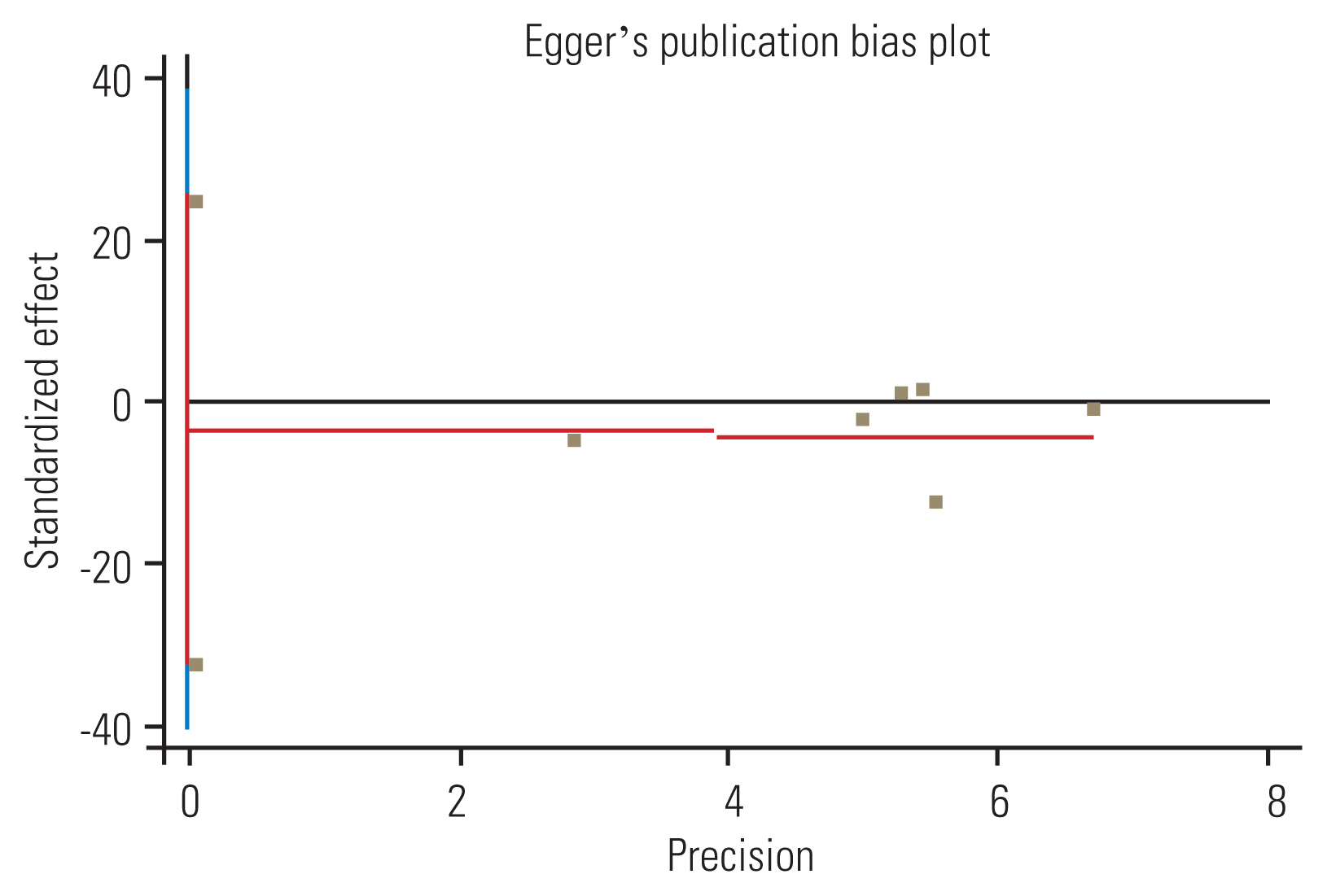
Routinely, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) curves that progress beyond 40° in skeletally immature adolescents require surgery. However, some adolescents with AIS and their parents utterly refuse surgery and insist on wearing a brace. Debate continues regarding the appropriateness of bracing for AIS curves exceeding 40° in patients who have rejected surgical intervention. This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted to review the literature on the effectiveness of bracing and its predictive factors in larger-magnitude AIS curves ≥40°. This study replicated the search strategy used by the PICOS system for formulating study questions, which include consideration of the patient/population (P), intervention (I), comparison (C), outcome (O), and study design (S). The search was conducted up to January 2022 in the following bibliographic online databases only in the English language: PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science. Two assessors reviewed the articles for qualification. Eligible studies were assessed for risk of bias at the study level using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. The effect size across the studies was determined using standardized mean differences (Cohen’s d) and 95% confidence intervals for the meta-analysis. Among the eight included moderate quality studies, evidence of potential publication bias (p<0.05) for the trials included was found in the Cobb angle outcome. Results obtained through meta-analysis indicated that the effectiveness of bracing in controlling Cobb angle progression in curves ≥40° is significantly positive. Additionally, initial curve severity, Risser stage, in-brace curve correction, curve type, and apical vertebral rotation were considered risk factors associated with brace effectiveness. This systematic review revealed that bracing could alter the normal course of AIS curves ≥40° in patients refusing posterior spinal fusion (PSF). However, the suggested course for patients refusing PSF remains unclear because of the significant heterogeneity in the risk factors associated with bracing failure.
Rigid bracing is the most effective nonsurgical intervention for treating Cobb angle curves of 20°–40° in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) [1,2]. With the introduction of novel brace designs in the treatment of AIS, manufacturers hope to prevent the progression of the curve, maintain proper alignment of the head relative to the pelvis, and reduce the physical appearance of curve magnitude [3,4]. A randomized controlled trial study revealed that the success rate of bracing for AIS curves of 20°–40° is 72% [2].
Surgeons usually recommend surgery for severe AIS curves exceeding 40°–45° [5,6]. Surgery improves the deformity and increases the patient’s quality of life and self-image [7,8]. However, posterior spinal fusion (PSF) is not without a significant risk of potentially morbid complications. A study of 84,320 patients between 2004 and 2016 revealed that the complication rate of scoliosis surgery was 1.5% [9]. Despite recent advances in PSF, which have substantially reduced surgical complications, such as infection, mortality, and neurological disorders, many patients and their families are still reluctant to undergo operative intervention and instead opt to continue wearing a brace [10].
