 |
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 16(3); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to evaluate the risk factor associated with pseudoarthrosis after placement of lateral interbody fusion (LIF) cages for adult spinal deformity (ASD) treatment.
Overview of Literature
LIF technique is widely used for ASD correction. Furthermore, pseudoarthrosis is a major complication of fusion surgery required for revision surgery.
Methods
This study included 42 patients with ASD (two men and 40 women; 112 segments; mean, 68.5±8.4 years; and mean follow-up, 31.6±17.0 months) who underwent LIF and posterior correction surgery. The concave slot of the LIF cage was filled with an autologous iliac crest bone graft (IBG), and the convex slot with a porous hydroxyapatite/collagen (HAp/Col) composite was soaked with bone marrow aspirate. Endplate injury, the gap between vertebral endplate and cage in the coronal or sagittal plane, and fusion status were evaluated using computed tomography multiplanar reconstruction at 12 months after surgery. Moreover, the associated risk factors for pseudoarthrosis were analyzed.
Results
Fusion at LIF segments were observed in 71.4% segments at 12 months after surgery. Fusion on the concave slot (autologous IBG side), convex slot (porous HAp/Col composite side), and both concave and convex slots were observed in 66.1%, 37.5%, and 36.6% of patients, respectively. Moreover, pseudoarthrosis was observed in 28.6% at 12 months after surgery. Consequently, logistic regression analysis of the fusion at the LIF segment revealed that the gap between the LIF cage and endplate in the coronal plane (p=0.030; odds ratio, 0.183; 95% confidence interval, 0.030–0.183) was significantly associated with pseudoarthrosis at the LIF segments.
Conclusions
ASD surgery fusion rate using LIF cages was 71.4% at 12 months after surgery. The fusion rate was higher on the concave slot filled with autologous IBG than on the convex slot filled with a porous HAp/Col composite. The gap in the coronal plane was a risk factor for pseudoarthrosis at the LIF segment.
Adult spinal deformity (ASD) is characterized by a degenerative change with a rigid and structural complex deformity. In ASD surgery, release for the fixed deformity (e.g., osteotomy) and three-dimensional correction sometimes require achieving a favorable spinal alignment. Previous studies reported a high incidence of postoperative complications (e.g., implant failure, neurological deterioration, hemorrhagic shock, heart failure, and surgical site infection) [1–3]. Moreover, Smith et al. [3] conducted a prospective multicenter study and reported that 69.8% of the overall perioperative and delayed complications are associated with ASD surgery. Furthermore, they reported that the incidence of pseudoarthrosis increased to 5.2% (15/291). Consequently, pseudoarthrosis was then considered a major complication of correction surgery for ASD because 10 out of 15 patients (66.7%) required revision surgery. Recently, a combined fusion technique using lateral interbody fusion (LIF) for ASD can obtain better coronal/sagittal correction with a lesser complication rate compared with conventional posterior fusion surgery [4,5]. The direct lateral approach allows the insertion of a large footprint cage into the degenerated intervertebral disc space, resulting in a greater amount of bone grafting in LIF than in the posterior LIF (PLIF). On the contrary, a larger LIF cage requires a larger amount of bone graft. However, obtaining enough bone graft from an autologous iliac crest was difficult. Hence, this study used a hybrid bone graft using an artificial bone graft, a porous hydroxyapatite/collagen (HAp/Col) composite, and an autologous iliac crest bone graft (IBG).
This study aimed to evaluate the predictors associated with intervertebral bony fusion after placement of LIF cages for ASD.
