 |
 |
- Search
| Asian Spine J > Volume 13(5); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate surgical outcomes and effectiveness of an autogenic rib graft for upper cervical fixation in pediatric patients.
Overview of Literature
Autogenic bone grafts have long been considered the ‘gold standard’ bone source for posterior cervical fusion in pediatric patients. However, there are some unsolved problems associated with donor-site morbidity and amount of bone grafting.
Methods
We studied five consecutive pediatric patients who underwent atlantoaxial fixation or occipitocervical fixation (OCF) using an autogenic rib graft with at least 2 years of follow-up (mean age, 9.8 years; mean follow-up period, 73.0 months). Two patients underwent OCF without screw-rod constructs and three patients with screw-rod constructs. Autogenic rib grafts were used in all patients. We evaluated the surgical outcomes including radiographic parameter, bony union, and perioperative complications.
Results
The atlantoaxial interval (ADI) was corrected from 11.6 to 6.0 mm, and the C1–2 angle was corrected −14.8° to 7.8°. The C2–7 angle was reduced from 31° to 9° spontaneously. Two patients with OCF required revision surgery due to loss of correction. Patients did not experience any complication associated with the donor sites (rib bone grafts). Six months postoperation X-rays clearly showed regeneration of the rib at the donor sites. Bony fusion was achieved in all patients; however, bony fusion occurred more slowly in patients without screw-rod constructs compared with patients with screw-rod constructs. Bone regeneration of the rib was observed in all patients with no complications at the donor site.
Atlantoaxial fixation (AAF) and occipitocervical fixation (OCF) are occasionally indicated in pediatric patients with cervical instability caused by a variety of congenital or acquired conditions [1]. If conservative treatments are not effective, surgical intervention is usually required to achieve atlantoaxial reduction and spinal cord decompression [2,3]. Over the past decade, the surgical procedure for upper cervical lesions in pediatric patients has evolved from a wiring technique to screw-rod constructs [2,4-6]. Screw-rod constructs provide biomechanical stable fixation and better bony fusion than the traditional wiring technique. However, screw placement may be technically difficult in very young children because of small bone size, congenital variations, possible growth potential, and immature ossification [7,8]. With regard to bone grafts, autogenic iliac crest bone has long been considered the ‘gold standard’ bone source for posterior cervical fusion in pediatric patients [5,9,10]. However, there are some unsolved problems associated with donor-site morbidity and amount of bone grafting. We performed upper cervical fixation using autogenic rib grafts with or without screwrod constructs on five consecutive pediatric patients. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the surgical outcomes and effectiveness of autogenic rib grafts for upper cervical fixation in pediatric patients.
