 |
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 14(3); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
The magnitude and potential duration of the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is something that most doctors currently in practice have yet to experience. While considerable information regarding COVID-19 is being published every day, it is challenging to filter out the most relevant or appropriate information for our individual practice. The Spine Society of Singapore convened via a teleconference on April 24, 2020 to collaborate on a national level and share collective wisdom in order to tackle the ongoing crisis. In the teleconference, 13 spine surgeons from across various hospitals in Singapore constituted the panel of experts. The following topics were discussed: repurposing of surgeons, continuity of spine services, introduction of telemedicine, triaging of spinal surgeries, preoperative testing, new challenges in performing spine surgery, and preparing for the post-pandemic era. While some issues required only the sharing of best practices, the Delphi panel method was adopted to form a consensus on others. Existing spine specific triage guidelines were debated and a locally accepted set of guidelines was established. Although preoperative testing is currently not performed routinely, the panel voted in favor of its implementation because they concluded that it is vital to protect themselves, their colleagues, and their patients. Solutions to operating room specific concerns were also discussed. This article reflects the opinions and insights shared during this meeting and reviews the evidence relevant to the issues that were raised. The rapid consensus reached during the teleconference has enabled us to be concerted, and thus stronger, in our national efforts to provide the best standard of care via our spine services in these challenging times. We believe that this article will provide some guidance for addressing COVID-19 in spine surgery and encourage other national/regional societies to conduct similar discussions that would help their navigation of this pandemic.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS CoV-2), was declared a worldwide pandemic on March 11, 2020 by the World Health Organization [1]. While exceptional amounts of healthcare and economic resources have been, and continue to be, diverted toward fighting this virus, the end of this modern-day world appears farther away. The magnitude and potential duration of this COVID-19 pandemic is something that most doctors currently in practice have yet to experience.
Both within and beyond the realm of the field of orthopedics, new perspectives, recommendations, and guidelines in relation to COVID-19 are being published every day, and this has been most useful in helping us survive in these unprecedented times. However, with a considerably high volume of information coming in, it is often difficult to identify the information that is most relevant or appropriate to individual practice. A phrase that has been increasingly used throughout this pandemic encapsulates the situation accurately: ŌĆ£We are in the same storm, but not the same boat.ŌĆØ This aptly describes the imperative for respective orthopedic societies to form a consensus on a national and subspecialty-specific level to tackle the ongoing crisis. To address this, the Spine Society of Singapore (SSS), comprising orthopedic and neurosurgical spine surgeons from institutions across Singapore, convened via a teleconference on the evening of April 24, 2020. This article reflects the opinions and insights shared during the meeting and reviews the evidence relevant to the various issues discussed.
The index case of COVID-19 in Singapore was an imported case from Wuhan, China, reported on January 23, 2020 [2]. The subsequent month saw the progressive implementation of proactive measures to slow the spread of COVID-19, including strict border controls, aggressive contact tracing, law-enforced quarantine in government facilities, and a low threshold for COVID-19 diagnostic swab tests. The efficacy of these swift draconian measures, guided in-part by bitter lessons learned during the 2003 SARS pandemic [3], was reflected by the low rate of new COVID-19 cases, garnering Singapore international praise for what appeared an early flattening of the curve [4,5]. However, this victory was relatively short-lived because the rapid spread of COVID-19 within migrant laborer dormitories emerged and soon resulted in Singapore having the highest number of confirmed cases among all South East Asian countries by April 21, 2020 [6]. This second wave of infection has highlighted the vulnerability of such underprivileged groups as well as the need to protect them. In response to the increasing rates of community spread, Singapore went into lockdown on April 7, 2020 and remains in lockdown at the time of writing this report [7].
