|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 15(5); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
The physiopathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis remains unknown. However, a multifactorial pathogenesis is being assumed. Besides biomechanical, biochemical, and genetic factors, some studies have focused on congenital or acquired abnormalities in the vestibular organ with consecutive development of scoliosis. This study aims to analyze a possible correlation between any vestibular organ congenital or acquired pathologies and scoliosis based on the current literature. Therefore, we conducted a literature search in three databases, with search terms such as “scoliosis,” “organ of balance,” “idiopathic scoliosis,” “vestibular organ,” “spine,” and “balance.” Fifteen studies were selected and used for research. The relationship between scoliosis and vestibular organ abnormalities was recorded from all included works. Seven studies demonstrated a direct correlation between vestibular organ anatomical abnormalities and the form of the scoliotic spine. Another study confirmed the influence of the pathology of the vestibular organ on scoliosis but questioned whether it had an impact on the formation or the progression of the curvature. Others demonstrated a temporal overlap of the embryonic development of the vestibular organ and the beginning of pre-scoliotic characteristics, but their relationship remained questionable. In three studies, the correlation remained unclear, and any context has been denied. It seems unlikely that an isolated vestibular disorder can trigger structural scoliosis. However, the vestibular system pathologies may certainly occur in the multifactorial genesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Whether the correlation refers to the expression or the progression of scoliosis or may even have an influence on both remains unclear. New treatment options could be derived from these findings with a positive influence on the course of the deformity.
Since the earliest human history (Galen 130–201 AD), scoliosis (scolios gr. Crooked, crooked) has been defined as a permanent lateral curvature of the spine with rotation and torsion of several vertebrae. With a total share of 80%, idiopathic scoliosis is the most common form, with the additional subdivision based on the first manifestation of infantile, juvenile, and adolescent. Its etiology, as the name idiopathic suggests, is unknown.
The theories for idiopathic scoliosis development are varied [1]. However, a multifactorial pathogenesis is being assumed [2]. Some previous studies stated that the cause of idiopathic scoliosis is not biomechanical, but biochemical. The endochondral length growth of the vertebral bodies occurs craniocaudally, while the periosteal thickness growth of vertebral arches occurs in an anterior-posterior direction. If the relationship between length and thickness growth is disturbed, a pathological curvature of the spine occurs, the direction of which is from the relative length of the vertebral bodies to the vertebral arches [3].
Other studies have suggested a genetic component, whereby the inheritance of the genetic factors is X-linked. Inhibited melatonin transfer (inhibition of the function of the inhibitory G proteins on the melatonin receptors) may also influence the development of scoliosis [4]. Interestingly, although controversial, a possible connection between the development of scoliosis and abnormalities in the vestibular organ may occur [5–8].
