|
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 10(3); 2016 > Article |
Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the relationship between ligamentum flavum (LF) hypertrophy and lumbar segmental motion.
Overview of Literature
The pathogenesis of LF thickening is unclear and whether the thickening results from tissue hypertrophy or buckling remains controversial.
Methods
296 consecutive patients underwent assessment of the lumbar spine by radiographic and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Of these patients, 39 with normal L4ŌĆōL5 disc height were selected to exclude LF buckling as one component of LF hypertrophy. The study group included 27 men and 12 women, with an average age of 61.2 years (range, 23ŌĆō81 years). Disc degeneration and LF thickness were quantified on MRI. Lumbar segmental spine instability and presence of a vacuum phenomenon were identified on radiographic images.
Results
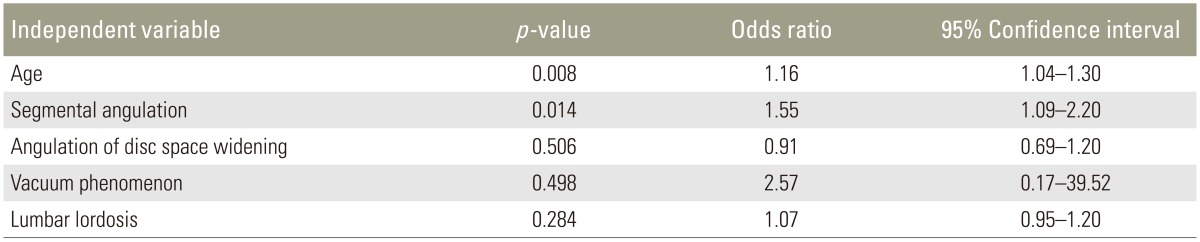
The distribution of disc degeneration and LF thickness included grade II degeneration in 4 patients, with a mean LF thickness of 2.43┬▒0.20 mm; grade III in 10 patients, 3.01┬▒0.41 mm; and grade IV in 25 patients, 4.16┬▒1.12 mm. LF thickness significantly increased with grade of disc degeneration and was significantly correlated with age (r=0.55, p<0.01). Logistic regression analysis identified predictive effects of segmental angulation (odds ratio [OR]=1.55, p=0.014) and age (OR=1.16, p=0.008).
Posterior spinal conditions including hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (LF) play a major role in the pathogenesis of lumbar spinal canal stenosis (LSCS) [123]. The LF covers a considerable part of the posterior and lateral walls of the spinal canal [45]. LF thickening of the LF can contribute in part to narrowing of the spinal canal and mechanical compression of the nerve roots and the cauda equine [6789]. This mechanical compression causes low back pain and sciatica, even in the absence of a bulging annulus fibrosus, herniated nucleus pulposus, or osseous spurs [10].
The pathogenesis of thickening of the LF is not clear and whether the thickening results from tissue hypertrophy or buckling remains controversial. Elastic fibers normally predominate in the LF, comprising 60% to 70% of the extracellular matrix [1112]. In contrast, the hypertrophied LF shows an increase in collagen fibers, calcification, ossification, and chondrometaplasia [131415161718].
The causes of LF hypertrophy are multifactorial and include activity levels, age, and mechanical stress on the LF. Tissue damage induced by mechanical stress might be the initial trigger of an inflammatory reaction and subsequent development of tissue scarring [1619], with the accumulation of such scarring resulting in LF hypertrophy [20].
The purpose of this study was to clarify the pathogenesis of LF hypertrophy associated with mechanical stress through an investigation of the relationship between LF hypertrophy and segmental instability of L4ŌĆōL5 level of the lumbar spine.
Prospective participants were 296 patients with clinical symptoms of low back pain with or without leg pain, who underwent radiographic and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination at our institution between January 2007 and September 2014. Patients with evidence of bone metastasis, congenital anomalies, scoliosis, discitis, osteomyelitis, spondylolysis, spondylolisthesis, ossification, or fracture were excluded. With the intended purpose of investigating pure hypertrophy of the LF, and excluding LF buckling, 39 patients with normal L4ŌĆōL5 disc height were selected for the study. A previous study reported that disc height on MRI obtained for healthy 20ŌĆō30 year old males is 11.8 mm [21]. Therefore, we selected patients whose disc height was more than two-thirds (8 mm) as normal. The study group consisted of 27 men and 12 women, with an average age of 61.2 years (range, 23ŌĆō81 years).
Dynamic radiographs in flexion and extension, and MRI data were obtained. For the dynamic radiographs, participants were placed in upright, axially loaded, positions of flexion and extension. For MRI, participants were placed in a prone position and images were obtained using an EXCELART Vantage 1.5-T magnet (Toshiba Medical, Tokyo, Japan). T1- and T2-weighted images in the sagittal and transverse planes were obtained.