Thus, the question remains whether bracing can still be considered a treatment option for immature patients with severe curves above 40° who refuse surgery. Contradictory results have been reported across the literature. Although a growing body of literature recognizes the effectiveness of bracing for curves above 40°, some studies show that the failure rate of brace is higher in these patients than in patients with a curve <40° [11,12]. Other authors reported very satisfactory results of brace treatment in advanced scoliotic curves [10,13]. Collectively, the results of studies on the effect of braces on curves exceeding 40° show a large discrepancy: efficacy rates are reported to be between 35% and 91% [10–15]. This wide range could be attributed to the heterogeneity of the inclusion criteria, the type of brace in use, and various other potentially impactful variables.
Despite the heterogeneity of the results of bracing in higher-magnitude AIS curves, 2020 consensus guidelines from experts in scoliosis treatment have established that bracing can be prescribed for AIS curves up to 60° [16]. Therefore, the current study was conducted to review the literature on the effectiveness of bracing and its predictive factors in AIS curves above 40°.
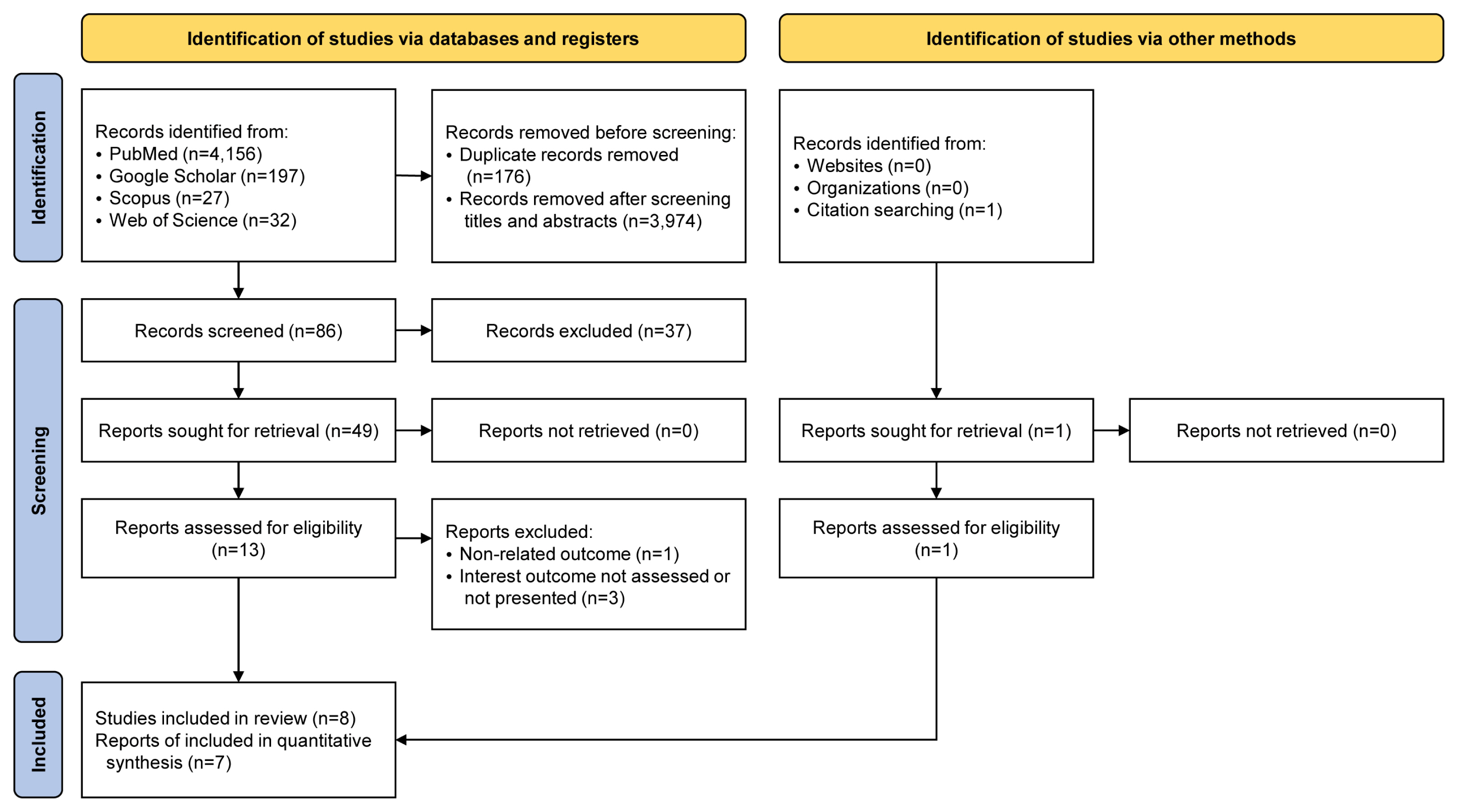
This study replicated the search strategy used by the PICOS system for formulating study questions, which include consideration of the patient/population (P), intervention (I), comparison (C), outcome (O), and study design (S) (Table 1). The search was conducted up to January 2022 in the following bibliographic online databases only in the English language: PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science. The following search strategy was considered: (idiopathic scoliosis [MeSH Terms] OR scolio* [Title/Abstract] OR idiopathic scoliosis [Title/Abstract]) AND (brace [MeSH Terms] OR brace [Title/Abstract] OR bracing [Title/Abstract]) AND effect* [Title/Abstract] OR treatment [Title/Abstract] OR result [Title/Abstract] OR results [Title/Abstract]) AND (curve [Title/Abstract]). We also checked the reference lists of the included studies to ensure that all eligible studies were reviewed. After conducting the search, the process of study selection followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis Protocols guideline, which was published in 2021 [17] (Fig. 1). Potential titles and abstracts were screened, and full-text articles were obtained for studies that appeared eligible. Two assessors (M.Kh. and T.B.) examined them and checked for eligibility. If necessary, a third investigator (V.M.) was also consulted.
Data were extracted independently by two reviewers (H.H. and T.B.). Any discrepancies were discussed and resolved with V.M. as the third reviewer. The duplicate articles were deleted, and the remaining titles and abstracts were screened. The full texts of the eligible papers were then obtained. Additionally, the first author’s name with publication year, study design, age at initiation of bracing, sample size, Risser stage at the initiation of bracing, curve type, prebrace Cobb angle, length of brace treatment, years of follow-up after discontinuation of bracing, and outcome measures were extracted. The current review consisted of retrospective and prospective studies. Studies were eligible if they evaluated Cobb angle ≥40° and included intervention consisting of bracing as a nonsurgical treatment (Table 2).
Eligible studies were assessed for the risk of bias at the study level using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), which is designed to examine the selection of participants and study design, comparability of groups, and ascertainment of exposure/outcome [18]. This tool consists of eight items. Except for the comparability item, a study can be awarded a maximum of one star for each numbered item within the selection and outcome categories. Additionally, a maximum of two stars can be given for the comparability item. Average scores for this quality assessment tool ranged from 0 (lowest score) to nine stars (highest score). The scores of 7–9, 4–6, and 0–3 stars indicated a high-, moderate-, and low-quality study, respectively. This was performed independently by two authors (H.H. and T.B.), and the findings were compared to achieve consensus. Table 3 lists the NOS for the selected papers.