This is a single-center retrospective study. This study was approved by the institutional review board of this study (IRB approval no., 20110142). The requirement for informed consent from individual patients was omitted because of the retrospective design of this study. All eligible patients were >40 years and had at least one of the following parameters: coronal lumbar curve of >30°, pelvic incidence–lumbar lordosis of >20°, sagittal vertical axis of >95 mm, and pelvic tilt of >30° [6]. The medical records and radiographic findings of the patients with ASD who underwent correction surgery at the institution of this study were retrospectively evaluated. Patients (1) who were diagnosed with ASD; (2) who underwent combined fusion surgery, LIF, and conventional posterior fusion surgery in more than three segments; (3) with two or more LIF segments; and (4) who underwent computed tomography (CT) scan both immediately after surgery and postoperative 1 year (PO1Y) were included in the study. This study retrospectively identified 56 consecutive patients from the database from 2013 to 2018. Among them, five who had a short follow-up, seven who lacked a CT scan at PO1Y, and two with missing data were excluded. Finally, 42 patients with ASD (two men and 40 women; mean age, 68.5±8.4 years; mean follow-up, 31.6±17.0 months) and 112 segments were enrolled in this study. Moreover, Table 1 shows the demographic parameters of the participants.
As the first stage, LIF was initially performed under fluoroscopic guidance in all patients. The concave slot of the LIF cage was filled with autologous IBG, and the convex slot filled with two porous HAp/Col composite blocks (10×10×10 mm) was soaked with bone marrow aspirate (Fig. 1). The material used to create the cage (titanium alloy or polyether ether ketone) was decided by the surgeon. The LIF approach was performed on the concave side. Moreover, conventional posterior correction surgery was performed using pedicle screw constructs 3–7 days after LIF. All pedicle screws were manually inserted without fluoroscopic guidance. Consequently, bilateral iliac screws were applied in all patients in the case of lumbosacral fusion. An S2 alar–iliac screw was not used in this series. Weekly teriparatide was applied in patients with a T score <−2.5 or a history of osteoporotic fracture.
Endplate injury, the gap between vertebral endplates, and the cage in the coronal or sagittal plane were evaluated using CT multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) immediately after surgery. All patients underwent a CT scan immediately after surgery and PO1Y. The endplate injury was defined as a cage sinking >2 mm from the vertebral endplate as reported by Nakashima [7]. The gap between the LIF cage and the endplate in the coronal or sagittal plane was defined as space ≥2 mm. Fusion status was also evaluated using CT-MPR images and coronal and sagittal planes at PO1Y. Fusion was defined as “a trabecular continuity of >1 mm between adjacent vertebrae, passing through the cage space in either coronal or sagittal planes” according to Lee et al. [8] and Kushioka et al. [9]. Furthermore, fusion in either concave or convex or both slots was regarded as fusion at the LIF segments. All radiographic parameters and CT-MPR images were assessed by a spine surgeon (E.O.). Consequently, an independent spine surgeon (Y.Y.) blindly evaluated the fusion status using CT-MPR images to evaluate the interobserver error. The two surgeons had over 10 years of clinical experience and were familiar with LIF and the interpretation of CT-MPR images of the lumbar spine. The subjects were classified on the basis of fusion status at the LIF segments. In the present study, bony fusion at the intervertebral disc space was regarded as fusion at the LIF segment. The