This systematic literature search aimed to answer the question whether a possible correlation between any vestibular organ congenital or acquired pathologies and scoliosis may occur.
We conducted an analysis of literature by searching in three databases, namely, Google Scholar, PubMed, and Livivo. The search terms “scoliosis,” “organ of balance,” “idiopathic scoliosis,” “vestibular organ,” “spine,” and “balance” were linked and entered.
The inclusion criteria are as follows: (1) participants had to be adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) patients, (2) patients must have undergone examination of the vestibular system, and (3) studies had to analyze the relationship between scoliosis and vestibular organ abnormalities.
Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) studies that included patients with other etiologies of scoliosis, (2) articles in a language other than English or German, and (3) case reports as well as follow-up investigations dealing with the same question. However, the latter two were included in the Discussion section.
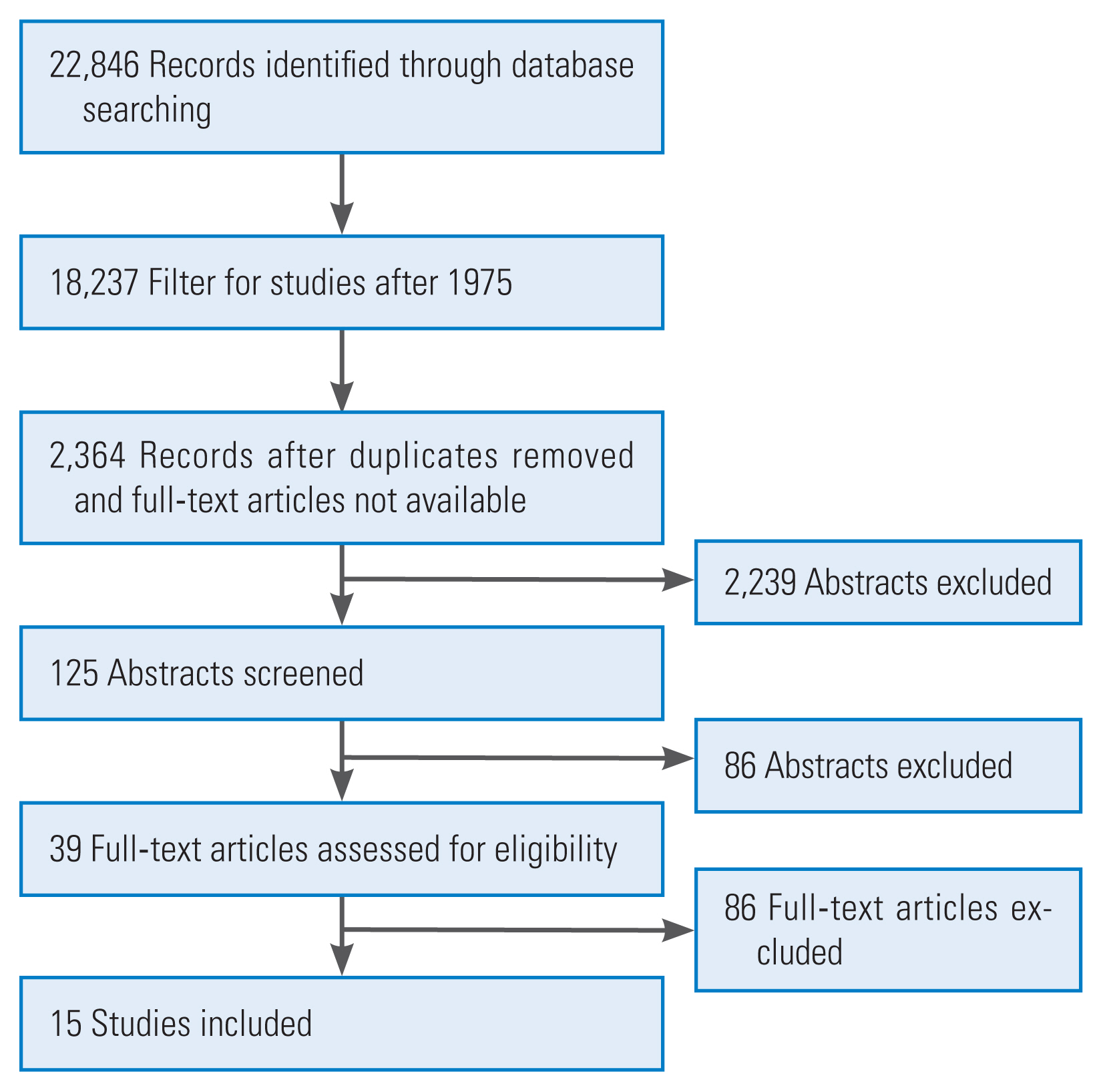
An initial search of all databases was performed, finding citations that could be included in the review. Firstly, titles and abstracts were screened and checked. If screening titles and abstracts was not enough to decide whether to accept or reject the study, the full text of the citation was analyzed for further evaluation. Afterwards, the full text of the potentially eligible articles was assessed for inclusion. At the end, 15 studies were selected for inclusion [9] (Fig. 1). The relationship between scoliosis and vestibular organ abnormalities was recorded from all included works.
The electronic search identified a total of 22,846 articles, of which 39 full-text articles were analyzed after considering the inclusion criteria. Fifteen studies were finally selected as they first provided a good overview of the range of correlation between the vestibular organ and the development or progression of scoliosis and second denied a correlation [5–8,10–20] (Table 1). Five studies demonstrated a direct relationship between an anatomical malformation of the vestibular organ and the form of the scoliotic spine [6,8,10–12]. Another study confirmed the influence of the pathology of the vestibular organ on scoliosis but questioned whether it had an impact on the formation or the progression of the curvature [8]. In three other studies, the relationship was not clearly verified; thus, further investigations were recommended [7,13,14]. Another study demonstrated a temporal overlap of the embryonic development of the vestibular organ and the beginning of pre-scoliotic characteristics, but their relationship remained questionable [5]. Three studies denied any context [15–17].
The development of AIS is based on a multifactorial genesis. The question of whether and, if so, to what extent the function and integrity of the vestibular organ have an influence on the formation or progression is an interesting approach, but still unclear.