Assessment of lumbar segmental spine motion was quantified from the dynamic flexion-extension radiographs. Angulation of disc space widening in flexion position and segmental angulation (segmental angulation=angle of flexionŌĆōangle of extension) were used to assess radiographic instability at the L4ŌĆōL5 segment. Presence of an intervertebral disc vacuum phenomenon at L4ŌĆōL5 and lumbar lordosis were investigated from T12 through S1 on lateral radiographs.
Disc degeneration is a major component of segmental stability. Disc degeneration was classified into five grades using Pfirmann's criteria based on T2-weighted sagittal images [22]. Grading of the disc status included identification of signs of degeneration at the level of the nucleus, annulus, and end-plate, with grade I indicative of a normal disc status and grade V indicative of the most advanced degeneration.
LF thickness was measured on axial T2-weighed MRI at the level of L4ŌĆō5 facet joint, with thickness of the middle portion of the LF obtained (Fig. 1). MRI scans were projected using the DICOM viewer and LF thickness measured using electronic calipers on a DICOM workstation. Measurements were performed by two experienced orthopedic surgeons at different times, with each surgeon obtaining two measurements. The mean value was used for analysis. In the case of asymmetrical thickness of the LF, the larger thickness value was used in the analysis.
Statistical analyses were performed using PASW ver. 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The association between thickness of the LF and age, disc degeneration, angulation of disc widening, segmental angulation, vacuum phenomenon, and lumbar lordosis were analyzed using Pearson's correlation analysis. To examine the relationship between thickness of the LF and disc degeneration, a Bonferroni correction was used. Logistic regression analysis was performed to test whether each parameter was independently associated with LF thickness. The cutoff for a positive thickening of the LF was set at a thickness Ōēź3.5 mm. Logistic regression analysis was performed using the end point Ōēź3.5 mm to identify predictive variables of LF thickness. Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were determined for each predictive variable. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05. The intra- and inter-observer agreement was assessed to be good-to-excellent, with a kappa statistic >0.70 for each parameter.
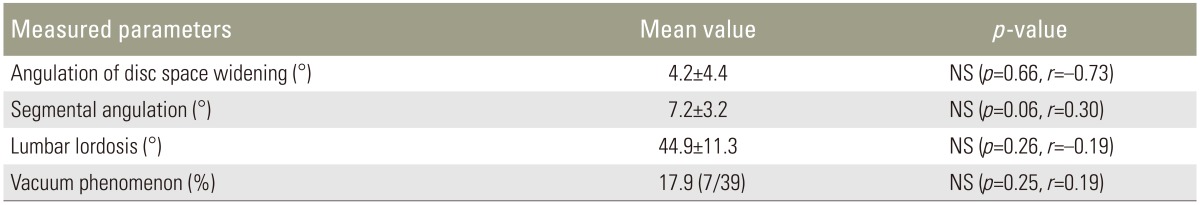
The mean angulation of disc space widening at L4ŌĆōL5 in a flexion position was 6.3┬░┬▒15.1┬░ (range, ŌĆō8┬░ to +12┬░), and the mean segmental angulation was 7.2┬░┬▒3.2┬░ (range, 2┬░ to 13┬░). The average lumbar lordosis was 44.9┬░┬▒11.3┬░ (range, 15┬░ to 73┬░). A vacuum phenomenon was evident in 7 (17.9%) patients (Table 1).
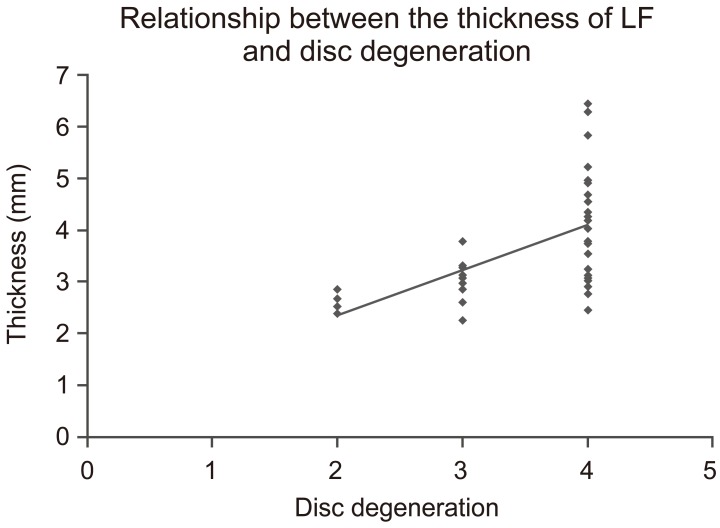
The mean thickness of the LF at L4ŌĆōL5 was 3.71┬▒1.1 mm. The distribution of grades of disc degeneration was grade II (n=4), thickness 2.43┬▒0.20 mm; grade III (n=10), 3.01┬▒0.41 mm; and grade IV (n=25), 4.16┬▒1.12 mm. There were no patients in the grade I and V classification groups. LF thickness was greater in the grade IV group compared to grade II (p<0.05) and grade III (p<0.01) groups, with a significant positive association between LF thickness and increasing severity of disc degeneration (Fig. 2). As well, LF thickness was significantly correlated with age (r=0.55, p<0.01) (Fig. 3). This association between LF thickness and age was mirrored by a significant positive correlation between age and grade of disc degeneration (r= 0.77, p<0.01). LF thickness increased significantly with disc degeneration (r=0.60, p<0.01) (Fig. 4). LF thickness was independent of the angulation of disc space widening, segmental angulation, vacuum phenomenon, and lumbar lordosis (p>0.05) (Table 2).