segment was classified as nonfusion if the LIF segment obtained posterior–lateral fusion without bony fusion at the intervertebral disc space. Conversely, the subject was classified into the fusion group if all the LIF segments were fused. However, the subject was classified into the nonfusion group if at least one segment was not fused. Moreover, the kappa coefficients were used to assess interobserver agreement using the method of Landis and Koch [10]. The coefficients of ≥0.75, between 0.75 and 0.40, and <0.40 indicate excellent concordance, good to fair, and poor, respectively.
The factors associated with intervertebral fusion were analyzed, including age, gender, performed intervertebral level LIF, material used to create the cage (titanium alloy or polyether ether ketone), number of fusion segments, number of LIF segments, T score, use of teriparatide, and SRS–Schwab classification [11].
Data were analyzed for significance using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). The associations between groups were compared using chi-square and Mann-Whitney U-tests. Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation. A logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the risk factor of pseudoarthrosis. Initially, a univariate analysis was performed on each assessed covariate. A multivariate logistic regression analysis was then employed to determine the independent relationship between bony fusion and LIF-related variables with p<0.10 on univariate analysis. A p-value of <0.05 was considered significant.
Intervertebral fusion at LIF segments was observed in 80 segments (71.4%) at 12 months after surgery. Fusions were observed on the concave (autologous IBG side), convex (porous HAp/Col composite side), and both concave and convex slots in 74 (66.1%), 42 (37.5%), and 41 (36.6%) segments, respectively. The fusion rate was significantly higher in the concave slot than in the convex slot (p<0.001) (Table 2). Consequently, pseudoarthrosis was noted in 32 segments (28.6%) at 12 months after surgery. Seventeen patients (40.5%) obtained fusion at all LIF segments and were classified into the fusion group. Alternatively, 25 patients (59.5%) were classified into the nonfusion group (Table 1). Moreover, no significant association was found between the correction rate and fusion status at the LIF segments (p=0.689).
The univariate analysis revealed that the SRS–Schwab classification (p=0.020), the gap in the coronal plane (p=0.002), and the gap in the sagittal plane (p=0.033) were significantly associated with intervertebral fusion (Table 3). On the contrary, other parameters had no association with intervertebral fusion at LIF segments. A logistic regression analysis of intervertebral fusion was performed with SRS–Schwab classification (N or other), the gap in the coronal plane, and the gap in the sagittal plane as independent variables from the results of the univariate analysis. Finally, the gap in the coronal plane (p=0.030; odds ratio, 0.183; 95% confidence interval, 0.030–0.183) was significantly associated with fusion at the LIF segments (Table 4).
The kappa coefficients were obtained to assess interobserver agreement. For interobserver agreement, the estimated interobserver error correlation was 0.682 and 0.500 in the concave and convex slots, respectively. Therefore, the independent findings showed good to fair agreement.
A 75-year-old woman who had coronal imbalance with the coronal vertical axis (CVA) of −52 mm, Cobb angle (T11–L4) of 53°, and SRS–Schwab classification of D underwent lateral lumbar fusion surgery at the L2–3, L3–4, and L4–5 followed by conventional posterior spinal fusion from the T6 to the ilium (Fig. 2). Immediately after surgery, CT showed the gap in the coronal plane at L2–3 and L4–5 (Fig. 3). Consequently, CVA and Cobb’s angle were corrected to −21 mm and 19°, respectively, 12 months after surgery (Fig. 4). Postoperative CT scan revealed that intervertebral fusion was not obtained at L2–L3 or L4–L5 (Fig. 5).