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of five consecutive pediatric patients (two boys and three girls) who underwent AAF or OCF using autogenic rib grafts. The mean age at surgery was 9.8 years (range, 5–16 years), and the average follow-up period was 73.0 months (range, 27–99 months). Four of the five patients were previously diagnosed with 21 trisomy. The indication for surgery was cervical myelopathy in four patients and axial neck pain in one patient. With regard to the etiology of upper cervical problems, four patients demonstrated os odontoideum and one demonstrated atlantoaxial subluxation. The following radiographic parameters were assessed with plain radiographs immediately prior to surgery, 1 week after surgery, and at the most recent follow-up: atlantoaxial interval (ADI), space available for the spinal cord (SAC), C1–2 lordosis (C1–2), and C2–7 lordosis (C2–7). Additionally, rib regeneration was evaluated using chest X-rays 6 months after surgery. Computed tomography (CT) scans in the cervical spine were repeated 3, 6, and 12 months after surgery until complete fusion could be confirmed, defined as an absence of hardware failure and presence of continuous bridging trabecular bone between dorsal elements on CT scans. Because of the small bone size, C1 and C2 were always obscured by instrumentation on lateral radiographs. Therefore, bone fusion was identified by reconstructive CT scan, which improves the accuracy to almost 90% [11,12]. This retrospective study was approved by the Osaka City General Hospital Institutional Review Board (IRB approval no., 1506028). Written informed consents were obtained from all patients.
Posterior spinal fusion was performed with screw-rod constructs in three patients and without instrumentation in two patients. O–C2 fixation with autogenic rib grafts and Tekmilon tape (Nespron Cable System; Alfresa Pharma Co., Tokyo, Japan) (Fig. 1), as described by Cohen et al. [13], was performed in two patients (cases 1 and 2). A novel technique using the C1 lateral mass and a C2 pedicle screw [14,15] combined with a C2 laminar screw [16] was used in two patients (cases 3 and 4). In these two patients, a modified Brooks method using autogenic rib grafts was combined with a screw-rod construct [17] (Fig. 2). In case 5, O–C4 fixation with laminar screws and lateral mass screw was performed. Autogenic rib bone was placed from the occipital bone to the C2 lamina (Fig. 3). In all cases, we harvested strut rib from the 7th or 8th rib through transverse skin incision.
Symptoms associated with cervical myelopathy improved after surgery. The preoperative static radiographic parameters in the neutral position were as follows: ADI, 11.6 mm; SAC, 8.4 mm; C1–2, −14.8°; and C2–7, 31°. These findings indicated atlantoaxial subluxation that resulted in spinal canal narrowing, segmental kyphosis at C1/2, and compensatory hyperlordosis at C2–7. After surgery, the ADI was corrected from 11.6 to 6 mm and C1–2 angle was corrected from −14.8° to 7.8°, respectively. The C2–7 angle was reduced from 31° to 9° spontaneously (Table 1). Bone union was established in all patients; however, the two patients without spinal instrumentation (cases 1 and 2) and one patient with C0–4 fusion who underwent revision surgery required more time for bone union. Halo vest fixation was needed for longer periods in two patients (cases 1 and 2) without spinal instrumentation. Revision surgeries were required for two patients (cases 2 and 5). In case 2, revision surgery was performed because of correction loss and pseudarthrosis 4 months after their initial surgery; we added an autogenic rib