Logistic regression analysis revealed that LF thickening was influenced by segmental angulation (OR=1.55, p=0.014) and age (OR=1.16, p=0.008). Angulation of disc widening, vacuum phenomenon, and lumbar lordosis were not associated with thickening of the LF (Table 2). Age-associated disc degeneration was associated with lumbar segmental instability, with greater segmental angulation occurring in older patients, indicative of an association between mechanical stress, resulting from lumbar segmental instability, and thickening of the LF.
The LF covers the posterior wall of the spinal canal, such that LF hypertrophy may eventually compress the spinal cord, cauda equina, or lumbo-sacral nerve roots [6232425]. Canal narrowing in LSCS results from degenerative changes in the posterior structures of the lumbar spine. LF thickening and bony proliferation of the facet joints are major factors [19]. Numerous studies have investigated the mechanism of LF hypertrophy concerning anatomy, histology, and biology. Causes of LF hypertrophy are multifactorial and include age, mechanical stress, and growth factors. Histological studies have demonstrated a positive association between LF thickness and increased fibrosis (i.e., increase in collagen fiber content) and decrease in elastic fibers [13161718]. Epidemiological studies have provided evidence of a causal role of mechanical stress resulting from spinal instability in initiating the pathological pathway of LF hypertrophy [16262728]. Presently, radiographic measures of L4ŌĆōL5 segmental instability were used to elucidate the mechanism between mechanical stress and LF thickness.
The pathogenesis of thickening of the LF is not clear, and whether LF thickening is due to tissue hypertrophy or buckling remains controversial. Part of the issue in elucidating the pathogenesis of the LF thickening is that the exact function of the LF is unknown. LF is connective tissue that is likely to play a role in maintaining the intrinsic stability of the spine, controlling intervertebral movement, and maintaining a smooth surface of the posterior dural sac [29]. A transmission electron microscopy assessment of the LF concluded that reduced elasticity of the LF may cause bulging of the ligament into the spinal canal, even in the standing position with a LF of normal thickness [14]. In addition, disc collapse causes further buckling of the thickened LF into the spinal canal. To evaluate this theory, Altinkaya et al. [30] examined the relationship between LF thickness, and intervertebral disc degeneration and disc height, reporting a significant increase in LF thickness with increased disc degeneration. Based on these findings, the authors hypothesized that buckling of the spinal segment occurring secondary to disc degeneration results in thickening of the LF and its bucking into the spinal canal. In contrast, Sakamaki et al. [4] did not identify a correlation between the LF thickness and disc degeneration. Currently, we evaluated only patients in whom L4ŌĆōL5 disc height was preserved, thereby excluding buckling as a component of our analysis. In this specific group of patients, disc degeneration was significantly correlated with increasing age, and LF thickness was significantly correlated to disc degeneration. Our reported increase in LF thickness with age is supported by previous studies that have identified an age-dependent phenomenon [41631]. Together, these findings provide evidence that LF thickening is not necessarily dependent on buckling of LF into the spinal canal with disc degeneration.
Normal LF is composed of 80% elastic fibers and 20% collagen fibers [32]. Histologically, LF hypertrophy is characterized by loss of elastic fibers, increase in collagen fibers resulting in fibrosis, calcification, ossification, degeneration of elastic fibers, and chondrometaplasia [131617181920]. These histological changes are similar to tissue scarring associated with post-inflammatory repair in other organs, such as the heart, skin, kidneys, and lungs [33343536]. Damage to LF tissue induced by mechanical stress might be the initial triggering event of an inflammatory reaction, leading to the development of scar tissue [1619]. Emerging evidence suggests a possible role of angiogenesis as a pivotal component of the process of tissue scarring and repair. Specifically, activation of the stroma, especially of the fibroblasts, has been linked to inflammation. Fibroblast activation drives the angiogenic response of endothelial cells [3738]. In particular, vascular endothelial growth factor from fibroblasts stimulates multiple components of the angiogenic cascade [3839]. Moon et al. [40] reported the interaction of LF cells with macrophage-like cells to produce angiogenesis-related factors, with the exception of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-╬▓) 1. Activated LF cells, which have been exposed to macrophage, can induce angiogenesis-related factors. This indicates that fibrosis and scarring triggered by an inflammatory reaction is the major pathomechanism of LF hypertrophy. Therefore, inflammatory reactions initiated by trauma, such as mechanical stress, trigger the process of repair. Furthermore, as the hypertrophied LF contains more collagen, it is stiffer, which increases its vulnerability to mechanical injury during repetitive motions of flexion-extension motion, leading to a vicious cycle of scar-repair-scar.
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are the largest subgroup in the TGF-╬▓ superfamily and play important roles during embryogenesis and chondrogenesis. Yoshida et al. [18] reported a proliferation of chondrocytes in 91% of patients with LSCS. Shafaq et al. [41] reported higher cellularity and increased cartilage matrix formation to be significant underlying processes of LF hypertrophy, with these processes being more evident in patients with LSCS associated with hypermobility compared to patients with LSCS without hypermobility. BMPs were expressed in many cells of the hypertrophied LF. Based on this evidence, mechanical stress and BMP signaling may influence LF hypertrophy by stimulating chondrogenesis and cartilage matrix production.
Mechanical stress is considered one of the most important factors for LF hypertrophy. However, it is not clear what precise mechanical stress leads to LF hypertrophy. Fukuyama et al. [26] reported more severe LF hypertrophy in patients with radiological evidence of spondylolisthesis or vacuum phenomenon, indicating that mechanical instability may be a possible cause of LF hypertrophy. In our study, segmental angulation was identified as a significant risk factor of LF thickening, although a vacuum phenomenon was not retained as a predictive factor in our logistic regression analysis. Abbas et al. [31] reported LF thickness at L3ŌĆōL4 and L4ŌĆōL5 segments results from the relative hypermobility of these two segments compared to L5ŌĆōS1 segment, which is stabilized by the iliolumbar ligaments and the large transverse processes of L5 vertebra. Sairyo et al. [16] used three-dimensional finite element modeling to characterize the effects of mechanical stresses in various layers of the LF. Stress in the LF was predicted to be a maximum for loaded flexion postures, such as in lifting. The authors further predicted that higher mechanical stress on the dorsal side of the LF, compared to the dural side, leads to LF hypertrophy.
In our study, logistic regression analysis showed that thickening of the LF was influenced by segmental angulation and patient age. Therefore, increasing age may increase disc degeneration and segmental instability during motions of flexion-extension motion, such that repetitive flexion-extension cycles may lead to LF hypertrophy.
Our study has several limitations that must be considered in interpretation of outcomes. Foremost, a number of factors contribute to narrowing of spinal canal beyond thickening of the LF, including facet osteoarthritis and spondylolisthesis. To understand further the pathogenesis of the canal narrowing, these additional factors should also be included in the analysis. Our study group was also limited in number and did not include a control group. Therefore, the correlation between thickness of the LF and symptoms of LSCS could not be evaluated within the context of our study. In addition, thickening of the LF was defined by a thickness of more than 3.5 mm, which represents a narrow range of the LF thickness identified in previous studies [162631424344].
Conflict of Interest
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Grenier N, Kressel HY, Schiebler ML, Grossman RI, Dalinka MK. Normal and degenerative posterior spinal structures: MR imaging. Radiology 1987 165:517ŌĆō525. PMID: 3659376.