Previous studies using a CT scan showed that the intervertebral fusion rate of LIF segments varied from 85% to 93% [12,13]. Berjano et al. [14] investigated 53 patients who underwent LIF at 34.5 months (range, 12–62 months) of follow-up. They reported that 87.1%, 10.2%, and 2.6% of the operated segments were completely fused, stable and probably fused, and diagnosed with pseudoarthrosis, respectively. In their study, both autologous bone and artificial bone materials, namely, calcium triphosphate, were used without basing on the criteria for selecting a bone graft. However, the difference between autologous bone and artificial bone materials for intervertebral fusion was not discussed. In 2018, Satake et al. [15] investigated 63 patients who underwent LIF surgery, using an allograft, and evaluated the fusion status using CT 2 years after surgery. Moreover, in this study, pseudoarthrosis was observed only in 16% of the patients. They concluded that the usage of percutaneous pedicle screws (PPs) was the only risk factor of pseudoarthrosis. Consequently, no allograft or PPs constructs were used in the present study. These previous studies mainly investigated patients with no spinal deformity but with degenerative conditions (e.g., lumbar spinal canal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, or degenerative disc disease). The pathogenesis (a degenerative disease in the previous study or spinal deformity in the present study) and the evaluation time after surgery (24–34.5 months in the previous study or 12 months in the present study) resulted in a lower fusion rate in the present study compared with those reported in previous CT-based studies.
The present study revealed a poor fusion rate of HAp/Col in the convex slot, although the previous clinical study indicated a better fusion rate of HAp/Col compared with the established porous β-tricalcium phosphate [16]. Moreover, HAp/Col was the bone substitute material with a bone-like nanostructure and was demonstrated to have a highly useful bone-like material in a previous clinical trial [17,18]. Kushioka et al. [9] evaluated the fusion rate of LIF filled with autologous IBG and HAp/Col for patients with ASD at postoperative 12 months. They reported that autologous IBG (71.2%) had a better fusion rate than porous HAp/Col (19.7%). Moreover, they reported that the concave side had a better fusion rate than the convex side (HAp/Col: concave 31.3%, convex side 8.8%, p=0.002; IBG: concave side 73.5%, convex side 68.8%, p=0044). They strictly evaluated the bony fusion status using a CT scan. However, the sample size was small (23 patients with ASD). Therefore, a large-scale study on patients with ASD is warranted. Similarly, the present study also indicated a superior intervertebral fusion rate in the concave slot filled with autologous IBG. Consequently, the intervertebral fusion rate was compared between the IBG graft and HAp/Col grafted manner to the concave and convex slots.
The previous study indicated the advantage of intervertebral fusion using teriparatide. Ebata et al. [19] conducted a randomized trial and evaluated the fusion rate in 66 patients who underwent PLIF or transforaminal LIF (TLIF). They classified the participants into two groups based on their weekly usage of teriparatide after PLIF/TLIF. They concluded that the weekly administration of teriparatide accelerated the bone formation at the fusion segment. Similarly, Ushirozako et al. [20] recently conducted a multicenter study to analyze the predictors of intervertebral fusion after PLIF. The result of their study also showed that a weekly teriparatide administration was significantly associated with a successful fusion at the operated segments. On the contrary, the results of the present study did not show any significant association between the usage of teriparatide and intervertebral fusion. However, the result of the present study indicated that the placement of LIF had an impact on intervertebral fusion rather than the usage of teriparatide.