graft and applied a Halo vest. In case 5, revision surgery was performed because of loss of correction and pseudarthrosis 6 months after their initial surgery. An occipital plate and screws were changed, and an autogenic rib graft was added. Patients did not experience any complications associated with the rib bone graft donor sites. Additionally, X-rays after 6 months clearly showed regeneration of the rib at the donor sites. The demographic, surgical, and clinical data of patients are summarized in Table 2.
Surgical treatment for upper cervical lesions in pediatric patients a challenge because of immature bone quality and smaller osseous structures, which sometimes make insertion spinal instrumentation quite difficult [1-4,8,18]. Following the development of spinal instruments, several authors reported surgical techniques using spinal instrumentation for the upper cervical spine in pediatric patients [5,19-21]. The C1 lateral mass screw described by Goel and Laheri [14] and Harms and Melcher [15], and the laminar screw established by Wright [16], were applied in our case series. Using spinal instrumentation, the orthoses could be removed earlier, and thus bony union was achieved earlier in our series without any complications. Additionally, spinal instrumentation provided better stability and prevented loss of correction. However, we did experience one instrumentation failure in case 5, in which occipital screws became dislodged leading to loss of correction. Our data suggest that a Halo vest should be considered to provide additional stability postoperatively in the case of poor bone quality and OCF, even if a screwrod construct is used.
In pediatric patients with upper cervical fixation, graft bone materials should be considered. The ideal grafting bone has two important functions: to facilitate osteogenesis and provide structural support [22]. Several graft materials are currently available, and allograft is one such candidate for cervical spinal fixation. Zhang et al. [12] compared the fusion rate between autograft and allograft for pediatric patients with AAF, reporting that 94% of the fusion rates with allograft was comparable with 100% of the fusion rate with autograft. However, Reintjes et al. [9] reported 80% rate of bony fusion with allograft and 94% bony fusion with autograft. The advantages of autogenic bone are the low cost and reduced potential risk of viral infection. However, morbidity at the donor site can be substantial in some cases. The iliac crest is the most frequently selected site to harvest autogenic bone to incorporate into cervical spinal fusion constructs. A major limitation of the iliac crest is donor-site morbidity, including chronic pain, wound infection, hematoma, abdominal wall hernia, meralgia paresthetica, buttock anesthesia, ‘gluteal gait’ disturbance, and fracture of the ilium [10]. Compared with the iliac crest, a rib autograft is rarely used in cervical spinal constructs. Sawin et al. [10] reviewed the fusion rates and donor-site morbidity for both autogenic rib and iliac crest bone grafts in posterior cervical fusions, finding that fusion rates were significantly higher with 98.8% of patients with rib graft constructs achieving fusion compared with 94.2% with crest graft constructs. Rib graft donor-site morbidity was significantly lower than iliac crest graft (3.7% versus 25.3%). Thus, they concluded that autogenic rib grafts were superior for upper cervical fixation in pediatric patients. In our series, bony union was achieved in all patients with no donor-site morbidity. Additionally, regeneration occurred within 6 months after surgery in all patients. Therefore, in our opinion, an autogenic rib graft should be the first choice for bone grafting in pediatric patients with upper cervical fixation.