2. Schneck CD. The anatomy of lumbar spondylosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1985 (193): 20ŌĆō37. PMID: 3971625.


3. Tsuji H, Itoh T, Tamaki T, et al. Natural history and pathogenesis of the lumbar spinal stenosis (in Japanese). Rinsho Seikei Geka 1981 16:598ŌĆō612.
4. Sakamaki T, Sairyo K, Sakai T, Tamura T, Okada Y, Mikami H. Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using MRI. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009 129:1415ŌĆō1419. PMID: 19280205.


5. Elsberg CA. Experiences in spinal surgery. Surg Gynecol Obset 1913 16:117ŌĆō135.
6. Beamer YB, Garner JT, Shelden CH. Hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. Clinical and surgical significance. Arch Surg 1973 106:289ŌĆō292. PMID: 4689802.


7. Brown HA. Enlargement of the ligamentum flavum. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1938 20:325ŌĆō338.
8. Rauschning W. Normal and pathologic anatomy of the lumbar root canals. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1987 12:1008ŌĆō1019. PMID: 3441815.


9. Schonstrom NS, Bolender NF, Spengler DM. The pathomorphology of spinal stenosis as seen on CT scans of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1985 10:806ŌĆō811. PMID: 4089655.


10. Kirkaldy-Willis WH. The relationship of structural pathology to the nerve root. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1984 9:49ŌĆō52. PMID: 6719256.


11. Evans JH, Nachemson AL. Biomechanical study of human lumbar ligamentum flavum. J Anat 1969 105:188ŌĆō189. PMID: 5803196.

12. Nachemson AL, Evans JH. Some mechanical properties of the third human lumbar interlaminar ligament (ligamentum flavum). J Biomech 1968 1:211ŌĆō220. PMID: 16329292.