The unique aspect of the present study was the evaluation of the LIF segment using CT scan immediately after surgery. The logistic regression analysis revealed that the location of the LIF cage, endplate injury, and gap in the sagittal plane were not associated with fusion at the LIF segments. In 2018, Alimi et al. [21] investigated 84 patients with 145 functional spinal segments and concluded that cage positioning had no impact on the radiographic outcome. The significance of the present study was that the gap between the endplate and LIF cage in the coronal plane was significantly associated with pseudoarthrosis at PO1Y. Conversely, the gap in the sagittal plane did not show a significant association with intervertebral fusion. Asymmetry wedging and the lateral slip of the intervertebral segment in the lumbar spine were characteristic radiographic findings in patients with ASD. Previous studies revealed that a larger LIF cage can provide a strong correction in the coronal plane with a 40%–75% correction rate, which is more than that in the sagittal plane [22]. Osseous tissue release, especially lateral bridging spur in the LIF procedure and compression force in the convex side in the posterior procedure, is recommended to eliminate the gap in the coronal plane. Otherwise, a coronal-angled LIF cage should be used for patients with a rigid wedged deformity.
This study has several limitations. First, this was not a prospective randomized control trial but a retrospective comparative study. In the present study, bone grafting to the LIF slot was defined in the series because several surgeons performed LIF for ASD. Numerous IBG is desirable to avoid pseudoarthrosis after correction surgery for ASD. However, obtaining enough bone graft from the iliac bone for multiple segments is sometimes difficult. A hybrid bone graft strategy was made before starting the LIF for treating ASD. IBG and HAp/Col was grafted in the concave and convex slots because the concave slots filled with autologous IBG exerted more compressive force on the cage than the convex filled with HAp/Col. Therefore, this study could not simply compare the intervertebral fusion rate by bone graft materials or by concave/convex side. Second, deriving the causal association between the predictor and fusion status was difficult because this was a cross-sectional study. Third, the sample size was small (n=42) because this was a single-institution study. Further evaluation, such as a prospective multicenter study, is needed to understand the definite risk factor for pseudoarthrosis at the LIF segment. However, it is believed that this is the first study to show that the gap in the coronal plane is associated with intervertebral fusion of ASD at the LIF segments. Moreover, this study is believed to significantly contribute to achieving better intervertebral fusion after correction surgery in patients with ASD.
The intervertebral fusion rate of patients who underwent ASD surgery at the LIF segment was 71.4% at PO1Y. Moreover, the intervertebral fusion rate was significantly higher on the concave slot filled with autologous IBG than on the convex slot filled with a porous HAp/Col composite. The gap in the coronal plane was a risk factor for pseudoarthrosis at the LIF segment. Therefore, grafting an autologous IBG in the LIF cage and proper fit of the LIF cage to the vertebral endplate are a key to enhancing the fusion rate.
Conflict of Interest
Conflict of interest