This study had some limitations that warrant discussion. We examined a small sample size with no control group, and the follow-up periods were relatively short.
Our data showed that autogenic rib grafts have advantages, including good potential bone regeneration, high fusion rate, and low donor-site morbidity. Additionally, screw-rod constructs are able to provide better bony fusion without Halo vests in pediatric patients with AAF. However, clinicians should consider Halo vests for OCF if a screw-rod construct is used.
Notes
Author Contributions
Corresponding author, conception, design, and analysis: Matsumura A; acquisition of data: Matsumura A, Namikawa T, Kato M, Hori Y, Iwamae M; and critically revising the article: Hidaka N, Konishi S, Nakamura H.
Fig. 1.
Case 1. A 5-year-old boy presented with cervical myelopathy due to os odontoideum associated with 21 trisomy. He underwent OCF without a screw-rod construct. He used a Halo vest for 11 months until bony fusion was achieved. (A) Preoperative X-ray shows that ADI and SAC were 12 and 7 mm, respectively. (B) Sagittal view of the CT image indicates os odontoideum. (C) Magnetic resonance imaging displays a high-intensity change in the spinal cord on T2-weighted imaging at the cervicomedullary junction. (D) Postoperative X-ray shows that ADI and SAC were reduced to 5 and 12 mm, respectively. (E) Sagittal view of the CT image displays the autogenic rib graft. (F) Clinical photo during surgery shows OCF with the autogenic rib and Tekmilon taping. (G) X-ray 8 years post-surgery shows that ADI and SAC were 10 and 9 mm, respectively. (H) Sagittal view of the CT image displaying bony union. OCF, occipitocervical fixation; ADI, atlantoaxial interval; SAC, space available for the spinal cord; CT, computed tomography.
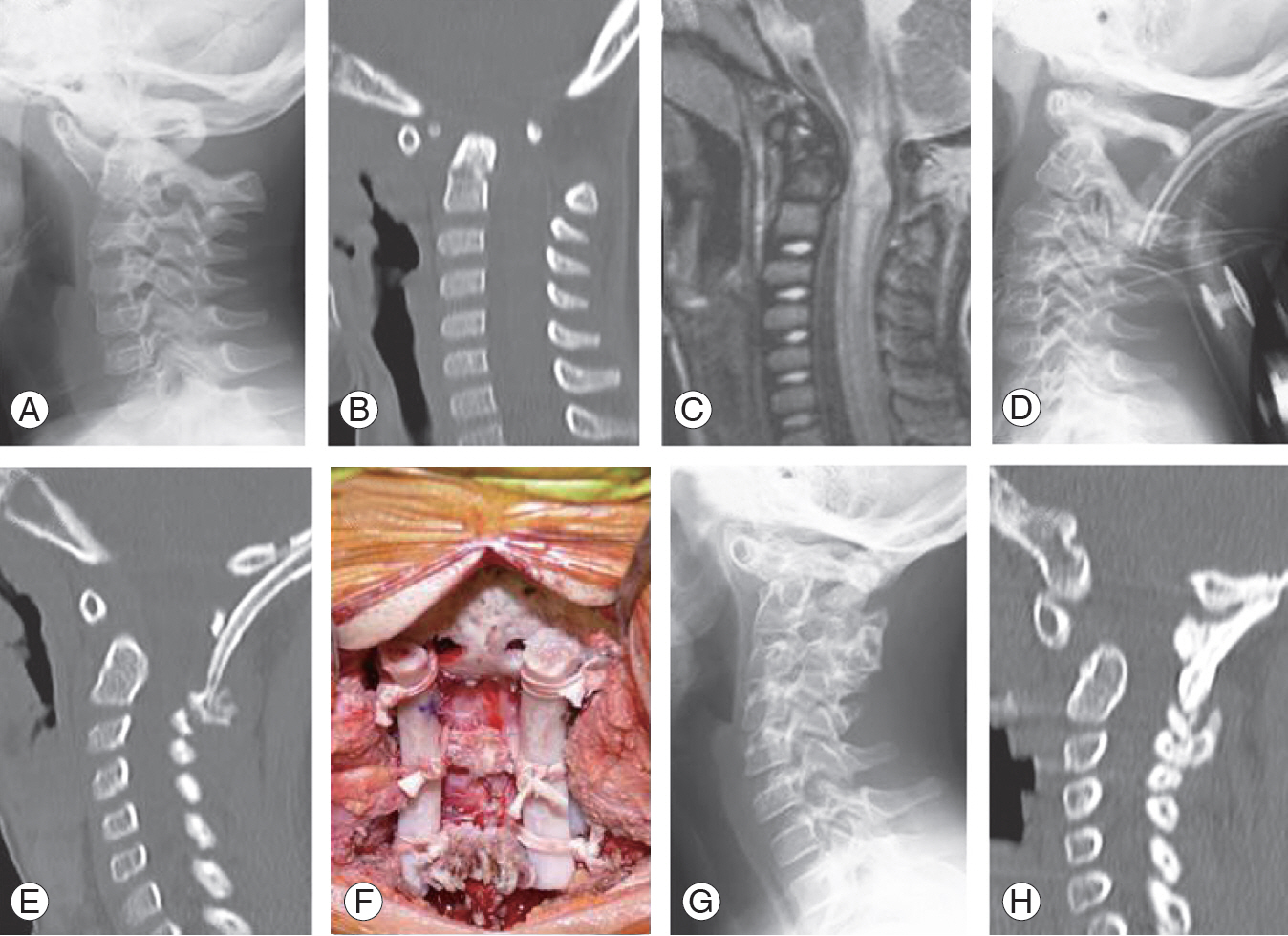
Fig. 2.
Case 3. A 9-year-old boy presented with neck pain due to os odontoideum but did not have any neurological deficit. He underwent AAF with a screw-rod construct and used a Philadelphia collar for 1 month. (A) Preoperative X-rays show that ADI and SAC were 12 and 7 mm, respectively. (B, C) Dynamic films show that ADI changed from −4 to 13 mm. (D) Sagittal view of the CT image indicates os odontoideum. (E) Postoperative X-ray shows that ADI and SAC were reduced to 1 and 18 mm, respectively. (F) Sagittal view of the CT image displays the modified Brooks method with an autogenic rib graft. (G) Clinical photo during surgery shows AAF with an autogenic rib and a screw-rod construct. (H) X-ray 6 years post-surgery shows that ADI and SAC were 1 and 19 mm, respectively. (I) Sagittal view of the CT image displays complete bony consolidation. (J) X-ray immediately after surgery. White arrows indicate absence of the rib because of the graft. (K) X-ray 6 months post-surgery. White arrows indicate regeneration of the rib. AAF, atlantoaxial fixation; ADI, atlantoaxial interval; SAC, space available for the spinal cord; CT, computed tomography.