During the aforementioned SSS teleconference, 13 spine surgeons from across various hospitals in Singapore, including all the public hospital heads of service, constituted the expert panel. All other local spine surgeons and orthopedic trainees who had expressed interest were invited to attend as members of the audience. The chairman of the meeting first updated the panel on the latest developments and evidence on COVID-19, with a focus on details relevant to spine surgery. Key issues were highlighted as per the section headings to follow. While some issues required only a sharing of the best practices, the Delphi panel method was adopted to form a consensus on issues [8], such as the triaging of spinal surgeries, preoperative testing, and new challenges during the surgery.
Similar to that in several other countries [9-11], the orthopedic workforce in Singapore is being repurposed in the aggressive management of the COVID-19 pandemic [12,13]. Spine services have inevitably experienced diversion of their manpower; however, with the culling of all elective load, most tertiary center-based spine services have not faced many consequences. However, smaller orthopedic spine services have had to adapt their rosters. While orthopedic spine surgeons in the latter context have usually already established close ties with their neurosurgeon colleagues, COVID-19 has mandated greater interdepartmental collaboration for ensuring the undisrupted provision of spine services despite diminished manpower.
Segregation of intra-department personnel is advised, especially in larger hospitals where this can be practically achieved. Within a tertiary hospitalŌĆÖs orthopedic department, consultants of the same subspecialty can divide themselves into two groups and strictly ensure that members of each group do not come in contact with one other. Some orthopedic departments have split themselves into teams to manage clinics and operating theaters. Segregation formats should also apply to the junior staff members who are attached to the teams of their respective consultants. Constant availability of care is paramount in orthopedic subspecialties, such as spine and trauma, that routinely receive patients who require urgent surgical intervention. Such segregation measures would help ensure continuity of service in case one of the subspecialty teams become contaminated and require to be quarantined.
Across all public hospitals in Singapore, surgical inpatient and outpatient workloads have already been reduced by 70% as per the government directive. The method used to achieve this in the outpatient setting is left to the discretion of individual spine surgeons, although the guiding principle has been, as described by Soh et al. [14], ŌĆ£all non-urgent spine appointments, such as referrals for osteoporotic compression fractures, or acute back pain without neurology, [being] rescheduled to later dates.ŌĆÖŌĆÖ Rescheduled patients are offered repeat analgesia prescriptions that they can collect without presenting to the clinic and given thorough return advice. Postoperative visits within 6 weeks of surgery have not been postponed because these fall under ŌĆ£essential services.ŌĆØ
Operating theaters are now running at about 20% capacity to ensure the conservation of resources, such as intensive care unit beds, personal protective equipment (PPE), and propofol, as well as to allow the diversion of nursing and anesthesia manpower for COVID-19 management. Consequently, all elective cases have been cancelled, and only urgent or semi-urgent cases are being treated. However, given the inherently wide spectrum and time-sensitive nature in which spine pathologies tend to present, triaging spine cases while balancing the duties of a spine surgeon and managing COVID-19 cases has proven challenging (as discussed in a subsequent section).