MM: relevant financial activities outside the submitted work: NuVasive Japan (consultancy, institutional grant). No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Fig. 1
The concave slot of the lumbar interbody fusion cage was filled with an autologous iliac crest bone graft (IBG), and the convex slot was filled with a porous hydroxyapatite/type 1 collagen (Hap/Col) composite.
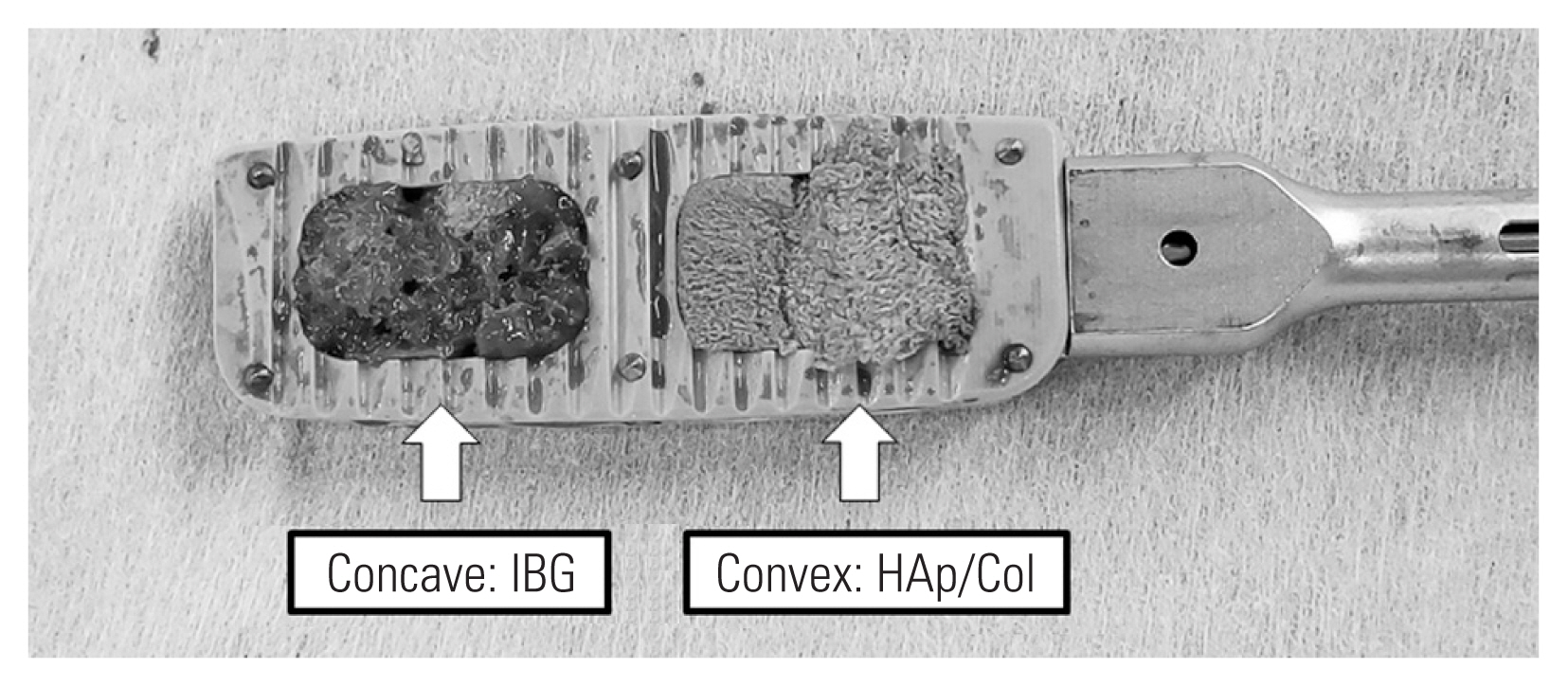
Fig. 2
Case illustration: a 75-year-old female. (A) Posterior-anterior whole spine radiograph in the standing position indicated coronal imbalance with coronal vertical axis of −52 mm. (B) Lateral whole spine radiograph in standing position.
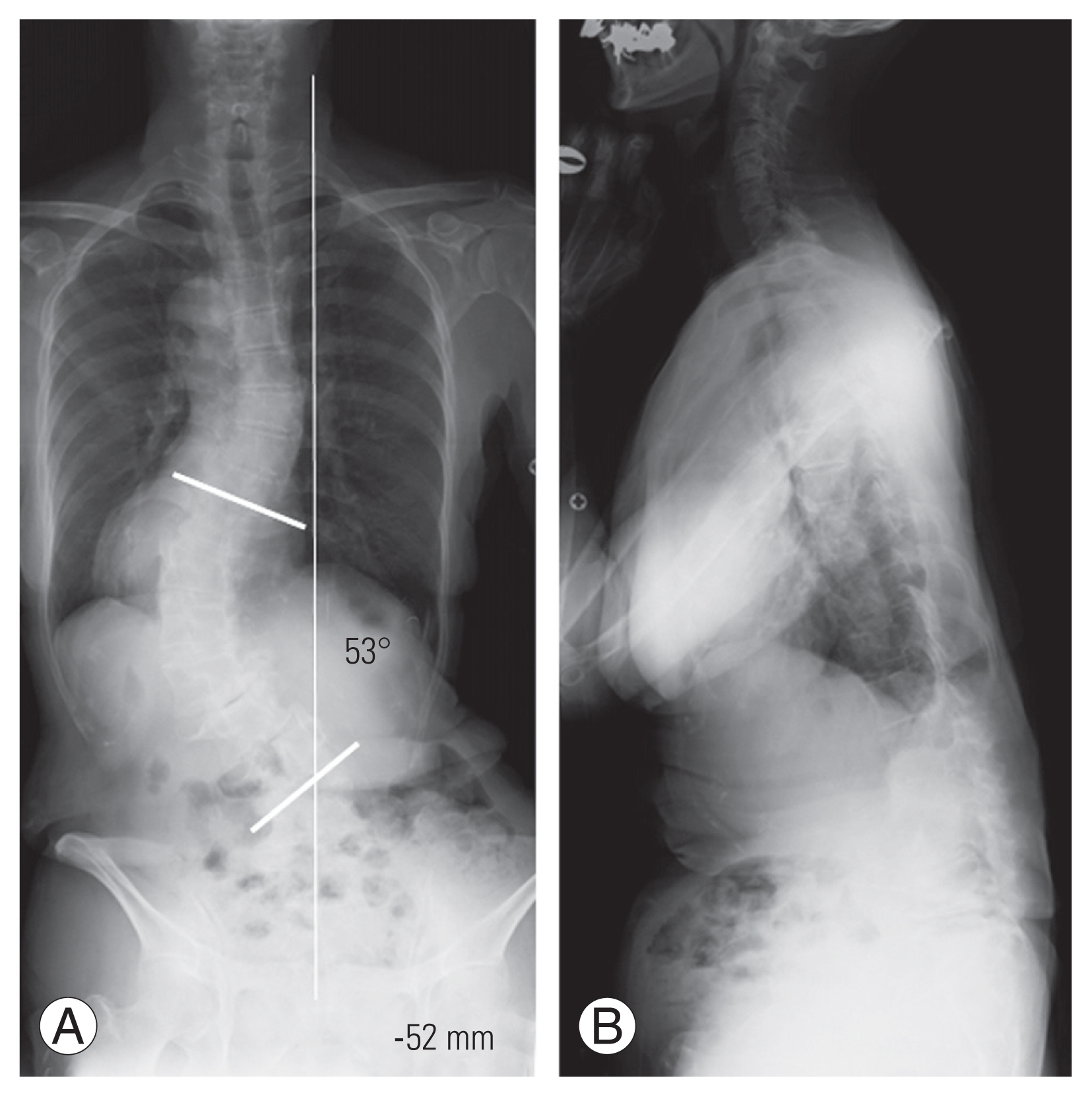
Fig. 3
Lumbar fusion at the L2–L3, L3–L4, and L4–L5, followed by conventional posterior spinal fusion from the T6 to the ilium was performed. Immediate after surgery, computed tomography showed the gap in coronal plane at L2–3 (A, arrow) and at L4–5 (B, arrow).
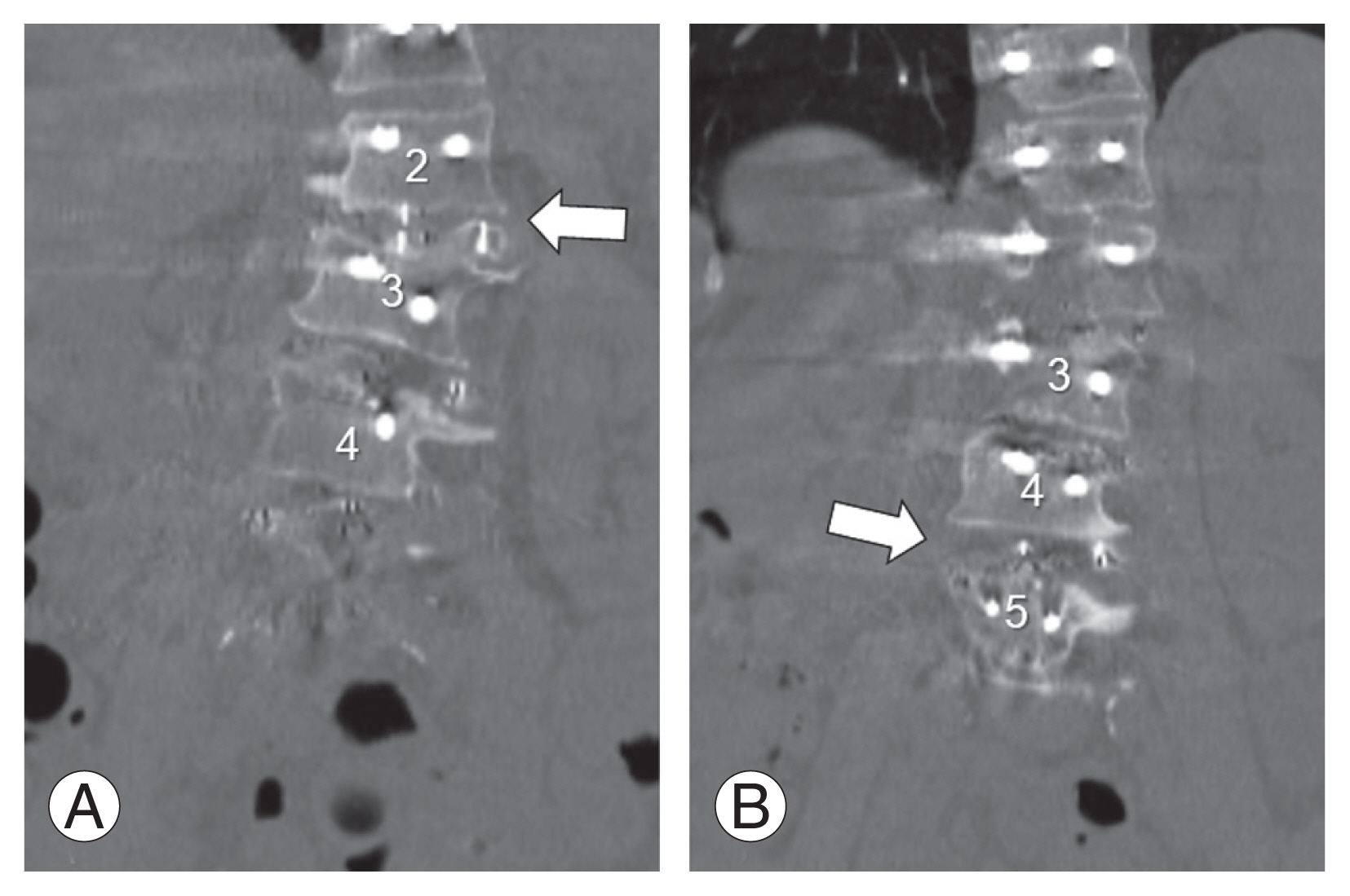
Fig. 4
(A) Posterior-anterior whole spine radiograph in the standing position 12 months after surgery. (B) Lateral whole spine radiograph in standing position 12 months after surgery.
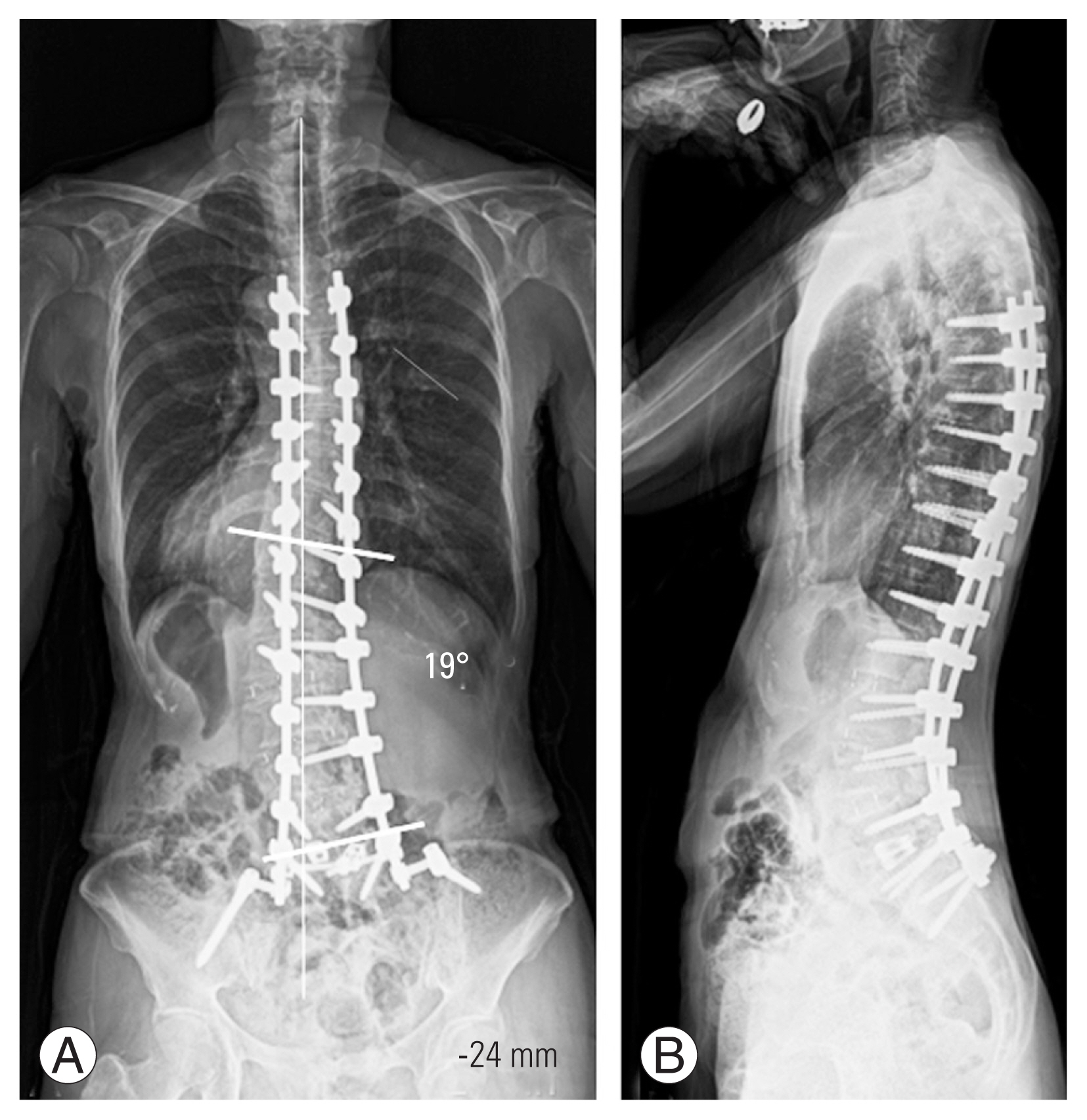
Fig. 5
Postoperative computed tomography scan 12 months after surgery. Intervertebral fusion was not obtained at the L2–L3 or L4–L5 (white arrows). White arrow indicated that the gap between the lumbar interbody fusion cage and inferior endplate in the coronal plane remained.
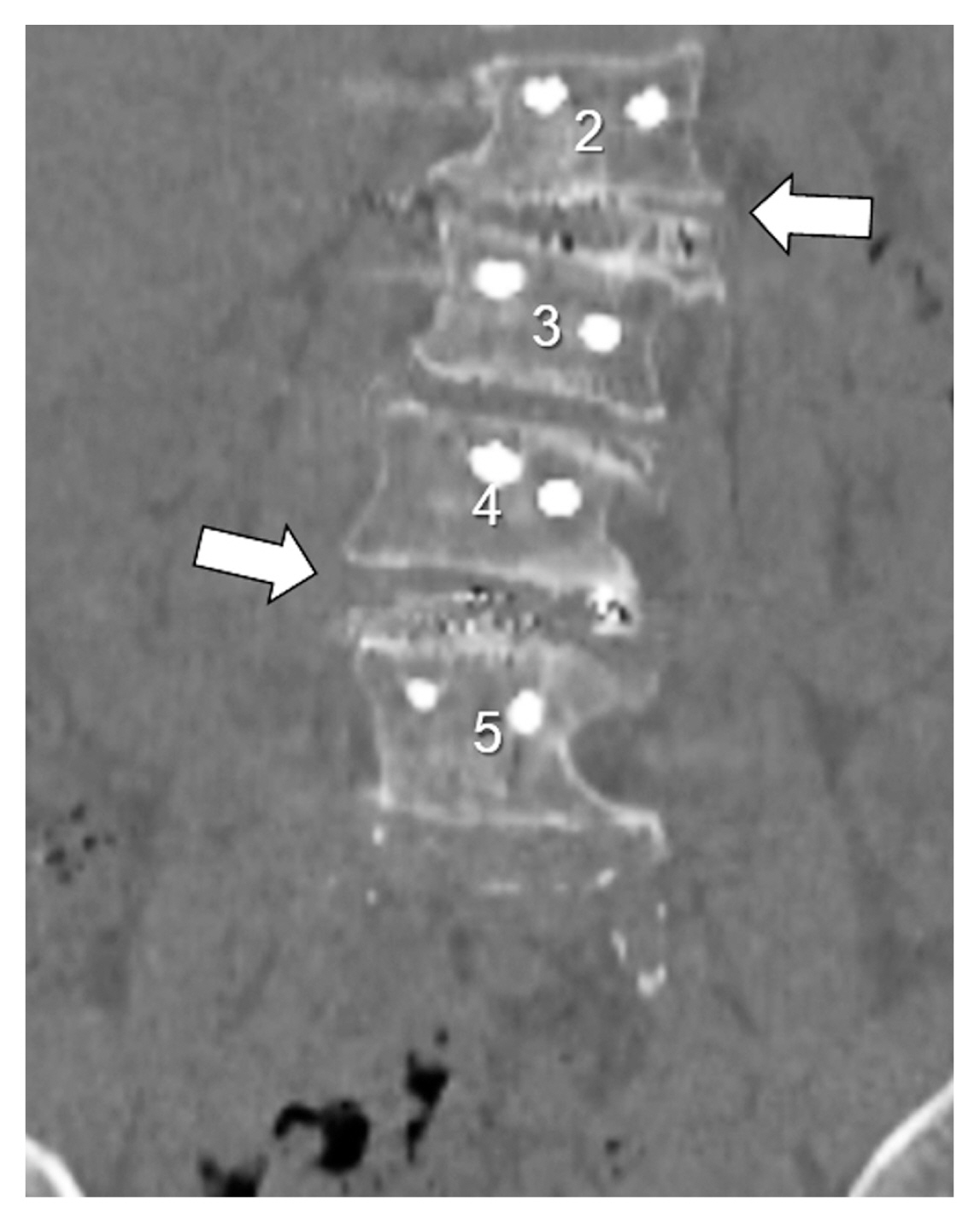
Table 1
Demographic characteristics of the participants
Table 2
Fusion rates of concave and convex slots at postoperative 1 year
| No. (%) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|
| Concave: IBG | 74 (66.1) | <0.001* |
| Convex: Hap/Col | 42 (37.5) |
Table 3
Results of the univariate analysis of fusion
| Variable | Value | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 0.547 | |
| <65 | 24/32 (75.0) | |
| ≥65 | 59/80 (73.8) | |
| Gender | 0.444 | |
| Male | 3/5 (60.0) | |
| Female | 77/107 (72.0) | |
| Smoking | 0.196 | |
| + | 1/3 (33.3) | |
| − | 79/109 (72.5) | |
| Intervertebral level LIF performed | 0.616 | |
| L1–2 | 5/9 (55.6) | |
| L2–3 | 22/32 (71.0) | |
| L3–4 | 33/43 (76.7) | |
| L4–5 | 20/29 (69.0) | |
| Material of LIF cage | 0.260 | |
| PEEK | 48/70 (68.6) | |
| Titanium alloy | 32/42 (76.2) | |
| No. of fusion segments | 0.214 | |
| ≤7 | 17/21 (81.0) | |
| >7 | 63/91 (69.2) | |
| Fusion to pelvis | 0.105 | |
| + | 51/76 (67.1) | |
| − | 29/36 (80.6) | |
| T score | 0.367 | |
| ≥1.0 | 30/46 (65.2) | |
| −1.0–>−2.5 | 29/40 (72.5) | |
| ≤−2.5 | 21/26 (80.8) | |
| Use of teriparatide | 0.537 | |
| + | 44/62 (71.0) | |
| − | 36/50 (72.0) | |
| SRS–Schwab classification | 0.020* | |
| T: thoracic only | 40/59 (67.8) | |
| T/L: thoracolumbar/lumbar only | 15/21 (71.4) | |
| D: double curve | 20/21 (95.2) | |
| N: no major coronal deformity | 5/11 (45.5) | |
| Location of LIF | 0.684 | |
| Anterior | 26/35 (74.3) | |
| Middle | 49/71 (69.0) | |
| Posterior | 5/6 (83.3) | |
| End plate injury | 0.159 | |
| + | 14/23 (60.9) | |
| − | 66/89 (74.2) | |
| Gap in coronal plane | 0.002* | |
| + | 6/16 (37.5) | |
| − | 74/96 (77.1) | |
| Gap in sagittal plane | 0.033* | |
| + | 11/21 (52.4) | |
| − | 69/91 (75.8) |
Table 4
Logistic regression analysis of the relationship between fusion and related factors
| Variable | p-value | Odds ratio (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| SRS–Schwab classification | 0.618 | 1.114 (0.728–1.706) |
| Gap in the coronal plane | 0.030* | 0.183 (0.040–0.845) |
| Gap in the sagittal plane | 0.928 | 0.936 (0.221–3.964) |
References
1. Soroceanu A, Burton DC, Oren JH, et al. Medical complications after adult spinal deformity surgery: incidence, risk factors, and clinical impact. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016 41:1718–23.