A large number of studies in the past have demonstrated a direct relationship between functional and anatomical norm deviations of the vestibular organ and a scoliotic change. The causes and explanations are different. In this context, it is important to differentiate if the faulty vestibular information arises due to a malformation of the organ itself or during the processing of the afferents at the cortical and subcortical levels (Fig. 2).
Hitier et al. [5] demonstrated morphological changes in the vestibular organ in idiopathic scoliosis patients. In addition to an increased vertical alignment of the left-sided semicircular canals in the structure of the temporal bone, a deviation of the lateral and posterior semicircular canals was also found ipsilaterally. In the scoliotic group, the latter were located more laterally. Moreau et al. [4] left open whether this resulted from a malformation of the petrous bone or the labyrinth itself. However, a clear relationship between the side of scoliosis and the observed asymmetry could not be found.
Similar observations were made in a study published in 2006 analyzing a young woman with left-sided scoliosis. Here a labyrinthine temporal bone abnormality was also found [20]. For instance, scoliosis patients had a shorter distance between the center of the lateral and superior semicircular canals. In addition, the posterior canal was smaller [21,22]. In scoliosis patients, an abnormal relationship between the lateral and posterior vestibular canals was also found [23]. Unexpectedly, nystagmus was also demonstrated in the accompanying vestibular examinations (three-dimensional video-oculography with kinetic stimulations), and the authors postulated in addition a potential functional consequence behind the anatomical variation [23].
Even in recent clinical studies, the focus is on semicircular canals and macular organs as possible causes of the development of scoliosis. Antoniadou et al. [10] assessed the course of the earth-vertical after active head rotation. During the said rotation, the information from the semicircular canals and otoliths is particularly necessary; if the position in the room is checked after turning the head (subjective vertical), the necessary information comes from the macular organs. Significantly more misjudgments were found in the scoliosis patient group than in the control group, concluding that the vestibular receptors must have been damaged and that the affected adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis perceived a more inclined earth-vertical than healthy adolescents [10].
Possible dysfunction of the macular organs on the development of scoliosis was also examined clinically. Pollak et al. [7] determined the so-called vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials, which are necessary to stabilize the position of the head. The group of scoliosis patients showed a longer latency between the first positive (P13) and the following negative (N23) wave. A significant left-right difference with greater latency on the right side was also found. Based on the results, the authors confirmed their hypothesis of the relationship between vestibular dysfunction and scoliosis; however, they could not prove a relationship to the form of scoliotic spine [7].