Tan Tock Seng Hospital and its affiliated National Centre for Infectious Diseases have collectively been designated as SingaporeŌĆÖs epicenter of the fight against COVID-19. All ambulances transporting patients with nonrespiratory and non-life-threatening conditions are being diverted away from this epicenter to other hospitals. Nationwide efforts to keep orthopedic inpatient admissions low have been aided by the publicŌĆÖs fear of being exposed to the virus within a hospital environment. However, it is difficult to deter some neurology-free, acute onset back pain, or sciatica patients from seeking hospitalization owing to their inability to cope with their symptoms at home. Similar to the situation before the break out of the COVID-19 pandemic, these patients continue to be admitted for appropriate work up and pain control before being discharged as early as possible to free up hospital beds. However, outpatient physiotherapy services (integral for the treatment of these patients) have been suspended following the implementation of lockdown laws.
The aforementioned challenges in clinical practice brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic raise the question of whether we can use present-day technology to improve patient care. In order to address the lack of outpatient physiotherapy services during the COVID-19 pandemic, telerehabilitation may prove a worthwhile solution. Telerehabilitation services were already gaining popularity before the COVID-19 pandemic because patients started to embrace the convenience and flexibility it affords [15]. In conjunction with wearables, telerehabilitation can also be used by surgeons to monitor their patientsŌĆÖ postoperative functional outcomes [16]. For example, a simple wearable device with an in-built pedometer could inform a surgeon about the postoperative improvement in the degree of spinal stenosis and claudication.
Rather than endless postponement of outpatient visits, where appropriate, spine surgeons should attempt to convert some of these into teleconsultations. This is especially applicable for simple cases, such as symptom review appointments for chronic back pain or appointments scheduled to analyze the imaging results. While a full physical examination is not possible during a teleconsultation, valuable information can be gained by asking the patient to demonstrate things, such as gait and power, or to perform tasks such as buttoning a shirt. Many spine services in Singapore have started trial teleconsultations to help provide continuity of care despite COVID-19. This has elicited a mixed response from the patients. In general, older patients find the technology challenging, while younger patients are glad to be spared a physical visit.
The shift in our meetings, teaching sessions, and conferences to online platforms has been an excellent way for us to familiarize ourselves with teleconferencing technology and to identify potential issues early to improve patient experience. Although the technology has already been available for few years, COVID-19 has encouraged doctors and patients to embrace and explore telemedicine [17]; while the COVID-19 pandemic is temporary, telemedicine is expected to continue in future clinical practices.
Thus far, only three sets of spine surgery-specific triage guidelines have been published in response to COVID-19 [18-20]. During the SSS teleconference, local spine surgeons largely agreed with these existing guidelines; however, they also debated over the following few:
(1) Cervical or thoracic myelopathy secondary to spinal stenosis should be considered semi-urgent if the patient has experienced recent or rapid deterioration. All other myelopathy cases should be considered elective, although the progressive nature of this disease warrants that these remaining cases be prioritized once elective surgeries are resumed. Care should be taken to avoid postponing these cases for too long (>4ŌĆō5 months), especially since we cannot predict the length of this crisis, and meanwhile, the list of patients requiring surgery will continue to grow.
(2) According to the National Health Service (NHS) guidelines, metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC) patients should not be offered surgery if resources are limited to the point where only selective emergency spinal surgery can be performed [20]. However, the North American Spine Society (NASS) guidelines categorized MSCC as its highest triage tier and recommended against its postponement [19]. While SSS acknowledged the stance of the NHS that the tendency for poorer prognosis and potential for significant resource utilization by MSCC patients meant that they should be given lower priority in times when resources are critically limited, it also recognized that cancer prognosis (as per the treating oncologist) as well as preoperative neurological function were crucial outcome determinants that need to be remembered. Tumor histology should also be considered because it influences to patient prognosis [21,22]. SSS thus stratified MSCC patients as per these factors, as shown in Table 1 [23-25].