2. Yamato Y, Matsuyama Y, Hasegawa K, et al. A Japanese nationwide multicenter survey on perioperative complications of corrective fusion for elderly patients with adult spinal deformity. J Orthop Sci 2017 22:237–42.


3. Smith JS, Klineberg E, Lafage V, et al. Prospective multicenter assessment of perioperative and minimum 2-year postoperative complication rates associated with adult spinal deformity surgery. J Neurosurg Spine 2016 25:1–14.


4. Dakwar E, Cardona RF, Smith DA, Uribe JS. Early outcomes and safety of the minimally invasive, lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach for adult degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus 2010 28:E8.

5. Isaacs RE, Hyde J, Goodrich JA, Rodgers WB, Phillips FM. A prospective, nonrandomized, multicenter evaluation of extreme lateral interbody fusion for the treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis: perioperative outcomes and complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010 35(26 Suppl): S322–30.

6. Schwab F, Ungar B, Blondel B, et al. Scoliosis Research Society-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: a validation study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012 37:1077–82.

7. Nakashima H, Kanemura T, Satake K, et al. Factors affecting postoperative sagittal alignment after lateral lumbar interbody fusion in adult spinal deformity: posterior osteotomy, anterior longitudinal ligament rupture, and endplate injury. Asian Spine J 2019 13:738–45.