In addition to anatomical and clinical results, a corresponding context could be observed in animal models. Lambert et al. [14] demonstrated in clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis) that unilateral vestibular lesions can provoke a scoliotic change in the spine and postulated that the asymmetrical pull of the muscles in connection with the soft, not yet ossified bone structure determines this structural modification. Since the skeletal system in humans is not mineralized for a long time, the authors concluded that the embryonic vestibular system pathology may already have caused scoliosis and then with increased length growth is exacerbated by constant asymmetrical muscular traction [14].
In addition to vestibular malformations, any other uncompensated bilateral disorder of the descending neural pathways and peripheral lesions can cause a unilateral change in the muscle tone of the autochthonous back muscles as well, resulting in a spine deformity [13].
Also, a dysfunction in the area of the brainstem favors the formation and progression of scoliosis [8,24]. In particular, if the vestibulospinal tract, whose function is to transmit position, balance reflexes, and control the axial muscles, is damaged unilaterally, an increased risk of developing scoliotic deformity is assumed. However, whether the damage is partly responsible for progression or for the development of scoliosis is unclear.
In addition to the subcortical neural pathways, magnetic resonance imaging examinations revealed that superior cerebral areas may be responsible for the development of scoliosis as well. For example, in scoliosis patients, those areas of the cerebral cortex involved in processing vestibular function were significantly smaller than in a corresponding group [25].
The abovementioned anatomical deviations could also be detected by clinical examination. In terms of body balance, significant differences could be demonstrated in scoliosis patients compared to healthy control groups. In this context, Byl and Gray [11] tried to differentiate if the cause was an anatomical-muscular malformation of the spine or faulty sensory afferences from the vestibular, visual, and/or proprioceptive systems. First, using a simple balance test, no abnormalities could be demonstrated between scoliosis patients and a healthy control group. However, if the tests became more complex, the scoliosis patients performed significantly worse, showing that the authors neglected a simple motor-related cause. Otherwise, they would have expected malfunctions, even during simple tests [11]. Rather, a fault in the entire sensorimotor process was assumed.
Other studies examined the correlation between the visual, proprioceptive, and vestibular systems in scoliosis patients. Independently of one another, they concluded that scoliosis patients showed an increased body fluctuation and poorer balance regulation in situations with visual or proprioceptive stimuli [26–29]. Pialasse et al. [30] observed an increased lateralization of the upper body as well as an increased weight distribution under the ipsilateral sole of the foot in comparison to a healthy control group after caloric stimulation of the vestibular organ. The authors assumed the cause to be pathological central sensory processing, which in turn leads to altered sensory processes [30]. Even after surgical correction of the deformity, these restrictions remained, which makes an influence of the spinal curvature unlikely [31]. In addition to the disturbed equilibrium reflexes, differences in the cognitive processing between visual and sensory information seem to exist [29].