After literature review, it was determined that ≥3 studies achieved qualification standards for inclusion in the meta-analysis. Regarding the statistical methodology for the meta-analysis portion of the current study, the mean, sample size, and standard deviations (SD) before and after the brace intervention were extracted from the included studies [19]. Furthermore, those studies that reported the mean and SD of the Cobb angle at the initiation of brace treatment and final follow-up were included in the meta-analysis. If the mean and SD were not reported, we contacted the authors via email to obtain their unpublished data. The effect size across the studies was determined using standardized mean differences (SMDs; Cohen’s d) and 95% confidence intervals. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model with the Stata ver. 12.0 software (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA). To better explain the pooled analyses, SMDs of 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, and >0.8 were selected to correspond to small, medium, large, and very large variations, respectively [20].
Heterogeneity was explored using the I2 statistic, with a probability value of <0.05, indicating significant heterogeneity. The findings were interpreted as follows: I2 of 0%–30%, unimportant heterogeneity; I2 of 30%–60%, moderate heterogeneity; I2 of 50%–90%, substantial heterogeneity; and I2 of 75%–100%, high heterogeneity [21]. When the number of articles was <10, Egger’s test was used to assess publication bias [22,23].
All included studies were obtained from an electronic search. Eighty-six articles remained after deleting duplicate and unrelated articles. Among them, eight articles met the inclusion criteria for this study [10–15,24,25]. However, one study did not provide sufficient information for conducting a meta-analysis [13]. Although we contacted the corresponding author, we received no response. Therefore, eight articles were included in the systematic review, and seven were included in the meta-analysis.
The sample size of the included studies was 25–100 patients, with a total sample of 518. The mean age of participants was approximately 12.9 years. In all studies, the major curve Cobb angle at the initiation of bracing was ≥40°, with a range of 43.4°–59.7°.
Braces used in the studies included Risser cast, Lyon brace, Sforzesco brace, Boston style thoracolumbosacral orthosis, Milwaukee brace, and Gensingen brace. The mean duration of bracing was 39.36 months (range, 18 to 63.12 months). The mean duration of follow-up was 29.42 months (range, 15.6 to 60.86 months).
Among all included studies, only one directly compared brace treatment with no treatment [13]. In the study by Lusini et al. [13], progression of the scoliotic curve occurred in 20.5% of patients in the braced group and 55.6% in patients without bracing. In patients with an initial Cobb angle <45° and ≥45°, the average curve reduction was 11.46° and 13.74°, respectively. In terms of apical vertebral rotation (AVR), for patients with initial AVR <20°, the average curve reduction was 16.02°, and in cases with AVR ≥20°, the average curve reduction was 8.4°. Furthermore, in patients with initial Risser stages 0–2, the average curve reduction was 14.7°, whereas in cases with Risser stages 3 to 4, the mean correction was 6.7°.
Seven studies reported the treatment results in a stratified manner as progression, stabilization, or improvement of the curve [10–12,14,15,24,25]. Progression or improvement is defined as higher than 5° alteration of curve magnitude in either the positive or negative direction. On the basis of these seven studies, the mean curve improvement after bracing was 38.8% (range, 11% to 78%), the mean curve progression was 35.4% (range, 3.5% to 64.8%), and the mean curve stabilization was 25.5% (range, 13% to 48%).