8. Lee HS, Lee JH, Lee JH. A comparison of dynamic views using plain radiographs and thin-section three-dimensional computed tomography in the evaluation of fusion after posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery. Spine J 2013 13:1200–7.


9. Kushioka J, Kaito T, Makino T, et al. Difference in the fusion rate and bone formation between artificial bone and iliac autograft inside an inter-body fusion cage: a comparison between porous hydroxyapatite/type 1 collagen composite and autologous iliac bone. J Orthop Sci 2018 23:622–6.


10. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977 33:159–74.


11. Terran J, Schwab F, Shaffrey CI, et al. The SRS-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: assessment and clinical correlations based on a prospective operative and nonoperative cohort. Neurosurgery 2013 73:559–68.

12. Rodgers WB, Gerber EJ, Patterson JR. Fusion after minimally disruptive anterior lumbar interbody fusion: analysis of extreme lateral interbody fusion by computed tomography. SAS J 2010 4:63–6.



13. Malham GM, Ellis NJ, Parker RM, Seex KA. Clinical outcome and fusion rates after the first 30 extreme lateral interbody fusions. ScientificWorldJournal 2012 2012:246989.



14. Berjano P, Langella F, Damilano M, et al. Fusion rate following extreme lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J 2015 24(Suppl 3): 369–71.

15. Satake K, Kanemura T, Nakashima H, Ishikawa Y, Segi N, Ouchida J. Nonunion of transpsoas lateral lumbar interbody fusion using an allograft: clinical assessment and risk factors. Spine Surg Relat Res 2018 2:270–7.



16. Sotome S, Ae K, Okawa A, et al. Efficacy and safety of porous hydroxyapatite/type 1 collagen composite implantation for bone regeneration: a randomized controlled study. J Orthop Sci 2016 21:373–80.


18. Tsuchiya A, Sotome S, Asou Y, et al. Effects of pore size and implant volume of porous hydroxyapatite/collagen (HAp/Col) on bone formation in a rabbit bone defect model. J Med Dent Sci 2008 55:91–9.

19. Ebata S, Takahashi J, Hasegawa T, et al. Role of weekly teriparatide administration in osseous union enhancement within six months after posterior or transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for osteoporosis-associated lumbar degenerative disorders: a multicenter, prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2017 99:365–72.

20. Ushirozako H, Hasegawa T, Ebata S, et al. Weekly teriparatide administration and preoperative anterior slippage of the cranial vertebra next to fusion segment < 2mm promote osseous union after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2019 44:E288–97.


-
METRICS

- Related articles in ASJ
-
Complications of Posterior Vertebral Resection for Spinal Deformity2012 December;6(4)