Despite the suspected relationship between scoliosis and vestibular organ abnormalities, which new treatment approaches can be derived remains unclear. Some authors underline the necessity to identify patients with sensomotoric control disorders to intervene in a targeted manner with the aim of avoiding progression of the curve [32]. However, no clinical studies have been conducted on this.
In summary, many of the currently available studies with an evidence level of III–IV indicate a correlation between scoliosis and vestibular organ abnormalities; however, a clear dependency could not be determined across all articles [15].
It seems unlikely that an isolated vestibular disorder can trigger structural scoliosis. However, vestibular system pathologies may certainly be a building block in the multifactorial genesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Whether the relationship refers to the expression or the progression of scoliosis or may even have an influence on both remains unclear. Based on the results, the question as to how far balance exercises, as an additional treatment option besides the common ones, can further influence the course of scoliosis positively should be addressed in further studies.
Conflict of Interest
Conflict of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Fig. 2
Different localization of pathologies of the whole vestibular system that might have an influence on the formation or progression of scoliosis.
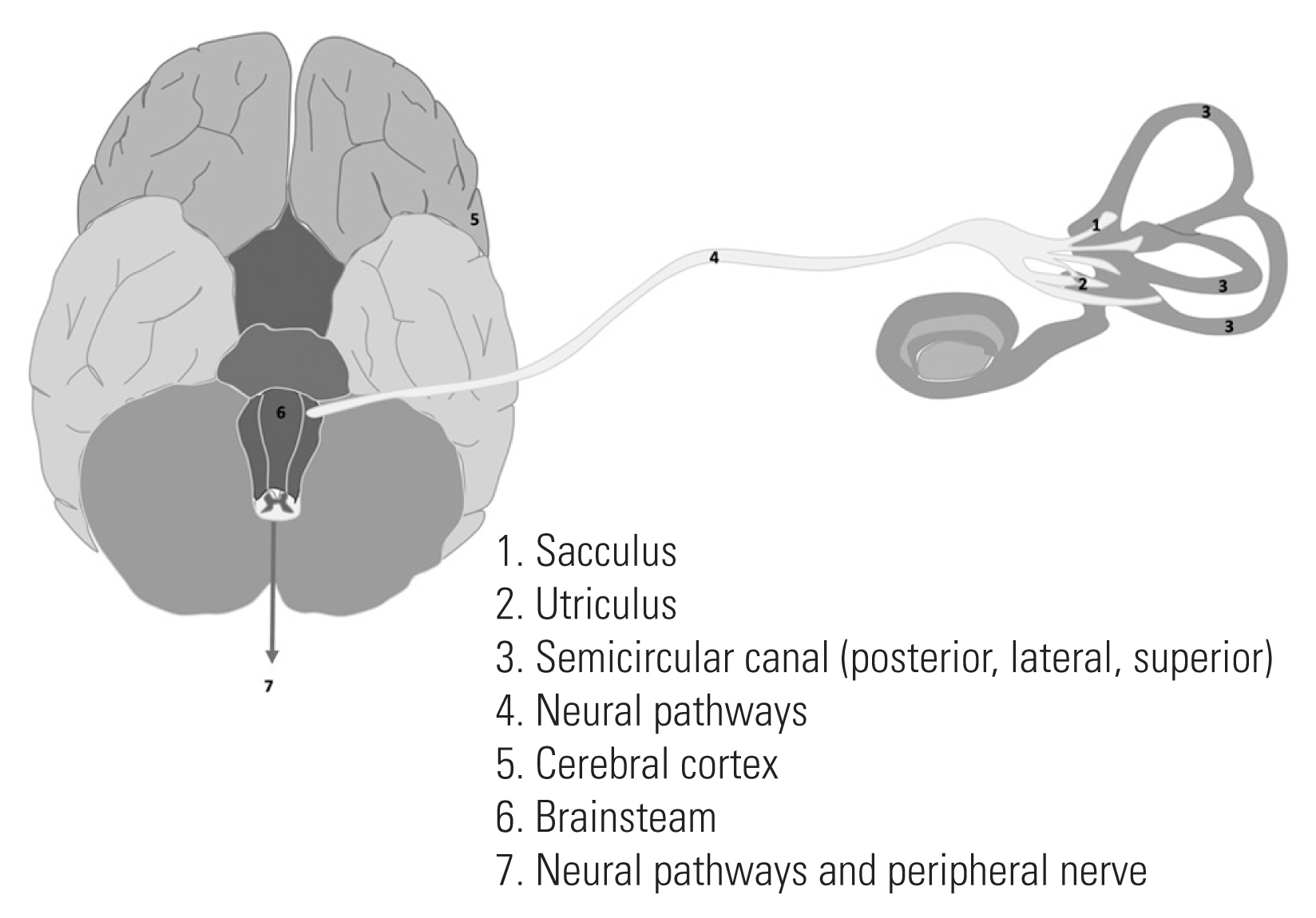
Table 1
Overview of the investigations
| Author | Test method | Follow-up | Results | Level of evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antoniadou et al. [10] (2018) | Measurement of the deviation from the vertical gravity with and without visual feedback using an electromagnetic location sensor | One-time measurement | Deviation from the gravitational vertical in AIS patients > control group (especially with closed eyes) | Level 3 |
| Byl and Gray [11] (1993) | Equilibrium reactions using a force plate stabilometer with and without the challenge of the somatosensory and visual system (active posturography) | 1 Year (every 3 months) | When the somatosensory / visual system is challenged: fluctuation of AIS patients > control group | Level 3 |
| Catanzariti et al. [15] (2014) | Question whether a unilateral, isolated vestibular lesion induces AIS | One-time measurement | It could not be confirmed that a unilateral, isolated vestibular lesion induces AIS | Level 2 |
| Cheung et al. [16] (2002) | Adaptation of a subjectively perceived laser line projection to the earth vertical (horizontal / vertical) in dark surroundings | One-time measurement | AIS patients = control group | Level 3 |
| Romano et al. [18] (2008) | Impact of scoliosis on balance and importance for physiotherapy | One-time measurement | Improvement in scoliosis leads to improved balance; training of the functionally impaired vestibular organ is more conceivable therapeutically than orthopedic bony correction. | Level 4 |
| Hawasli et al. [6] (2015) | Idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents and the role of the vestibular organ | One-time measurement | Many studies with evidence categories III–IV found a connection between the malfunction of the vestibular organ and scoliosis. However, this could not be confirmed in all studies. | Level 3 |