13. Okuda T, Baba I, Fujimoto Y, et al. The pathology of ligamentum flavum in degenerative lumbar disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004 29:1689ŌĆō1697. PMID: 15284518.


14. Postacchini F, Gumina S, Cinotti G, Perugia D, DeMartino C. Ligamenta flava in lumbar disc herniation and spinal stenosis. Light and electron microscopic morphology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1994 19:917ŌĆō922. PMID: 8009349.


15. Ramsey RH. The anatomy of the ligamenta flava. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1966 44:129ŌĆō140. PMID: 5910242.


16. Sairyo K, Biyani A, Goel V, et al. Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: a multidisciplinary investigation based on clinical, biomechanical, histologic, and biologic assessments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005 30:2649ŌĆō2656. PMID: 16319751.


17. Schr├żder PK, Grob D, Rahn BA, Cordey J, Dvorak J. Histology of the ligamentum flavum in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J 1999 8:323ŌĆō328. PMID: 10483836.



18. Yoshida M, Shima K, Taniguchi Y, Tamaki T, Tanaka T. Hypertrophied ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis Pathogenesis and morphologic and immunohistochemical observation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1992 17:1353ŌĆō1360. PMID: 1462211.


19. Sairyo K, Biyani A, Goel VK, et al. Lumbar ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is due to accumulation of inflammation-related scar tissue. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007 32:E340ŌĆōE347. PMID: 17495768.


20. Kosaka H, Sairyo K, Biyani A, et al. Pathomechanism of loss of elasticity and hypertrophy of lumbar ligamentum flavum in elderly patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007 32:2805ŌĆō2811. PMID: 18246001.


21. Roberts N, Gratin C, Whitehouse GH. MRI analysis of lumbar intervertebral disc height in young and older populations. J Magn Reson Imaging 1997 7:880ŌĆō886. PMID: 9307915.


22. Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001 26:1873ŌĆō1878. PMID: 11568697.


23. Towne EB, Reichert FL. Compression of the Lumbosacral Roots of the Spinal Cord by Thickened Ligamenta Flava. Ann Surg 1931 94:327ŌĆō336. PMID: 17866626.



24. Naylor A. Factors in the development of the spinal stenosis syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1979 61:306ŌĆō309. PMID: 479253.


26. Fukuyama S, Nakamura T, Ikeda T, Takagi K. The effect of mechanical stress on hypertrophy of the lumbar ligamentum flavum. J Spinal Disord 1995 8:126ŌĆō130. PMID: 7606119.


27. Nakamura T, Hashimoto N, Maeda Y, Ikeda T, Nakagawa H, Takagi K. Degeneration and ossification of the yellow ligament in unstable spine. J Spinal Disord 1990 3:288ŌĆō292. PMID: 1724936.


28. Nakatani T, Marui T, Hitora T, Doita M, Nishida K, Kurosaka M. Mechanical stretching force promotes collagen synthesis by cultured cells from human ligamentum flavum via transforming growth factor-beta1. J Orthop Res 2002 20:1380ŌĆō1386. PMID: 12472256.


29. Safak AA, Is M, Sevinc O, et al. The thickness of the ligamentum flavum in relation to age and gender. Clin Anat 2010 23:79ŌĆō83. PMID: 19941359.


30. Altinkaya N, Yildirim T, Demir S, Alkan O, Sarica FB. Factors associated with the thickness of the ligamentum flavum: is ligamentum flavum thickening due to hypertrophy or buckling? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011 36:E1093ŌĆōE1097. PMID: 21343862.


31. Abbas J, Hamoud K, Masharawi YM, et al. Ligamentum flavum thickness in normal and stenotic lumbar spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010 35:1225ŌĆō1230. PMID: 20216339.