Fig. 3.
Case 5. A 7-year-old girl presented with cervical myelopathy due to AAS and VS. She underwent occipitocervical fixation with a screw-rod construct. Six months after surgery, she underwent an additional surgery due to correction loss and pseudarthrosis. (A) Preoperative X-ray shows that ADI and SAC were 10 and 9 mm, respectively. (B) Sagittal view of the CT image indicates AAS and VS. (C) Magnetic resonance imaging displays a high-intensity change of the spinal cord on T2-weighted imaging at the cervicomedullary junction. (D) A three-dimensional CT image indicates the 1st intersegmental artery on the left side. (E) Postoperative X-ray shows that ADI and SAC were reduced to 7 and 12 mm, respectively. (F) Sagittal view of the CT image displays the occipital plate and screw construct with an autogenic rib graft. (G) X-ray 6 months after initial surgery indicates dislodgement of the occipital screws and loss of correction. (H) Sagittal view of the CT image 6 months following the initial surgery demonstrates dislodgement of the screw and fracture of the skull. (I) X-ray 6 months post revision surgery shows that ADI and SAC were 8 and 11 mm, respectively. (J) Sagittal view of the CT image displays complete bony union. AAS, atlantoaxial subluxation; VS, vertical subluxation; ADI, atlantoaxial interval; SAC, space available for the spinal cord; CT, computed tomography.
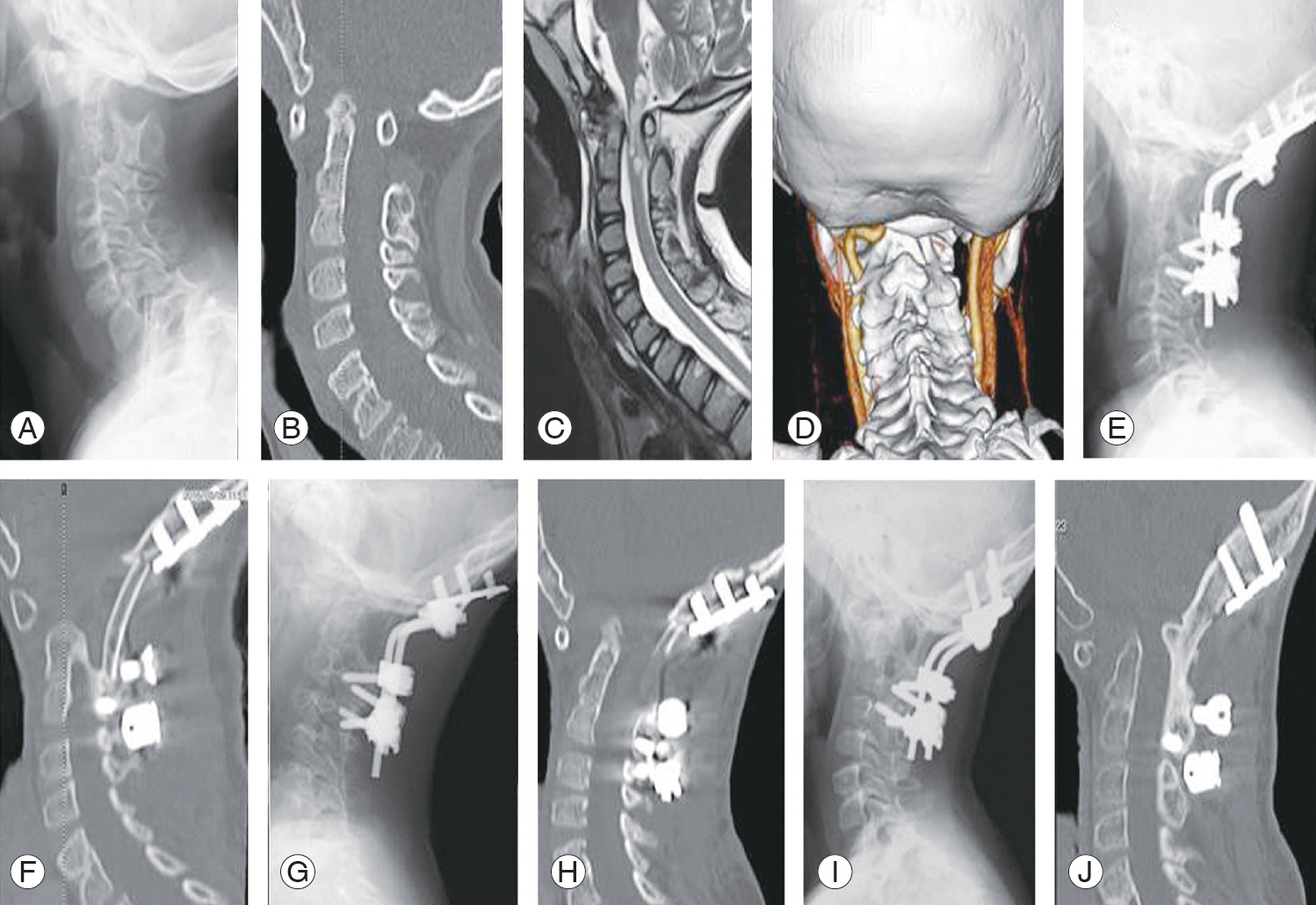
Table 1.
Radiographic parameters
Table 2.
Patient characteristics, surgical, and clinical data for all patients
| Case | Sex/age (yr) | FU (mo) | Etiology | Comorbidity | Myelopathy | Op time (min) | Blood loss (g) | Fusion area | Type of anchors | Orthosis type/duration (mo) | Bone union (mo) | Additional surgery | Prognosisa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M/5 | 99 | Os | 21 Trisomy | + | 365 | 75 | O–C2 | Tape | Halo/44 | 12 | +b) | Improvement |
| 2 | F/16 | 96 | Os | 21 Trisomy | + | 370 | 50 | O–C2 | Tape | Halo/32 | 12 | - | Improvement |
| 3 | M/9 | 75 | Os | None | - | 178 | 120 | C1–2 | Screw+rodc) | Philadelphia/1 | 6 | - | Stable |
| 4 | F/12 | 68 | Os | 21 Trisomy | + | 200 | 55 | C1–2 | Screw+rodd) | Philadelphia/3 | 6 | - | Improvement |
| 5 | F/7 | 27 | AAS | 21 Trisomy | + | 348 | 80 | O–C4 | Screw+rode) | Philadelphia/3 | 12 | +f) | Improvement |
FU, follow-up; M, male; F, female; Os, os odontoideum; Tape, tekmilon tape; AAS, atlantoaxial subluxation.
b) Revision surgery was done because of correction loss and pseudoarthrosis 4 months after initial surgery. We added an autologous bone graft from the rib and applied a Halo vest.
References
1. Crostelli M, Mariani M, Mazza O, Ascani E. Cervical fixation in the pediatric patient: our experience. Eur Spine J 2009;18 Suppl 1:20–8.