(3) Chronic and persistent neurological deficit (that is relatively stable and not progressive) due to neurological compression, such as a foot drop from lumbar spondylosis or spondylolisthesis, should be managed conservatively during the crisis. However, if the case can be effectively treated via smaller day procedures, such as nerve root blocks, endoscopy, and microdiscectomy, they may be considered for the procedure sooner (during crisis time); however, these cases should not be prioritized over any other cases that have already been defined as urgent or semi-urgent (Table 1) [23-25].
The SSS used the terminology ŌĆ£urgent,ŌĆØ ŌĆ£semi-urgent,ŌĆØ and ŌĆ£elective,ŌĆØ to define the hierarchy of triage for surgery. An urgent case was defined as one that should not be postponed despite the ongoing crisis, a semi-urgent case was defined as one that should be allowed to proceed during the crisis if resources are available, and an elective case was defined as one that should be postponed until after the crisis. Table 1 summarizes the consensus of SingaporeŌĆÖs spine surgeons on how to triage spine surgeries during the COVID-19 crisis [23-25] and has been adapted from the comprehensive NASS guidelines to reflect the local opinion [19]. The orthopedic spine service of the National University Hospital has had a long-standing tradition of auditing all upcoming spine surgery cases every week and has reported this to be especially beneficial during the COVID-19 pandemic where resource availability is constantly changing. While the following set of guidelines provide a framework to help spine services triage their patients, the need to continually evaluate the operating lists on a case-by-case and resource-dependent basis remains crucial during this pandemic.
Preoperative testing for COVID-19 would play a key role in providing safety for all the stakeholders involved in non-emergency surgeries. The relevant types of testing that are currently available include real time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), the current gold standard [26,27], and serological testing for antibodies. RT-PCR may be performed with nasopharyngeal (NP), oropharyngeal (OP) or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL). Inadequate sampling, illness duration at the time of testing, and a low real time viral load may affect the sensitivity of the test.
While BAL RT-PCR samples provide the best sensitivity (93.3%) [28], OP and NP testing are used owing to their practical and less invasive nature. Initial NP RT-PCR testing is more sensitive than OP testing in both severe (73.3% versus 60.0%) and mild (72.1% versus 61.3%) COVID-19 cases [29]. A separate study demonstrated improvement in NT-PCR sensitivity (from 88.6%ŌĆō95.7%) when repeated after 24 hours in patients who initially tested negative [30]. Thus, NP RT-PCR is the current recommended investigation [31]. Conflicting findings, varying accessibility, and rapid innovation make it challenging to recommend a single ideal serological test [32]. However, the use of available serological testing as an adjunct with either NP or OP RT-PCR has been shown to yield combined sensitivities of >98% [33,34].
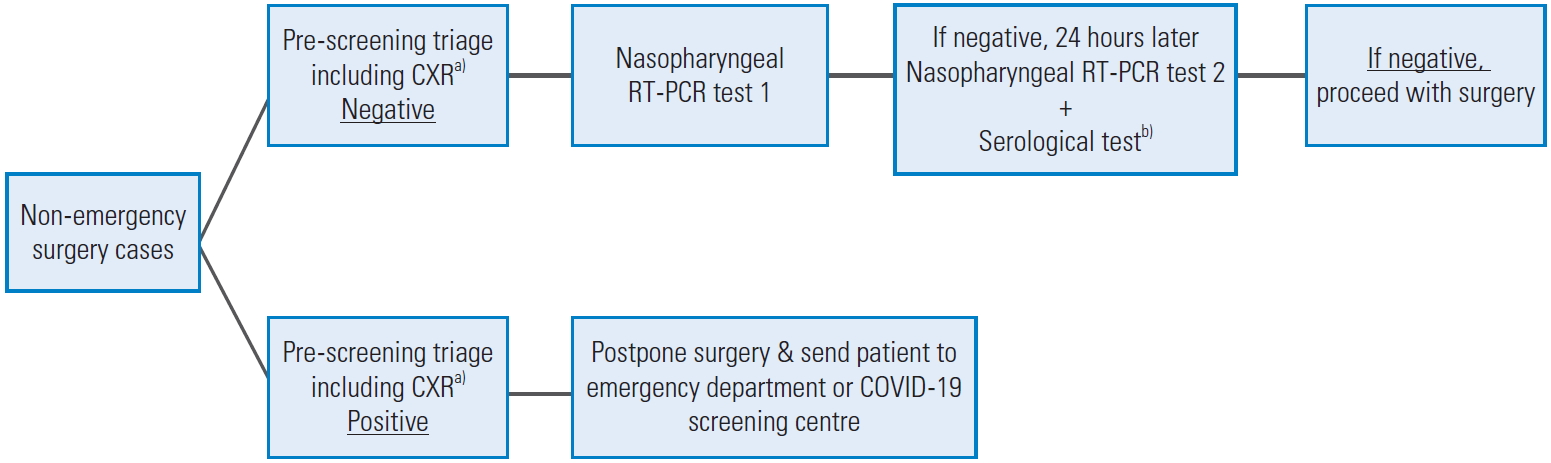
Currently, in Singapore, unless there is reason to suspect that a patient has contracted COVID-19, preoperative testing for the virus is not performed. Member surgeons of the SSS find this lack of preoperative testing concerning, especially in light of the current local situation where community spread is sufficiently rampant to warrant a nationwide lockdown. While acknowledging that newer testing kits may soon prove faster or more sensitive [35], based on the aforementioned evidence, the authors propose the implementation of a preoperative testing protocol, as shown in Fig. 1.
Ideally, 2 days before the surgery, patients should be admitted to isolation rooms in a contained ward designated for preoperative COVID-19 testing. If the designation of such a contained ward is not feasible, the patients may be required to self-quarantine at home for 2 days before the surgery, and travel between the hospital and home for testing strictly via private transport while donning N95 respirators (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health-approved respirators). As a standalone test, computed tomography (CT) imaging of the chest reportedly yields the best sensitivity (97%ŌĆō98%) for COVID-19 diagnosis [36,37]; although it would offer a great advantage in preoperative testing, considering the resource limitations, the authors feel that any available CT scanners would be better utilized in actual COVID-19 management; thus, this modality has not been included in our proposed protocol. To protect ourselves, our families, our colleagues and our patients, preoperative testing for COVID-19 should be implemented as early as possible [38]