32. Viejo-Fuertes D, Liguoro D, Rivel J, Midy D, Guerin J. Morphologic and histologic study of the ligamentum flavum in the thoraco-lumbar region. Surg Radiol Anat 1998 20:171ŌĆō176. PMID: 9706675.


33. Frangogiannis NG. Chemokines in the ischemic myocardium: from inflammation to fibrosis. Inflamm Res 2004 53:585ŌĆō595. PMID: 15693606.


34. Furuichi K, Kaneko S, Wada T. Chemokine/chemokine receptor-mediated inflammation regulates pathologic changes from acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 2009 13:9ŌĆō14. PMID: 19085040.


35. Strieter RM, Mehrad B. New mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2009 136:1364ŌĆō1370. PMID: 19892675.



36. Wilgus TA, Vodovotz Y, Vittadini E, Clubbs EA, Oberyszyn TM. Reduction of scar formation in full-thickness wounds with topical celecoxib treatment. Wound Repair Regen 2003 11:25ŌĆō34. PMID: 12581424.


37. Bauer SM, Bauer RJ, Liu ZJ, Chen H, Goldstein L, Velazquez OC. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C promotes vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and collagen constriction in three-dimensional collagen gels. J Vasc Surg 2005 41:699ŌĆō707. PMID: 15874936.


38. Enzerink A, Rantanen V, Vaheri A. Fibroblast nemosis induces angiogenic responses of endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 2010 316:826ŌĆō835. PMID: 19932095.


39. Bao P, Kodra A, Tomic-Canic M, Golinko MS, Ehrlich HP, Brem H. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in wound healing. J Surg Res 2009 153:347ŌĆō358. PMID: 19027922.


40. Moon HJ, Park YK, Ryu Y, et al. The angiogenic capacity from ligamentum flavum subsequent to inflammation: a critical component of the pathomechanism of hypertrophy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012 37:E147ŌĆōE155. PMID: 21673619.


41. Shafaq N, Suzuki A, Terai H, Wakitani S, Nakamura H. Cellularity and cartilage matrix increased in hypertrophied ligamentum flavum: histopathological analysis focusing on the mechanical stress and bone morphogenetic protein signaling. J Spinal Disord Tech 2012 25:107ŌĆō115. PMID: 21430570.


42. Park JB, Chang H, Lee JK. Quantitative analysis of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in ligamentum flavum of lumbar spinal stenosis and disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001 26:E492ŌĆōE495. PMID: 11679833.


43. Park JB, Lee JK, Park SJ, Riew KD. Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal stenosis associated with increased proteinase inhibitor concentration. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005 87:2750ŌĆō2757. PMID: 16322626.