2. Martinez-Del-Campo E, Turner JD, Rangel-Castilla L, Soriano-Baron H, Kalb S, Theodore N. Pediatric occipitocervical fixation: radiographic criteria, surgical technique, and clinical outcomes based on experience of a single surgeon. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2016;18:452–62.


3. Yang SY, Boniello AJ, Poorman CE, Chang AL, Wang S, Passias PG. A review of the diagnosis and treatment of atlantoaxial dislocations. Global Spine J 2014;4:197–210.



4. Doyle JS, Lauerman WC, Wood KB, Krause DR. Complications and long-term outcome of upper cervical spine arthrodesis in patients with Down syndrome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996;21:1223–31.


5. Gluf WM, Brockmeyer DL. Atlantoaxial transarticular screw fixation: a review of surgical indications, fusion rate, complications, and lessons learned in 67 pediatric patients. J Neurosurg Spine 2005;2:164–9.


6. Kennedy BC, D’Amico RS, Youngerman BE, et al. Long-term growth and alignment after occipitocervical and atlantoaxial fusion with rigid internal fixation in young children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2016;17:94–102.


7. Anderson RC, Ragel BT, Mocco J, Bohman LE, Brockmeyer DL. Selection of a rigid internal fixation construct for stabilization at the craniovertebral junction in pediatric patients. J Neurosurg 2007;107(1 Suppl): 36–42.


8. Vara CS, Thompson GH. A cadaveric examination of pediatric cervical pedicle morphology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:1107–12.


9. Reintjes SL, Amankwah EK, Rodriguez LF, Carey CC, Tuite GF. Allograft versus autograft for pediatric posterior cervical and occipito-cervical fusion: a systematic review of factors affecting fusion rates. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2016;17:187–202.


10. Sawin PD, Traynelis VC, Menezes AH. A comparative analysis of fusion rates and donor-site morbidity for autogeneic rib and iliac crest bone grafts in posterior cervical fusions. J Neurosurg 1998;88:255–65.


11. Sugiyama S, Wullschleger M, Wilson K, Williams R, Goss B. Reliability of clinical measurement for assessing spinal fusion: an experimental sheep study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37:763–8.


12. Zhang YH, Shen L, Shao J, Chou D, Song J, Zhang J. Structural allograft versus autograft for instrumented atlantoaxial fusions in pediatric patients: radiologic and clinical outcomes in series of 32 patients. World Neurosurg 2017;105:549–56.


13. Cohen MW, Drummond DS, Flynn JM, Pill SG, Dormans JP. A technique of occipitocervical arthrodesis in children using autologous rib grafts. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:825–9.


14. Goel A, Laheri V. Plate and screw fixation for atlanto-axial subluxation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1994;129:47–53.



15. Harms J, Melcher RP. Posterior C1-C2 fusion with polyaxial screw and rod fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26:2467–71.


16. Wright NM. Posterior C2 fixation using bilateral, crossing C2 laminar screws: case series and technical note. J Spinal Disord Tech 2004;17:158–62.


17. Saito R, Hase H, Mikami Y, et al. Clinical study of a modified Brooks technique for atlanto-axial subluxation using polyethylene tape. J Spinal Disord Tech 2006;19:11–7.


18. Cronk C, Crocker AC, Pueschel SM, et al. Growth charts for children with Down syndrome: 1 month to 18 years of age. Pediatrics 1988;81:102–10.



19. Zhang YH, Shao J, Chou D, Wu JF, Song J, Zhang J. C1-C2 pedicle screw fixation for atlantoaxial dislocation in pediatric patients younger than 5 years: a case series of 15 patients. World Neurosurg 2017;108:498–505.


20. Ito K, Imagama S, Ito Z, et al. Screw fixation for atlantoaxial dislocation related to Down syndrome in children younger than 5 years. J Pediatr Orthop B 2017;26:86–90.


- TOOLS