Several new challenges in the performance of spine surgery have arisen owing to the COVID-19 pandemic. Total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA), and thus intraoperative neuromonitoring, are rapidly becoming unaffordable luxuries, considering the global shortage of propofol and the need to conserve these for the present and future COVID-19 patients requiring mechanical ventilation. While the use of TIVA and intraoperative monitoring remains warranted in cervical spine surgery as well as in cord compression cases, spine surgeons should be much more judicious in its use in any other types of spine surgery that is being performed during this pandemic.
Full PPE should be used when managing patients in whom COVID-19 infection has not been ruled out. Current recommendations on PPE effective against COVID-19 include either a pair of protective goggles or a face shield [39,40]; however, both the gears cause poor visualization when operating with a microscope. While day procedures, such as microdiscectomies, have become more relevant during the present resource-limited time, this challenge has begun to frustrate many spine surgeons. However, one of the authors recently decided to try a pair of swimming goggles and found the visibility of his surgical field to be better than that with the use of conventional PPE options (anti-fog swimming goggles are advised). Alternatively, this may also be a good opportunity for spine services to try or invest in a digital microscope.
Spine surgery often involves frequent and prolonged use of diathermies and high-speed burrs that are known to generate aerosols [41,42]. While there neither been a reported case where COVID-19 transmission occurred from patient to surgeon within the operating room, nor the existence of studies sampling these aerosols to determine their viral titers, the knowledge that significant SARS-CoV-2 viral loads can be found in the blood of infected patients is concerning to spine surgeons [43,44]. Therefore, the use of these tools should be minimized as much as possible. Where appropriate, Kerrison punches and osteotomes should be preferred over high-speed burrs. Although the relative vascularity of the spinal soft tissues effectively precludes the use of a scalpel blade in favor of a cutting diathermy, by keeping the sucker close to the diathermy tip, aerosolization can be minimized by eliminating as much of the aerosol as possible before it disperses [45]. It is advised that full PPE be worn by all operating room personnel during these aerosol generating procedures; further, it is recommended that these procedures be performed in facilities with high-efficiency particulate air┬Āfilters and closed circuit ventilation [39,46,47].
With countless outpatient appointments and surgeries being postponed and re-postponed, spine surgeons worldwide are bracing for the inevitable post-pandemic increase in surgical patients. While we remain hopeful regarding the ready availability of a COVID-19 vaccine in the near future, this is an ideal scenario that is not being depended on by majority of the medical community. The current reality is that if and when the situation improves, there will be slow and cautious reinstatement of our clinical capacities, with persistent risk of recurrent waves of COVID-19. Therefore, in this immediate post-pandemic era, it is likely that operating lists will remain stringent and that the triaging of cases will remain necessary. Preoperative testing for COVID-19 should continue, and the use of telemedicine in our outpatient services requires further development. Spine surgeons should take advantage of this critical time to adapt as much as possible because our clinical practice may never be the same again.
The SSS teleconference discussed many important issues that affect spine surgery in the presence of the COVID-19 pandemic. The rapid consensus has enabled us to be concerted, and thus stronger, in our national efforts to provide the best standard of care via our spine services in this challenging time. We hope that this article provides some guidance in addressing COVID-19 in spine surgery and encourages other national/regional institutes to conduct similar discussions to aid in their navigation of this pandemic.
Notes
Author Contributions