After the meta-analysis was performed, the SMD value did not cross zero; thus, it could be concluded that the brace effectiveness on Cobb angle ≥40° is significantly positive (Fig. 2). Therefore, using a brace for curves ≥40° in adolescents with AIS can be an effective strategy, especially when the alternative option is no treatment at all.
Five radiological predictive factors, including Risser stage, curve type, initial curve severity, in-brace curve correction, and AVR, were considered for bracing success/failure in the included studies. Verhofste et al. [15], Zhu et al. [12], and Xu et al. [25] discovered that initial curve magnitude has no effect on the final bracing outcome in AIS curves ≥40°, whereas Razeghinezhad et al. [11] reported that the least curve progression was noted in patients with AIS curves of 40°–45° and the most was noted in those with AIS curves of 51°–55°. Zhu et al. [12] and Xu et al. [25] reported that the mean grade of the initial Risser sign in patients with curve progression was significantly lower than that in patients with stable or improved curves. Verhofste et al. [15] revealed that patients with open triradiate cartilage and the lowest Risser stage had the highest curve progression. Razeghinezhad et al. [11] determined that in-brace curve correction and the initial Risser stage significantly correlated with curve magnitude at the final follow-up. Moreover, Xu et al. [25] revealed that patients with Risser stage 0 (p=0.04) and initial in-brace correction rate <10% (p<0.001) experienced the greatest extent of curve progression (70.9%). To further support this finding, Aulisa et al. [14] reported that in patients with Risser stages 0–2, the mean reduction in final curve magnitude was 14.7°, whereas in patients with Risser stages 3 to 4, it was 6.7° (p<0.0001). In this study, the progression rate was noted to be higher in thoracic curves than in lumbar curves. However, contradicting this finding, in the studies of Zhu et al. [12] and Xu et al. [25], there was no statistically significant difference in the rate of curve progression between patients with different curve types (p=0.392 and p=0.17, respectively).
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to examine the effectiveness of bracing in AIS cases with curves ≥40°. The meta-analysis revealed that bracing is effective for treating scoliosis curves ≥40°. Initial curve severity, Risser stage, in-brace curve correction, curve type, and AVR were introduced as risk factors associated with brace effectiveness. Because of the small number of studies and heterogeneity of the data, these factors were excluded from the meta-analysis.
In response to the main query of this study, contrary to expectations, our findings indicated that the use of a brace is effective for controlling the curve progression of patients with AIS curves ≥40°. This finding was obtained from eight moderate quality studies. However, a significant range in the effectiveness of bracing across different studies indicates a high heterogeneity of results, which may alter the strength of the analysis. Several factors may explain this discrepancy in the data, including the nonuniform initial curve magnitude of the studied patients, the brace type, the degree of skeletal maturity, and the correction of the initial curve inside the brace. Findings regarding crucial factors that may contribute to long-term results of brace treatment for patients with AIS curves ≥40° are discussed in the following section.