Fig.┬Ā1
Measurement of the ligamentum flavum thickness on axial T2-weighed magnetic resonance images at the level of the facet joint.
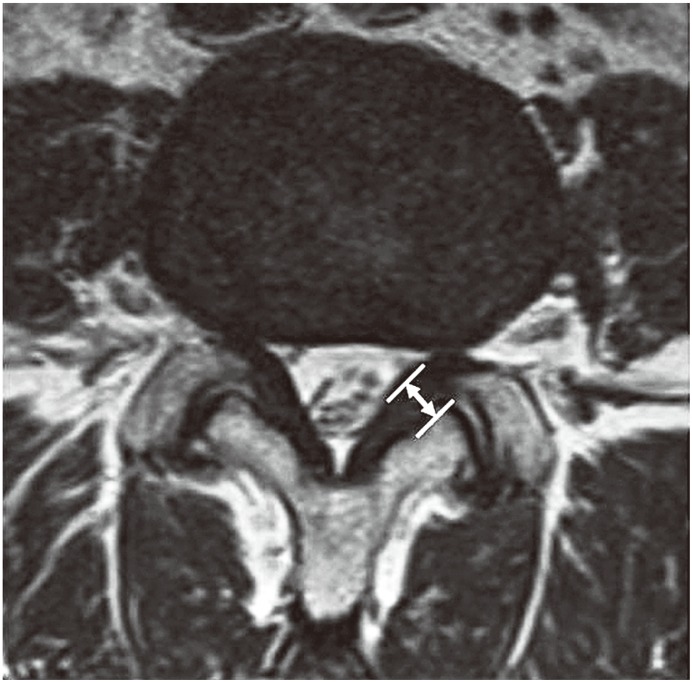
Fig.┬Ā2
Mean thickness of the ligamentum flavum (LF) at L4ŌĆōL5 for each grade of disc degeneration. The mean thickness of grade II was 2.43┬▒0.20 mm; grade III, 3.01┬▒0.41 mm; and grade IV, 4.16┬▒1.12 mm. The mean LF thickness was greater for grade IV compared to grade II (*p<0.05) and grade III (**p<0.01).
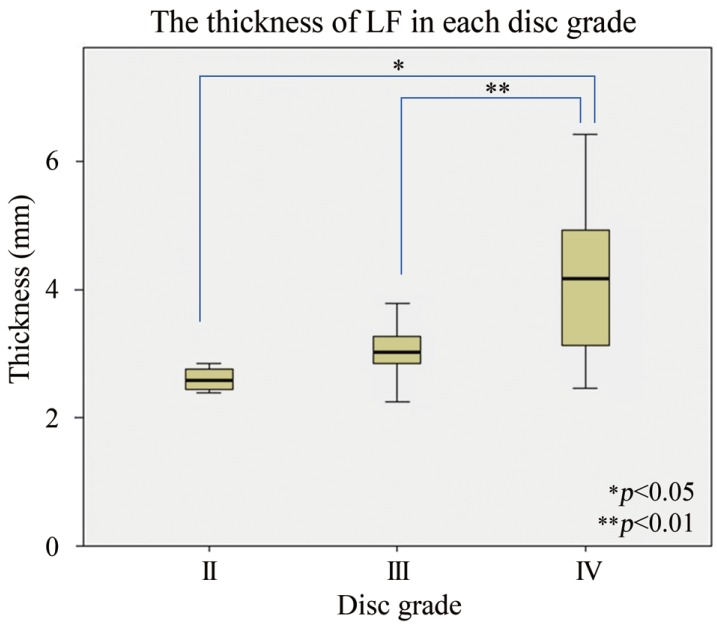
Fig.┬Ā3
Relationship between ligamentum flavum (LF) thickness and age. The thickness of the LF was significantly correlated with age (r=0.55, p<0.01)
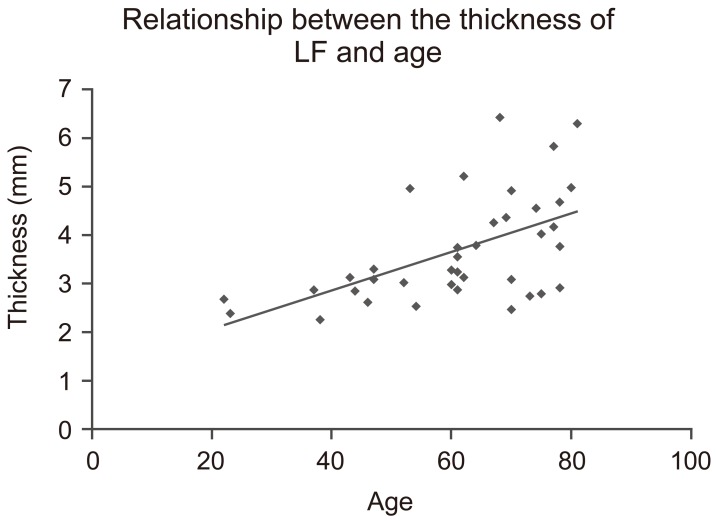
Fig.┬Ā4
Relationship between the thickness of ligamentum flavum (LF) and disc degeneration. There was a significant correlation between the thickness of the LF and the grade of disc degeneration (r=0.60, p<0.01).