Conception & design: KAT, JYLO, GKPL; data acquisition: KAT, VNT, DC, GKPL; drafting of the manuscript: KAT, VNT; critical revision: KAT, VNT, DC, JYLO, GKPL; administrative support: KAT; and supervision: DC, JYLO, GKPL.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Preoperative testing for COVID-19 (protocol to start 2 days before the surgery). CXR, chest X-ray; RT-PCR, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019. a)Positive feature of pre-screening triage includes: temperatures >37.5┬░C, upper respiratory tract infection symptoms, dyspnoea, anosmia, positive travel history, positive contact history, and CXR findings suggestive of infection. b)Serological testing as per latest evidence and local capabilities (e.g., immunoglobulin G, immunoglobulin M, and total antibody titers).
Table┬Ā1.
Triage hierarchy for spinal conditions requiring surgical intervention (by consensus of the Singapore Spine Society)
| Triage category | Spinal conditions and considerations |
|---|---|
| Urgent | - Progressive or severe neurological deficit due to neurologic compression resulting from: |
| - Trauma | |
| - Disc herniation, especially if resulting in cauda equina syndrome | |
| - Infection (e.g., epidural abscesses) | |
| - Tumor | |
| - Spinal instability from any cause at risk of causing neurological injury (e.g., TLICS score Ōēź4 [23], SINS score Ōēź13 [24])a) | |
| - Surgical site infections | |
| Semi-urgent | - Myelopathy due to spinal stenosis with recent or rapid deterioration |
| - Tumors causing neurological compromise or spinal instability (SINS score >6) in cases that do not meet above urgent criteria | |
| - Infections yet to cause neurological deficit/spinal instability, but with inadequate response to pharmacological treatment | |
| - Spinal conditions causing intractable pain or severe functional limitations that have failed conservative management (to consider day procedures such as nerve root blocks, endoscopy, or microdiscectomy where appropriate) | |
| Elective | - Myelopathy due to spinal stenosis with neither recent nor rapid deterioration |
| - Chronic and persistent neurological deficit due to neurological compression, that does not already fall into the above categoriesb) | |
| - Spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis, or any degenerative spinal conditions that can be managed conservatively (at least for the duration of the crisis)b) | |
| - Deformity corrections (e.g., scoliosis, kyphosis, flatback syndrome) | |
| - Revision surgery that does not fall into the above categories |
a) Tumor cases are considered urgent if the following criteria are met: (1) present neurology no worse than the American Spinal Injury Association [25] C (2) prognosis >1 year. If these criteria are not met, and the patient remains a surgical candidate, then the case is considered semi-urgent.
References
1. World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
2. Ministry of Health Singapore. Confirmed imported case of novel coronavirus infection in Singapore: multi-ministry taskforce ramps up precautionary measures. Singapore: Ministry of Health Singapore; 2020.
4. CNA. WHO ŌĆśvery impressedŌĆÖ with SingaporeŌĆÖs COVID-19 response [Internet]. Singapore: CNA. 2020 [cited 2020 Apr 27]. Available from: https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/singapore/singaporevery-impressed-covid-19-coronavirus-responsewho-chief-12448486#main
5. Warrell M. COVID-19 leadership lessons from Singapore: be ready, be bold, be decisive. Forbes 2020 Mar 30
6. Smith N. How Singapore went from leading global Covid-19 efforts to having the most cases in SouthEast Asia. The Telegraph 2020 Apr 21
7. Ministry of Health Singapore. Circuit breaker to minimise further spread of COVID-19. Singapore: Ministry of Health Singapore; 2020.
8. Hsu CC, Sandford BA,The Delphi technique: use, consideration, and applications in the conventional, policy, and on-line environments. Silva CN, editors. Online research methods in urban and planning studies: design and outcomes. Hershey (PA): IGI Global; 2012. p.173ŌĆō92.
9. Stewart A. Italian spine surgeon aids respiratory care in converted orthopedic hospital: hereŌĆÖs his story. BeckerŌĆÖs Spine Review [Internet]. 2020 Apr 8 [cited 2020 Apr 27]. Available from: https://www.beckersspine.com/spine/item/48786-italian-spine-surgeon-aids-respiratory-care-in-converted-orthopedichospital-here-s-his-story.html
10. Meneghini RM. Resource reallocation during the COVID-19 pandemic in a suburban hospital system: implications for outpatient hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2020 S0883-5403(20): 30438ŌĆō1.