Various radiological and clinical factors may impact the efficacy of full-time bracing in AIS. These factors include coronal deformity angular ratio (C-DAR), age, sex, menarchal status, body mass index, initial curve magnitude, in-brace curve correction, curve flexibility, curve type, skeletal maturity, vertebral rotation, and compliance [26–28]. In a review study by van den Bogaart [27], it was shown that there is strong evidence between lack of in-brace correction and failure of brace treatment in AIS. Additionally, moderate evidence was reported for an association between lack of brace compliance and treatment failure.
In this study, after a thorough literature review, five studies examined the related risk factors for success/failure of bracing while evaluating its effectiveness in AIS curves ≥40° [11,12,14,15,25]. Findings from a review of these factors showed that among the factors related to brace effectiveness, AVR was examined in only one study [14], and in-brace curve correction was assessed in two studies [11,25]. Also, the role of the Risser stage was examined in five studies [11,12,14,15,25]. Four of these studies reported that the lower the Risser stage, the higher the risk of curve progression [11,12,15,25]. In contradiction with these results, Aulisa et al. [14] reported that the lower the Risser stage, the higher the average curve correction. As a potential explanation for this discrepancy, a recent study reported that the magnitude of initial C-DAR altered the amount of in-brace curve correction and the final results of brace treatment in AIS [28]. It is possible that the heterogeneity in the results of the initial Risser stage on the final bracing outcome of patients with curves exceeding 40° is due to differences in the amount of initial C-DAR. Simultaneous consideration of the C-DAR and the Cobb angle during the evaluation for bracing efficacy may help characterize results more accurately and should be considered in future studies.
Four studies evaluated initial curve magnitude as a factor in the effectiveness of bracing [11,12,15,25]. In one study, initial curve magnitude significantly correlated with bracing efficacy [11], whereas no correlation was observed in the other three studies [12,15,25]. These relationships may partly be explained by differences in the curve type of the included patients. In the study by Razeghinezhad et al. [11], the rate of curve progression between patients with curves of 40°–45°, 46°–50°, and 51°–55° was examined. The results showed that the rate of curve progression was significantly different between individuals with curves of 40°–45° and 51°–55°. Failing to account for this observed difference, in two studies, patients were divided into two groups of less and more than 45° Cobb angles [12,15]. In one study, only patients with an initial curve magnitude of 40°–45° were included [25].
Collectively, the current study highlights the need for further and higher-quality studies that adhere rigidly to the Scoliosis Research Society guideline. In future studies, it is prudent to carefully examine the parameters that predict the outcome of brace treatment for AIS cases with ≥40° curves. The use of more accurate and newer skeletal maturity methods, such as the Sanders staging method [29], is recommended in addition to the Risser stage. Finally, although the compliance rate was reported to be high in all articles included in this review, the compliance evaluation method was subjective. Patients’ desire to avoid PSF may have impacted their reported compliance with bracing. Using objective methods, such as heat-sensitive technology, to monitor the daily hours of wearing a brace may provide more accurate information [30].