| Hitier et al. [5] (2015) | MRI examination of the orientation of the lateral semicircular canal, position of the semicircular canals to the midline; vestibulonystagmography of the lateral semicircular canal after bithermal caloric irrigation | One-time measurement | MRI: AIS patients ≠ control group | Level 3 |
| In AIS patients, the lateral semicircular canal on the left side was more vertical and further from the midline than in the control group | ||||
| Krödel et al. [17] (1997) | Body fluctuation with force plate; subjective visual vertical; electronystagmography | One-time measurement | No significant differences between scoliosis patients and control group | Level 4 |
| Lambert et al. [13] (2009) | Unilateral labyrinthectomy (n=15); removal of the horizontal and anterior semicircular canal ampoule (n=4) | Until the metamorphosis to the frog is completed | Removal in early larval stage: stagnation of development; removal in the later larval stage: curvature of the body and tail in the direction of the lesion due to weaker contraction of the axial muscles on this side scoliosis in young adult frogs, no skeletal deformations | Level 2 |
| Lambert et al. [14] (2013) | Unilateral labyrinthectomy followed by neurological examination of the vestibulospinal pathways | Until the metamorphosis to the frog is completed | Significantly lower increase in SVr discharges on the contralateral side regardless of the strength or frequency of the stimulus; ipsilateral SVr unaffected. | Level 2 |
| Pi_alasse and Simoneau [19] (2014) | Balance test by means of a force plate under triggering of the vestibular system with 1 mA (electrode on the mastoid) | 12 Months | 3 Case reports: (1) improvement of balance after surgical correction; (2) no significant improvement through bracing; (3) operative spinal straightening did not adjust the balance ability to that of the control group. | Level 4 |
| Pialasse et al. [8] (2013) | Hypothesis that patients with larger Cobb-Winkel (>35°) show more vestibular reactions | One-time measurement | Confirmation of the influence of the vestibular organ in the axial length growth. Further studies are required. | Level 3 |
| Pollak et al. [7] (2013) | VEMP of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, latency comparison | One-time measurement | (1) Significantly longer N23 (first negative wave) latencies than controls | Level 3 |
| (2) High correlation between the age and N23 latencies on the right | ||||
| (3) No correlation between scoliosis angle and VEMP latencies | ||||
| Sahlstrand et al. [12] (1978) | Stabilometry using a force plate, fluctuation in the sagittal and lateral direction | 6 Weeks (before the start of treatment, after 1 week, after 6 weeks) | AIS patients with significantly poorer posture control, especially with proprioceptive challenges, both mild and left convex scoliosis had poorer posture control than more severe cases | Level 3 |
| Shi et al. [20] (2006) | MRI skull for abnormalities | One-time measurement | Posterior vault of the skull in AIS smaller, left larger than in the control group | Level 4 |
References
1. Kikanloo SR, Tarpada SP, Cho W. Etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a literature review. Asian Spine J 2019;13:519–26.