11. Sarpong NO, Forrester LA, Levine WN. WhatŌĆÖs important: redeployment of the orthopaedic surgeon during the COVID-19 pandemic: perspectives from the trenches. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2020 Apr 14 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.20.00574

12. Soh TL, Ding BT, Yap WM, Oh JY. Spine surgery and COVID-19: early experiences from Singapore. Spine 2020 Apr 16 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000003532

13. Liang ZC, Ooi SB. COVID-19: a Singapore orthopedic residentŌĆÖs musings in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med 2020 27:349ŌĆō50.



14. Soh TL, Ho SW, Yap WM, Oh JY. Spine surgery and COVID-19. J Bone Joint Surg 2020 Apr 15 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.20.00503

15. Van Egmond MA, van der Schaaf M, Vredeveld T, et al. Effectiveness of physiotherapy with telerehabilitation in surgical patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiotherapy 2018 104:277ŌĆō98.


16. Kim DH, Nam KH, Choi BK, Han IH, Jeon TJ, Park SY. The usefulness of a wearable device in daily physical activity monitoring for the hospitalized patients undergoing lumbar surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2019 62:561ŌĆō6.




17. Tanaka MJ, Oh LS, Martin SD, Berkson EM. Telemedicine in the era of COVID-19: the virtual orthopaedic examination. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2020 Apr 24 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.20.00609

18. American College of Surgeons. COVID-19 guidelines for triage of orthopaedic patients [Internet]. Chicago (IL): American College of Surgeons. 2020 [cited 2020 Apr 30]. Available from: https://www.facs.org/covid-19/clinical-guidance/elective-case/orthopaedics
19. Bono CM, Dohring EJ, Finkenberg JG, et al. NASS guidance document on elective, emergent and urgent procedures [Internet]. Burr Ridge (IL): North American Spine Society. 2020 [cited 2020 Apr 29]. Available from: https://www.spine.org/Portals/0/assets/downloads/Publications/NASSInsider/NASSGuidanceDocument040320.pdf
20. NHS England. Clinical guide for the management of patients requiring spinal surgery during the coronavirus pandemic [Internet]. Leeds: NHS England. 2020 [cited 2020 Apr 30]. Available from: https://www.england.nhs.uk/coronavirus/wp-content/uploads/sites/52/2020/03/specialty-guide-management-of-patients-requiring-spinal-surgery-v1-20-march-2020.pdf
21. Tan KA, Tan JH, Zaw AS, Tan JY, Hey HW, Kumar N. Evaluation of prognostic factors and proposed changes to the modified Tokuhashi score in patients with spinal metastases from breast cancer. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018 43:512ŌĆō9.


22. Tan JH, Tan KA, Zaw AS, et al. Evaluation of scoring systems and prognostic factors in patients with spinal metastases from lung cancer. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016 41:638ŌĆō44.


23. Lee JY, Vaccaro AR, Lim MR, et al. Thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score: a new paradigm for the treatment of thoracolumbar spine trauma. J Orthop Sci 2005 10:671ŌĆō5.



24. Fisher CG, DiPaola CP, Ryken TC, et al. A novel classification system for spinal instability in neoplastic disease: an evidence-based approach and expert consensus from the Spine Oncology Study Group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010 35:E1221ŌĆō9.