As an initial limitation, five studies included in this analysis had a retrospective observational design that can result in bias due to inherent limitations of a retrospective study design [10–12,15,25]. Additionally, only articles in English were included, potentially limiting the inclusion of important findings in non-English-language manuscripts. Furthermore, because of the high heterogeneity of the data and the small number of studies, it was impossible to pool the data. According to the bracing committee of the Scoliosis Research Society, patients with initial Risser stages 0–2 are at higher risk for curve progression than those with Risser stages 3–5 [5]. In this systematic review, three studies included patients with initial Risser stages 0–2 [11,15,24], two included patients with initial Risser stages 0–3 [12,25], and three included patients with initial Risser stages 0–4 [10,13,14]. This can affect the generalizability of our findings. A recently published study revealed that 14.8% of AIS cases with Risser stage ≥3 and an average curve magnitude of 31°, which were not treated with a brace, experienced curve progression [31]. What is now needed is a study involving patients with Risser stage ≥3 and curve magnitude >40° to determine the progression rate of this population. As a final limitation, the type of brace may affect the treatment outcome. Various braces were used in the eight articles included in this systematic review, potentially altering the generalizability of the results.
Fig. 2
Fix-effects model analysis for bracing on Cobb angle outcome. Weights are from random effects analysis. SMD, standardized mean difference; CI, confidence interval.
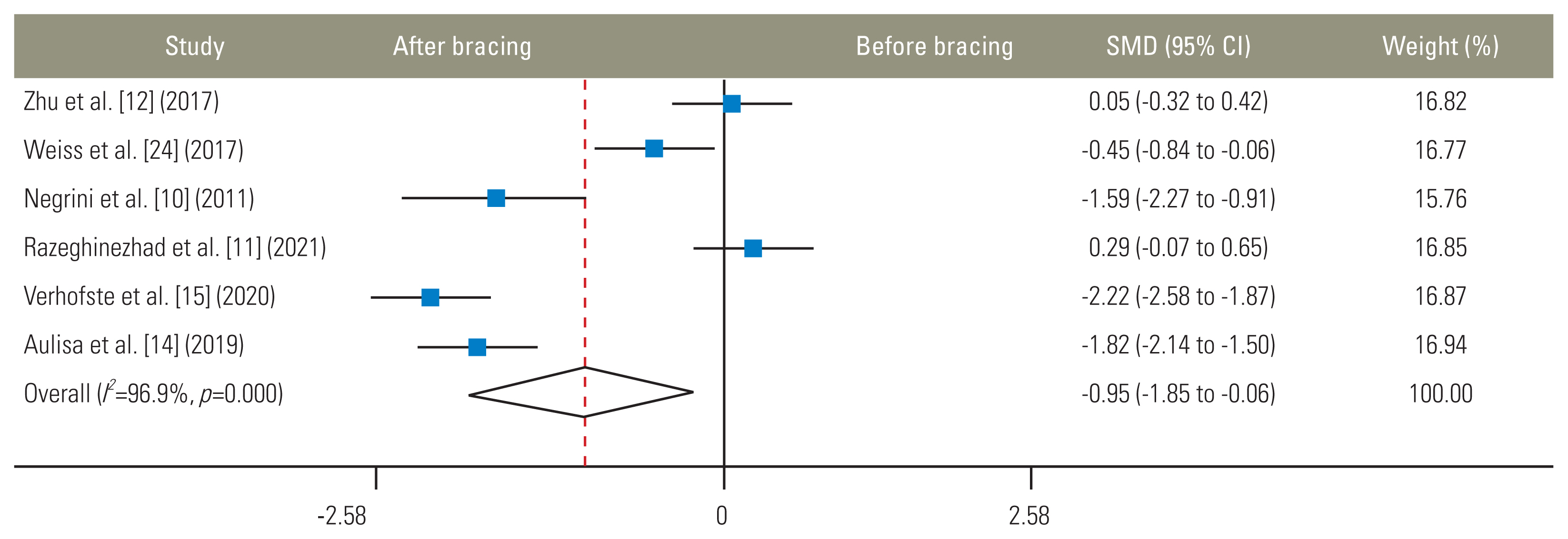
Table 1
Eligibility criteria for including articles in this systematic review
Table 2
Characteristics of included studies
| Reference | Study design | Age at initiation of bracing (yr) | Sample size | Risser sign at the initiation of bracing | Curve type (no.) | Pre-brace Cobb angle (range) | Brace treatment length | FU duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verhofste et al. [15] (2020) | Retrospective case-series | 11.8±2.36 (6.1–16.5) | 100 | 0–2 | 45°±3.9° (40°–59°) | 1.8 yr (0.4–7.1 yr) | 4.1 yr (1.0–11.6 yr) | 43 Patients (43%) were considered brace success. 57 curves (57%) progressed >5°, 32 (32%) stabilized within −5° and 5°, and 11 (11%) improved >5°. No outcome differences were detected between curves ≥45° or <45° (p=0.91). Of curves ≥45°, 54% (25/46) progressed as compared to 59% (32/54) of curves <45°. | |
| Aulisa et al. [14] (2019) | Observational cohort | 12.88±1.86 | 104 | 0–4 | 47.02°±5.25° | 63.12±17.44 mo | 60.86±57.85 mo (24–276 mo) | 81 Patients (78%) obtained a curve correction. Stabilization was achieved in 14 cases (13%). Nine patients experienced curve progression (9%), 16 patients were recommended for surgery because the curve at FU was over 45°. The analysis of subgroups showed that with Cobb <45° at baseline, the average curve reduction was 11.46°. In cases with Cobb ≥45° at baseline, the mean correction was 13.74°. In subgroups with Perdriolle <20° at baseline, the average curve reduction was 16.02°, while in cases with Perdriolle ≥20° at baseline, the mean correction was 8.4°. In subgroups with Risser 0–2 at baseline, the average curve reduction was 14.7°, while in cases with Risser 3–4 at baseline, the mean correction was 6.7°. | |
| Lusini et al. [13] (2014) | Observational prospective cohort controlled study | 15 yr 3±22 mo | 57 | 0–4 | - | 52.5° (45°–93°) | 5 yr and 3 mo±13 mo | Not provided | 20.5% failures in bracing group and 55.6% in control group. Relative risks of failure in control group were 4.3 (95% CI, 3.6–4.9) in efficacy analysis and 2.7 (95% CI, 2.0–3.5) in intent to treat (p<0.05). Relative risks of improvement in brace group were 1.6 (95% CI, 1.46–1.9) in efficacy analysis and 1.9 (95% CI, 1.6–2.2) in intent-to-treat (p<0.05). Patients who joined the treatment achieved a 10.4°±10.7° Cobb improvement, an apical trunk rotation reduction of 4.2°±4.3°, and an esthetic improvement of 2.8±1.9 of 12 points (TRACE). At final FU, in bracing group, 24 patients were below 45° and 6 patients below 35° and 17 patients below 40°. |