2. Kouwenhoven JW, Castelein RM. The pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:2898–908.


3. Neugebauer H. Scoliosis, metabolism and growth of the vertebral column (author‘s transl). Arch Orthop Unfallchir 1976;85:87–99.



4. Moreau A, Akoume Ndong MY, Azeddine B, et al. Molecular and genetic aspects of idiopathic scoliosis: blood test for idiopathic scoliosis. Orthopade 2009;38:114–6.



5. Hitier M, Hamon M, Denise P, et al. Lateral semicircular canal asymmetry in idiopathic scoliosis: an early link between biomechanical, hormonal and neurosensory theories? PLoS One 2015;10:e0131120.



6. Hawasli AH, Hullar TE, Dorward IG. Idiopathic scoliosis and the vestibular system. Eur Spine J 2015;24:227–33.



7. Pollak L, Shlamkovic N, Minewicz A, Mirovsky Y. Otolith dysfunction as a possible cause for the development of idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop 2013;33:293–7.


8. Pialasse JP, Laurendeau S, Descarreaux M, Blouin J, Simoneau M. Is abnormal vestibulomotor responses related to idiopathic scoliosis onset or severity? Med Hypotheses 2013;80:234–6.


9. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Open Med 2009;3:e123–30.



10. Antoniadou N, Hatzitaki V, Stavridis SI, Samoladas E. Verticality perception reveals a vestibular deficit in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Exp Brain Res 2018;236:1725–34.



11. Byl NN, Gray JM. Complex balance reactions in different sensory conditions: adolescents with and without idiopathic scoliosis. J Orthop Res 1993;11:215–27.


12. Sahlstrand T, Ortengren R, Nachemson A. Postural equilibrium in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Acta Orthop Scand 1978;49:354–65.


13. Lambert FM, Malinvaud D, Glaunes J, Bergot C, Straka H, Vidal PP. Vestibular asymmetry as the cause of idiopathic scoliosis: a possible answer from Xenopus. J Neurosci 2009;29:12477–83.



14. Lambert FM, Malinvaud D, Gratacap M, Straka H, Vidal PP. Restricted neural plasticity in vestibulospinal pathways after unilateral labyrinthectomy as the origin for scoliotic deformations. J Neurosci 2013;33:6845–56.



15. Catanzariti JF, Agnani O, Guyot MA, Wlodyka-Demaille S, Khenioui H, Donze C. Does adolescent idiopathic scoliosis relate to vestibular disorders?: a systematic review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 2014;57:465–79.


16. Cheung J, Sluiter WJ, Veldhuizen AG, Cool JC, van Horn JR. Perception of vertical and horizontal orientation in children with scoliosis. J Orthop Res 2002;20:416–20.


17. Krodel A, Straube A, Angerer M, Fritsch K. Spatial orientation and postural regulation in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 1997;135:203–9.


18. Romano M, Ziliani V, Atanasio S, Zaina F, Negrini S. Do imbalance situations stimulate a spinal straightening reflex in patient with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Stud Health Technol Inform 2008;140:307–9.

19. Pialasse JP, Simoneau M. Effect of bracing or surgical treatments on balance control in idiopathic scoliosis: three case studies. J Can Chiropr Assoc 2014;58:131–40.


20. Shi L, Heng PA, Wong TT, Chu WC, Yeung BH, Cheng JC. Morphometric analysis for pathological abnormality detection in the skull vaults of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis girls. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 2006;9:175–82.


21. Shi L, Wang D, Chu WC, et al. Automatic MRI segmentation and morphoanatomy analysis of the vestibular system in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Neuroimage 2011;54(Suppl 1): S180–8.


22. Shi L, Wang D, Chu WC, et al. Volume-based morphometry of brain MR images in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and healthy control subjects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:1302–7.



23. Rousie DL, Deroubaix JP, Joly O, Baudrillard JC, Berthoz A. Abnormal connection between lateral and posterior semicircular canal revealed by a new modeling process: origin and physiological consequences. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2009;1164:455–7.


24. Yamamoto H, Tani T, MacEwen GD, Herman R. An evaluation of brainstem function as a prognostication of early idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop 1982;2:521–8.


25. Wang D, Shi L, Chu WC, Burwell RG, Cheng JC, Ahuja AT. Abnormal cerebral cortical thinning pattern in adolescent girls with idiopathic scoliosis. Neuroimage 2012;59:935–42.


26. Haumont T, Gauchard GC, Lascombes P, Perrin PP. Postural instability in early-stage idiopathic scoliosis in adolescent girls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011;36:E847–54.


27. Kuo FC, Wang NH, Hong CZ. Impact of visual and somatosensory deprivation on dynamic balance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010;35:2084–90.


28. Lao ML, Chow DH, Guo X, Cheng JC, Holmes AD. Impaired dynamic balance control in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis and abnormal somatosensory evoked potentials. J Pediatr Orthop 2008;28:846–9.


29. Simoneau M, Mercier P, Blouin J, Allard P, Teasdale N. Altered sensory-weighting mechanisms is observed in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. BMC Neurosci 2006;7:68.




30. Pialasse JP, Descarreaux M, Mercier P, Blouin J, Simoneau M. The vestibular-evoked postural response of adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis is altered. PLoS One 2015;10:e0143124.