25. Ditunno JF Jr, Young W, Donovan WH, Creasey G. The international standards booklet for neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. American Spinal Injury Association. Paraplegia 1994 32:70ŌĆō80.

26. Lippi G, Simundic AM, Plebani M. Potential preanalytical and analytical vulnerabilities in the laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin Chem Lab Med 2020 Mar 16 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2020-0285

27. World Health Organization. Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in suspected human cases: interim guidance. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
28. Wang W, Xu Y, Gao R, et al. Detection of SARSCoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. JAMA 2020 e203786.

29. Yang Y, Yang M, Shen C, et al. Evaluating the accuracy of different respiratory specimens in the laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of 2019-nCoV infections. medRxiv 2020 Feb 17 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.11.20021493

30. Lee TH, Lin RJ, Lin RT, et al. Testing for SARS-CoV-2: can we stop at two? Clin Infect Dis 2020 ciaa459.



31. Ministry of Health Singapore; National Centre for Infectious Diseases; Agency for Care Effectiveness. PCR testing for COVID-19: where to swab? [Internet]. Singapore: Ministry of Health Singapore. 2020 [cited 2020 Apr 30]. Available from: https://www.moh.gov.sg/docs/librariesprovider5/default-document-library/pcr-testing-for-covid-19---where-to-swab-(24-april-2020).pdf
32. Long QX, Liu BZ, Deng HJ, et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat Med 2020 Apr 29 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0897-1


33. Guo L, Ren L, Yang S, et al. Profiling early humoral response to diagnose novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Clin Infect Dis 2020 ciaa310.



34. Zhao J, Yuan Q, Wang H, et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients of novel coronavirus disease 2019. SSRN Electron J 2020 Mar 3 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3546052

35. Tang YW, Schmitz JE, Persing DH, Stratton CW. The laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 infection: current issues and challenges. J Clin Microbiol 2020 JCM.00512-20.

36. Fang Y, Zhang H, Xie J, et al. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology 2020 200432.


37. Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, et al. Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: a report of 1014 cases. Radiology 2020 200642.


38. Lei S, Jiang F, Su W, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients undergoing surgeries during the incubation period of COVID-19 infection. EClinicalMedicine 2020 100331.



39. Rodrigues-Pinto R, Sousa R, Oliveira A. Preparing to perform trauma and orthopaedic surgery on patients with COVID-19. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2020 e20.00454.


40. Ong SWX, Tan YK, Sutjipto S, et al. Absence of contamination of personal protective equipment (PPE) by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2020 41:614ŌĆō6.


41. Nogler M, Lass-Florl C, Wimmer C, Mayr E, Bach C, Ogon M. Contamination during removal of cement in revision hip arthroplasty: a cadaver study using ultrasound and high-speed cutters. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2003 85:436ŌĆō9.


42. Yeh HC, Turner RS, Jones RK, Muggenburg BA, Lundgren DL, Smith JP. Characterization of aerosols produced during surgical procedures in hospitals. Aerosol Sci Technol 1995 22:151ŌĆō61.

43. Chen W, Lan Y, Yuan X, et al. Detectable 2019-nCoV viral RNA in blood is a strong indicator for the further clinical severity. Emerg Microbes Infect 2020 9:469ŌĆō73.



44. Lescure FX, Bouadma L, Nguyen D, et al. Clinical and virological data of the first cases of COVID-19 in Europe: a case series. Lancet Infect Dis 2020 S14733099(20): 30200-0.

45. Simpson AH, Dall G, Haas JG. COVID-19: potential transmission through aerosols in surgical procedures and blood products. Bone Joint Res 2020 9:200ŌĆō1.



46. Ti LK, Ang LS, Foong TW, Ng BS. What we do when a COVID-19 patient needs an operation: operating room preparation and guidance. Can J Anaesth 2020 67:756ŌĆō8.




47. Chang Liang Z, Ye Chong MS, Sim MA, et al. Surgical considerations in patients with COVID-19: what orthopaedic surgeons should know. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2020 Apr 24 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.20.00513

- TOOLS