| Negrini et al. [10] (2011) | Retrospective cohort from a prospective database | 14.2±1.8 | 28 | 0–4 | 49.4° (45°–58°) | 4 yr and 10 mo (1.45–7.42 yr) | 2 yr | 2 Patients (7%) remained above 50° Cobb, 6 patients (21%) finished between 30° and 35° Cobb and 12 patients (43%) finished between 36° and 40° Cobb. Improvements in 71% patients and a 5° Cobb progression in 1 patient. | |
| Weiss et al. [24] (2017) | Prospective cohort | 12.4±0.82 | 25 | 0–2 (0.84±0.94) | 49°±8.4° (40º–71º) | 1.5 yr | 30.4±9.2 mo | The average Cobb angle after FU was 44.2°. Two patients progressed, 12 patients were able to achieve halted progression, 11 patients improved. | |
| Zhu et al. [12] (2017) | Retrospective | 13.7±1.8 (10–15) | 54 | 0–3 (0.91±1.6) | 43.4°±2.4° (40°–50°) | 2.1 yr (1.2–3) | 2.3 yr (1.8–2.6 yr) | Curve progressed in 35 patients, remained stable in 12 patients and improved in the else 7 patients. All the patients with curve progression finally received surgical intervention. The mean grade of initial Risser sign in patients with curve progression was significantly lower than that in patients with stable or improved curve (0.3±0.8 vs. 1.2±1.4, p=0.02). The results of the logistic regression analysis showed that initial Risser sign of grade 0 or 1 had significant associations with the curve progression of patients with curves larger than 40° (OR, 7.51; 95% CI, 1.27–24.43; p=0.02). | |
| Razeghinezhad et al. [11] (2021) | Retrospective cohort study | 12.63±1.44 | 60 | 0–2 | 44.93°±4.86° (40°–55°) | 37.23±20.70 mo | 27.92±10.03 mo (24–60 mo) | The scoliosis curve had increased in 57% of patients, stabilized in 25%, and improved in 18% of the patients. in-brace curve correction and initial Risser sign had a significant correlation with curve magnitude at the final FU (p<0.05). The progression rate was higher in thoracic curves compared to lumbar curves. The least curve progression was in those with 40° to 45° curves and the most in those with 51° to 55° curves. | |
| Xu et al. [25] (2019) | Retrospective | 12.6±1.3 | 90 | 0–3 | 42.5°±2.1° (40°–45°) | 2.4±1.3 yr | 1.3±0.4 yr | The curve was improved in 34 patients (37.8%) and stabilized in 12 patients (13.3%). In 44 patients (48.9%), remarkable curve progression >50° was observed. By the end of the last FU, 51 patients (56.7%) received correction surgery. Patients with lower Risser grade or less initial in-brace correction rate were found to have a significantly higher incidence of curve progression (p=0.04 for Risser grade; p=0.001 for in-brace correction). Patients with Risser grade of 0 (OR, 1.46; p=0.04) and initial in-brace correction rate of <10% (OR, 12.82; p<0.001) had the highest incidence of curve progression (70.9%). |
Table 3
The NOS results and total score
| Included studies | Items of NOS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (Representative-ness of the exposed cohort) | Q2 (Selection of the non-exposed cohort) | Q3 (Ascertainment of exposure) | Q4 (Demonstration that outcome of interest was not present at start of study) | Q5 (Comparability) | Q6 (Assessment of outcome) | Q7 (Was follow-up long enough for outcomes to occur) | Q8 (Adequacy of follow-up) | Total score | |
| Verhofste et al. [15] (2020) | * | - | - | * | - | * | * | * | 5 |
| Aulisa et al. [14] (2019) | * | - | - | * | - | * | * | * | 5 |
| Lusini et al. [13] (2014) | * | * | - | * | - | * | * | * | 6 |
| Negrini et al. [10] (2011) | * | - | - | * | - | * | * | * | 5 |
| Weiss et al. [24] (2017) | - | - | - | * | - | * | * | * | 4 |
| Zhu et al. [12] (2017) | * | - | - | * | - | * | * | * | 5 |
| Razeghinezhad et al. [11] (2021) | * | - | - | * | - | * | * | * | 5 |
| Xu et al. [25] (2019) | * | - | - | * | - | * | * | * | 5 |
References
1. Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord 2018 13:3.




2. Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Wright JG, Dobbs MB. Effects of bracing in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. N Engl J Med 2013 369:1512–21.



3. Kwan KY, Cheung AK, Koh HY, Cheung KM. Brace effectiveness is related to 3-dimensional plane parameters in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2021 103:37–43.


4. Matsumoto H, Warren S, Simhon ME, et al. It is not just about the frontal plane: sagittal parameters impact curve progression in AIS patients undergoing brace treatment. Spine Deform 2020 8:921–9.



5. Richards BS, Bernstein RM, D’Amato CR, Thompson GH. Standardization of criteria for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis brace studies: SRS Committee on Bracing and Nonoperative Management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005 30:2068–77.

6. Cheung K. Is there a role for conservative treatment for large curvatures in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis?: commentary on “The effect of brace treatment on large curves of 40° to 55° in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis who have avoided surgery: a retrospective cohort study”. Neurospine 2021 18:445–6.




7. Helenius L, Diarbakerli E, Grauers A, et al. Back pain and quality of life after surgical treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis at 5-year follow-up: comparison with healthy controls and patients with untreated idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2019 101:1460–6.

8. Mens RH, Bisseling P, de Kleuver M, van Hooff ML. Relevant impact of surgery on quality of life for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a registry-based two-year follow-up cohort study. Bone Joint J 2022 104–B:265–73.
9. Kwan KY, Koh HY, Blanke KM, Cheung KM. Complications following surgery for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis over a 13-year period. Bone Joint J 2020 102-B:519–23.



10. Negrini S, Negrini F, Fusco C, Zaina F. Idiopathic scoliosis patients with curves more than 45 Cobb degrees refusing surgery can be effectively treated through bracing with curve improvements. Spine J 2011 11:369–80.


11. Razeghinezhad R, Kamyab M, Babaee T, Ganjavian MS, Bidari S. The effect of brace treatment on large curves of 40° to 55° in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis who have avoided surgery: a retrospective cohort study. Neurospine 2021 18:437–44.




12. Zhu Z, Xu L, Jiang L, et al. Is brace treatment appropriate for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients refusing surgery with cobb angle between 40 and 50 degrees. Clin Spine Surg 2017 30:85–9.


13. Lusini M, Donzelli S, Minnella S, Zaina F, Negrini S. Brace treatment is effective in idiopathic scoliosis over 45°: an observational prospective cohort controlled study. Spine J 2014 14:1951–6.


14. Aulisa AG, Guzzanti V, Falciglia F, Giordano M, Galli M, Aulisa L. Brace treatment of idiopathic scoliosis is effective for a curve over 40 degrees, but is the evaluation of Cobb angle the only parameter for the indication of treatment? Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 2019 55:231–40.


15. Verhofste BP, Whitaker AT, Glotzbecker MP, et al. Efficacy of bracing in skeletally immature patients with moderate-severe idiopathic scoliosis curves between 40° and 60°. Spine Deform 2020 8:911–20.



16. Roye BD, Simhon ME, Matsumoto H, et al. Establishing consensus on the best practice guidelines for the use of bracing in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deform 2020 8:597–604.



17. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021 372:n71.



18. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 2010 25:603–5.



19. Sullivan GM, Feinn R. Using effect size-or why the P value is not enough. J Grad Med Educ 2012 4:279–82.




20. Ioannidis JP, Patsopoulos NA, Rothstein HR. Reasons or excuses for avoiding meta-analysis in forest plots. BMJ 2008 336:1413–5.



21. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 2002 21:1539–58.


22. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994 50:1088–101.


23. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997 315:629–34.



24. Weiss HR, Tournavitis N, Seibel S, Kleban A. A prospective cohort study of AIS patients with 40° and more treated with a Gensingen brace (GBW): preliminary results. Open Orthop J 2017 11:1558–67.



25. Xu L, Yang X, Wang Y, et al. Brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients with curve between 40° and 45°: effectiveness and related factors. World Neurosurg 2019 126:e901–6.


26. Hawary RE, Zaaroor-Regev D, Floman Y, Lonner BS, Alkhalife YI, Betz RR. Brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: risk factors for failure: a literature review. Spine J 2019 19:1917–25.


27. van den Bogaart M, van Royen BJ, Haanstra TM, de Kleuver M, Faraj SS. Predictive factors for brace treatment outcome in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a best-evidence synthesis. Eur Spine J 2019 28:511–25.



28. Babaee T, Kamyab M, Ganjavian MS, Rouhani N, Khorramrouz A, Jarvis JG. Coronal deformity angular ratio as a predictive factor for in-brace curve correction and long-term outcome of brace treatment in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deform 2022 10:543–51.



29. Sanders JO, Khoury JG, Kishan S, et al. Predicting scoliosis progression from skeletal maturity: a simplified classification during adolescence. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008 90:540–53.


-
METRICS

- Related articles in ASJ
-
Etiology of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Literature Review2019 June;13(3)